Symptom Relief
advertisement

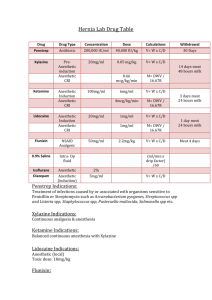
Symptom Relief Provincial Reciprocity Attainment Program Terms Pharmacodynamics The study of how a drug acts on a living organism. Pharmacokinetics The study of how the body handles a drug over a period of time, including the processes of: Pharmacology Absorption Distribution Biotransformation Excretion. The science of drugs used to prevent, diagnose, and treat disease. Toxicology The scientific study of poisons, their detection, their effects and treatments for the conditions they create. Drug Nomenclature Generic Reflects the chemical structure of the drug Diazepam Trade Also the brand name, is registered by manufacturer Valium Official The official name used to list the drug Valium USP Chemical The precise chemical description Chloro-1,3 dehydor, 1 methyl, 5 phenyl -2H, 1,4 benzodiazepine one Medications given by the PCP ASA Nitroglycerine Ventolin Epinephrine 1:1,000 Oral Glucose Glucagon Tetracaine (Alcaine, Diocaine…) Routes Sub-Lingual (Nitroglycerine) Orally (ASA, Glucose) Subcutaneous (Epinephrine 1:1,000, Glucagon) Inhaled (Ventolin) Intravenous Endotracheal 6 Rights of Drug Administration The Right Patient The Right Drug The Right Dose The Right Route The Right Time The Patients’ Right to Refuse ASA Origin: Class: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID); Analgesic; Antipyretic; Anti-coagulant Action: Synthesized version of salicin found in the White Willow tree Anti-coagulant effects: ASA inhibits Thromboxane A2 production which is responsible for platelet aggregation. With the decrease in platelet aggregation the blood does not form clots as easily. The changes to the blood cell from ASA are irreversible, though the cell only lives from 5 to 7 days. Other information: At high doses there is a direct stimulation of the respiratory center in the medulla which increases rate and depth of respirations (hyperventilation). You may also find increase of respiratory alkalosis from the hyperventilation as O2 consumption and CO2 production increase. Also at high doses ASA will block the secretion and reabsorption of uric acid. ASA Onset: Peak: Duration: Indications: Contraindications: Sensitivity Active peptic ulcer Side Effects: 30 minutes 2 hours (6 - 8 hours with enteric coated) dose dependent Ischemic Chest Pain Acute MI Unstable Angina GI: Heartburn, N & V, diarrhea @ high doses, hemorrhage Renal: Necrosis of renal papillary with long term use Reye’s syndrome (a CNS infection relative to viral infection in children such as chicken pox or influenza) ASA Precautions: History of Gastrointestinal ulcers Previous intake of daily aspirin Asthma (asthmatic patients may have hypersensitivity to ASA and precaution should be taken with first time use, a good history prior to administration is essential) Dose: Preparation: Route: PO Antidote: 500 mg/kg is fatal Induce vomiting and administer activated charcoal 160 mg PO 80 mg tablets Nitroglycerine Class: Actions: It was originally believed that nitroglycerin dilated coronary blood vessels, thereby increasing blood flow to the heart. It is now believed that atherosclerosis limits coronary dilation and that the benefits of nitrates are due to dilation of arterioles and veins in the periphery, reducing preload and to a lesser extent, after load. Nitrate, Antianginal Therefore: Relaxes vascular smooth muscle (Veins…arterioles. arteries) Decreases peripheral vascular resistance (PVR) Decreases myocardial workload Decreases myocardial oxygen consumption (MvO2) Onset/Peak/Duration: Onset: Duration: Indications: Spray/Tabs/IV: Paste: 20 - 30 minutes 18 - 24 hours (paste) 1 – 3 minutes 30 minutes Ischemic chest pain Hypertension Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) (ICP and ACP only) Nitroglycerine Adverse Effects: headache, postural syncope reflex tachycardia, hypotension muscle twitching diaphoresis, skin rash nausea, vomiting Precautions/Interactions: CNS: Cardiovascular: PNS: Integumentary: GI: Additive effects may occur with other vasodilators. Hypotension may result when combined with alcohol. Contraindications: Relative: Glaucoma Absolute: Allergy Hypotension (BP < 100/50 mmHg) Viagra usage 24 hours prior If used within last 72 contact OLMC Hypovolemia Head injury Cerebral hemorrhage Nitroglycerine Preparation: spray bottle (0.4 mg per spray) Dose: 0.4 mg SL q.5min (max of 3 doses) Max Dose: No maximum (the administration of NTG SL should be titrated to effect while maintaining blood pressure >= 100 systolic.) Route: Antidote: SL Manage