PREVENTIVE CAREMORE THAN JUST A PAP
SMEAR
ANN HONEBRINK MD
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA
DEPARTMENT OF OB GYN
WHAT MAKES A GOOD
PREVENTIVE INTERVENTION?
DEALS WITH A COMMON PROBLEM
ACCEPTABLE TO PATIENTS
LOW FALSE POSITIVE AND FALSE
NEGATIVE
COST EFFECTIVE
LOW RISK ”BACK UP TEST”
INTERVENTION BASED ON TEST RESULTS
HAS POSITIVE IMPACT ON OUTCOME
ORGANIZE BY AGE
13-18
19-39
40-64
65+
ORGANIZE BY
ASSESSMENT/INTERVENTION
SCREENING HISTORY/EXAM/LABS
EVALUATION AND COUNSELING
IMMUNIZATIONS
LEADING CAUSES OF MORBIDITY AND
MORTALITY-TRY TO ADDRESS THESE
WITH ABOVE TOOLS
13-18
First, set the ground rules
History
Sex/Drugs/Etc!!!
Exam
Height/Weight/BP
Secondary sexual characteristics
What about that first pelvic
Labs
Pap- NO- start at 21 as long as patient immune competent
STD screen
HIV-opt out?
13-18
Sexuality
Contraception-don’t forget Plan B
STD prevention
Orientation
Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Fitness and Nutrition
Psychosocial Eval
Evaluation and Counseling
Safe at home?
Suicide/Depression
Health Risk Behaviors
Seat Belts
Gun exposure
Sun Screen
Tobacco/Alcohol/Drug abuse
13-18
Immunizations
TDP booster(once between 11-18
Hep B
HPV(9-26yo)
Menignococcal conjugate vaccine
(before high school)
Influenza
Varicella/MMR (if not immune/no prior
vaccination)
13-18 – LEADING CAUSES OF
DEATH
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Accidents
Cancer
Suicide
Homicide
Diseases of the heart
Congenital Anomalies/Chromosomal abnormalities
Chronic lower respiratory diseases
Cerebrovascular Diseases
Influenza and pneumonia
In situ and benign neoplasms, neoplasms of uncertain
or unknown behavior
Pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum complications
19-39
History
Exam
Labs
Pap- Age21-30- every 2 years, over 30q 3yrs
+/- HPV if low risk
STD screen-when to stop?
HIV-opt out?
Think about Rubella Immunity testing if
planning a pregnancy soon
19-39
Evaluation and Counseling
Sexuality, including pregnancy intentions
Fitness and Nutrition-remember folic acid and
calcium
Preconceptual counseling (fam hx pt and
partner, occupational exposures, etc)
Psychosocial Eval
Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Health Risk Behaviors
19-39
Immunizations
TDP booster
Hep B
HPV??
Flu
Varicella if not immune
19-39 – LEADING CAUSES OF
DEATH
Cancer
Accidents
Diseases of the heart
Suicide
HIV
Homicide
Cerebrovascular disease
Diabetes
Chronic Liver diseases/cirrhosis
40-64
History
Exam
Start asking about incontinence and menopausal symptoms
Don’t forget to look in the mouth!
Labs-it gets a little more complicated!
Pap- what about lower risk women?
STD screen-when to stop?
HIV-opt out?
Mammogram
Lipids at 45 and q 5 yr
FBS at 45 and q 3 yr
TSH at 50 and then every 5 yrs
Colon Cancer at 50(colonoscopy seems best)
Dexa- when?
40-64
EVALUATION AND COUNSELLING
Sexuality- ask about postmenopausal atrophy
symptoms, don’t forget contraception/std
prevention
Fitness and Nutrition-remember folic acid and
calcium
Psychosocial Eval
Sleep hygiene
Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Health Risk Behaviors-Menopausal
symptoms????
40-64
Immunizations
TDP booster
Flu Vaccine
Zoster at 60
Varicella if no immunity
40-64 – LEADING CAUSES OF
DEATH
Cancer
Diseases of the heart
Accidents
Chronic lower respiratory diseases(including COPD)
Cerebrovascular disease
Diabetes
Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Septicemia
Suicide
HIV
Over 65
History
Exam
Keep asking about incontinence/atrophy
Don’t forget to look in the mouth!
When to stop pelvic exams?
Labs-it gets a little more complicated!
Pap- what about lower risk women? When to stop?
Mammogram yearly
Lipids- q 5 yr
FBS - q 3 yr
TSH-q 5 yr
Colon cancer screen- FOBT/Sigmoidoscopy/Colonoscopy
Urinalysis
Bone Density
HIV???
Over 65
Evaluation and Counseling
Sexuality- ask about postmenopausal
atrophy symptoms, reinforce “safer” sex
Fitness and Nutrition-remember calcium
and Vitamin D
Psychosocial Eval- Sleep hygiene, Fall
Prevention
Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Health Risk Behaviors-Menopausal
symptoms????
Over 65
Immunizations
TD booster every 10 yrs
Flu Vaccine yearly
Pneumococcal Vaccine- once
Zoster if not already done
Varicella if not immune
Over 65 – LEADING CAUSES OF
DEATH
Diseases of the heart
Cancer
Cerebrovascular disease
Chronic Lower respiratory diseases, including COPD
Alzheimer’s Disease
Pneumonia and Influenza
Diabetes
Renal disease
Accidents
Septicemia
PAP SMEAR TRIAGE
Bethesda Systemadequate?
Reading
Normal
Ascus (+ or – HPV)
ASC-H
AGUS
LGSIL
HGSIL
Cancer
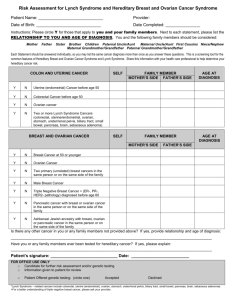
Special Issues- Genetic Risk
BRCA1- 39-45% lifetime risk ovarian cancer
BRCA2 – 12-20% lifetime risk ovarian cancer
Both have 65-74% lifetime risk of developing
Breast Cancer
1in 300-800 Americans are carriers, 1/40
Ashekanazi Jews are carriers
Who to screen?
20-25%risk of having BRCA 1 Or 2
gene mutation:
Personal hx breast AND ovarian cancer
Personal hx ovarian cancer and close relative
with ovarian cancer or premenopausal breast
cancer
Ashkenazie Jewish descent with hx breast
cancer dx before 40 OR ovarian cancer at any
age
Women with dx Br cancer before 50 ewho have
a close relative with ovarian cancer or a male
relative with breast cancer
Close relative with known Br Ca mutation
5-10%risk
Breast cancer before age 40
Ovarian, primary peritoneal or tubal cancer dx at
any age
Bilateral breast cancer dx, especially if one dx
pre 50
Breast cancer dx at any age with 2 or more
close relatives with Breast cancer dx at any age
(especially if anyone <50 at dx)
Unaffected women with a close relative that
meets any of the above criteria
What can we do differently if
screening positive?
Ca 125 and tvus annually starting at 35 or 5-10
years prior to youngest relative’s dx
Prophylactic BSO at 40 or when childbearing
completed, this reduces risk by 85-90%
Semiannual CBE, annual MRI alternating with
Mammogram starting at age 25 or sooner based
on youngest age at dx in family hx
Tamoxifen chemoprevention
Bilateral prophylactic mastectomy (reduces risk
by 90-95%)
As with everything we teach you
This is all subject to change without notice
US Preventive Services Task Forcewww.ahrq.gov/clinic/uspstfix/.htm
American College of Obstetricians and
Gynecologists-www.acog.org
American Cancer Society-www.cancer.org