public_health_in_newham_and_the_role_of_pharmacies
advertisement

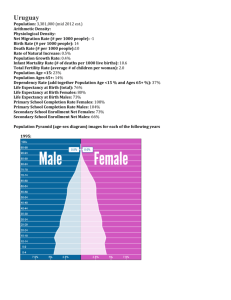
Public health in Newham Local health needs of the Borough André Pinto Regeneration and Social Determinants of Health Specialist 1 Slide 2 In context… 3 Index of Multiple Deprivation by LSOA ….within Newham… 5 Trend of life expectancy at birth for males and females in Newham, London and England, 1991-1993 to 2008-2010 86 84 82 80 78 Males Newham 76 Males London 74 Males England 72 Females Newham 70 Females London 68 Females England 66 64 Source: The NHS Information Centre for health and social care Slide 6 Dahlgren and Whitehead (M Benzeval, K. Judge and M. Whitehead (ed.s) Tackling Inequalities In Health: An Agenda For Action. Kings Fund.) 7 Life expectancy and disability free life expectancy at birth, persons by neighbourhood income level, England, 1999-2003 Age 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 Life expectancy DFLE 50 Pension age increase 2026-46 Poly. (DFLE) 45 0 5 10 15 Source: ONS 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 Poly. 75 (Life 80 85 90 95 100 expectancy) Neighbourhood Income Deprivation (Population Percentiles) The scale of the challenge Local Authorities in London compared to the Strategic Health Authority average Source: Health Profiles 2011, Public Health Observatories Slide 9 Significant worse than England average PHOF Indicators for Newham Deprivation Children in poverty GCSEs achieved Violent crime Long term unemployment Physically active adults Hospital stays for alcohol related hard Drug misuse People diagnosed with diabetes New cases of tuberculosis Life expectancy – male Life expectancy – female Deaths from smoking Early deaths: heart disease and stroke Pharmaceutical Needs Assessment JSNA 10 Pharmacies delivering Public Health – Track record Stop Smoking Medicines Use Review Minor ailments service Emergency Hormonal Contraception Service Condom Distribution Service Chlamydia Screening Service Needle Exchange Service and Supervised Consumption Service Tuberculosis Treatment Supervision Scheme NHS Health Checks New cases of tuberculosis Flu vaccination 11 Pharmacies delivering Public Health in Newham – scope for improvement Stop Smoking – make process easier. Medicines Use Review – develop further. Address concerns regarding quality. Encourage uptake. Minor ailments service – Provide additional primary care capacity. NHS Health Checks – Encourage uptake. Extend existing scope? (atrial fibrillation, hypertension, weight management and lifestyle interventions. Flu vaccination – increase uptake and training. Widen the scope (target groups)? HIV Point of Care testing – consider expanding pilot Anticoagulant Monitoring Service – Therapy initiated in the hospital but then monitored in community setting. Self Care – Promote community ownership of health outcomes and disease management (diabetes). Overcome resistance and access EMIS as a standard. Integrate pharmacy in care pathway. Communications Strategy 12 Health Inequalities Different Gestation Times for Interventions For example supporting individuals to reduce risk of mortality in people with established disease such as CVD, cancer, diabetes A For example supporting individuals through lifestyle and behavioural change such as stopping smoking, reducing alcohol related harm and weight management to reduce mortality in the medium term B For example intervening to modify the social determinants of health such as worklessness, poor housing, poverty and poor education attainment to impact on mortality in the long term C 2005 2010 2015 2020 Population Level Interventions Systematic community engagement Systematic and scaled interventions through services Partnership, Vision and Strategy, Leadership and Engagement Intervention Through Services Service engagement with the community Intervention Through Communities Producing Percentage Change at Population Level C. Bentley 2007 Achieving Percentage Change in Population Outcomes Programme characteristics will include being :– Evidence based – concentrate on interventions where research findings and professional consensus are strongest – Outcomes orientated – with measurements locally relevant and locally owned – Systematically applied – not depending on exceptional circumstances and exceptional champions – Scaled up appropriately – “industrial scale” processes require different thinking to small “ bench experiments” – Appropriately resourced – refocus on core budgets and services rather than short bursts of project funding – Persistent – continue for the long haul, capitalising on, but not dependant on fads, fashion and policy priorities Making every contact count