nitroglycerin induced hypotension by terminating SL, Trendelenburg position, and administration of NaCl bolus to reestablish normotensive state may be attempted if protocols allows Epinephrine (1:1,000) Type: Action: Sympathomimetic; Sympathetic Agonist This drug acts directly on the (veins) and (1-heart, 2- lungs) receptor sites in the heart, lungs, skeletal muscles, skin, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and other viscera. There is a vasodilatation of the coronary arteries and the vessels of the lungs and skeletal muscles. Epinephrine has an inhibitory effect causing widespread vasoconstriction in all other receptors sites within the body. Therefore: Increased vascular resistance Increased BP and Pulse Increased coronary & cerebral flow Increased MVO2 Increased automaticity Bronchodilatation Epinephrine (1:1,000) Onset: < 2 minutes Peak: Is usually reached approximately 10 minutes after administration. Duration: relatively short may require readministration to maintain therapeutic levels. Indications: Severe Anaphylaxis Contraindications: hypersensitivities no indications present Precautions: None Epinephrine (1:1,000) Adverse Effects: Preparation: Ampules 1 mg/ml (1:1,000) Epipens 0.3mg/2ml (1:1,000 adult) 0.15mg/2ml (1:2,000 child) Dose: Palpitations, anxiety, tremulousness, headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting. Due to its strong inotropic (force of contraction) and chronotropic (speed) effects epinephrine increases myocardial oxygen demand. Hypertension, tachycardia Even low doses can result in myocardial ischemia. Anaphylaxis: Antidote: Adult Child 0.3 mg of 1:1,000 SC q 10-20 min 0.01 mg/kg of 1:1,000 SC q 20 min There is no known antidote for epinephrine Salbutamol Classification: Mechanism Of Action: β-2 stimulation causing smooth muscle relaxation of the bronchioles resulting in bronchodialation Slight β-1 stimulation causing a possible tachycardia Dosage: Adult > 30kg (66 lbs) 5.0 mg nebule with 8-10 lpm O2 4-6 puffs MDI prn Peds 10-30kg (22 - 66 lbs) 2.5 mg nebule & 8-10 lpm O2 2-3 puffs MDI Infant < 10kg (< 22 lbs) β-2 agonist 1.25mg nebule & 8-10 lpm O2 Indications: Wheezing Anaphylaxis Salbutamol Contra-Indications: Side effects Tachycardia, Hypertension Tremor, Headache Dry Nose, throat Arrhythmias Supplied Allergy Ischemic chest pain 5.0 mg nebules (2.5 mg/ml) 90 - 100 μg MDI Precautions Vital signs before Transport must not be delayed Glucose Classification: Anti-hypoglycemic Mechanism Of Action: Provides glucose to the system to allow for proper metabolism Dosage: 1-2 tubes PO Indications: Hypoglycemic patient with Glucose less < 4.0 Glucose Contra-Indications: No indications present Loss of gag reflex Side effects May progress to hyperglycemia Supplied 24 g tubes of carbohydrates Precautions Should be given to conscious patients Glucagon Classification: Anti-hypoglycemic Mechanism Of Action Stimulates glycogen release from the liver. Dosage: 1.0 mg SQ Mid Deltoid area Indications: Hypoglycemic patient with altered Level of consciousness & Glucose less <4, Unable to start IV & give D50 Unable to give sugar PO Glucagon Contra-Indications: Side effects nausea, vomiting Dizziness Possible BP Changes Supplied No indications present Allergy History of pheochromocytoma 2 vials #1 #2 1.0 mg powder 1.0 cc of diluting solution Precautions Do not dilute powder with saline Tetracaine Classification: Mechanism Of Action: Xylocaine Family Topical Anesthetic Stabilizes membranes of conjunctival and corneal pain fibers to inhibit depolarization and perception of pain Dosage: 2-3 gtts in affected eye(s) Indications: To allow flushing of the eye Contraindications: Possible penetrating injuries Allergy to local anaesthetics Tetracaine Supplied: Single disposable ampules Side effects: May briefly increase eye irritation Precautions: Removes patient’s blink reflex Charcoal Classification: None (Prevention of Toxic Absorption) Mechanism Of Action: Dosage: Adult: Pediatric: 1.0 – 2.0 g/kg 1.0 g/kg Indications: Binds to most toxins or poisons Reabsorbs poisons from liver or GI tracts Alert and cooperative Pts who have ingested a toxic substance Contraindication Acid/alkali ingestions Patient not alert/cooperative No bowel sounds Charcoal Side effects: Constipation Supplied: Bottles of 50 g Precautions: Stains clothing Not effective against Lithium or Acids/Alkali Calculations Amount to be administered in volume= Want/Have X Volume Ex: give 0.1 ml/kg to a 70 kg pt vial comes 10 mg/5 ml 0.1 mg/kg X 70 kg=7.0 mg (7.0 mg/10 mg) X 5.0 ml=3.5 ml