Clinical and Translational Science Institute
Translating Research Into Improved Health
David Nelson, MD
Director, Clinical and Translational Science Institute
Associate Dean, Clinical Research
Outline
• Challenges
– Health of our Nation
– Impact of diabetes
– The Translation Gap
• Opportunity
– UF Clinical and Translational Science Institute
• Research metrics (T1-T4)
• Resources and services
• Clinical trials infrastructure
• Implementation science: personalized medicine
2000, UC Atlas of Global Inequality http://ucatlas.ucsc.edu/spend.php
Infant Mortality: Common Indicator of the Health of a Country
The Burden of Diabetes in the
United States
• Approximately 21 million Americans have diabetes
• Diabetes is the sixth leading cause of death in the United States
– approximately 225,000 deaths annually
• Diabetes accounts for 19% of health care expenditures in the US
• Direct and indirect cost associated with diabetes (2007) exceed
$174 billion
Source: American Diabetes Association
Age-adjusted Percentage of U.S. Adults Who Were Obese
or Who Had Diagnosed Diabetes
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National Diabetes Surveillance System
http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/statistics
Percentage with complications
Prevalence of Diabetes Macrovascular and
Microvascular Complications
Diagnosed diabetes
Normal blood sugar levels
30
27.8
22.9
18.9
20
10
9.8
9.5
1.8
9.1
1.7
10
7.9
2.1
6.6
1.1
6.1
1.8
0
Heart attack Chest pain
Coronary
heart
disease
Congestive
heart failure
Macrovascular
Stroke
Chronic
kidney
disease
Foot
problems
Eye damage
Microvascular
American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. State of Diabetes Complications in America Report.
Available at: http://www.aace.com/newsroom/press/2007/images/DiabetesComplicationsReport_FINAL.pdf.
How Do We Build A Healthier America?
Factors That Drive Health Outcomes
Mortality (length of life)
Health Outcomes
Morbidity (quality of life)
Tobacco use
Health behaviors
(30%)
Diet & exercise
Alcohol use
Unsafe sex
Clinical care
(20%)
Health Factors
Access to care
Quality of care
Education
Employment
Social & economic factors
(40%)
Income
Family & social support
Community safety
Programs and
Policies
Physical environment
(10%)
Environmental quality
Built environment
Adapted from County Health Rankings model © 2010 UWPHI
The Translation Gap for T1 Research
More $ ≠ More Output
The Productivity Gap
New Molecular Entities and Biologic License Applications
Average R&D cost for each approved drug = $1.3 billion
Nat Rev Drug Disc 2010;9:89-92
Clinical Research to Clinical Practice (T3/T4)
-Lost in Translation.
NEJM 349(9) 868-874 August 28 2003
• …both health providers and
members of the public, are
not applying what we know.
• …we are not reaping the full
public health benefits of our
investment in research.
• …there is plenty of evidence
that "old" research outcomes
have been lost in translation
as well.
It takes 17 years to turn 14 per cent of original
research to the benefit of patient care
Original research
18%
Negative
results
variable
Submission
46%
0.5 year
Acceptance
Negative
results
0.6 year
Publication
35%
Lack of
numbers
0.3 year
Bibliographic databases
50%
6. 0 - 13.0 years
Reviews, guidelines, textbook
Inconsistent
indexing
9.3 years
Implementation
E.A. Balas, 2000
This is Not a New Problem: The Case of Scurvy
• 1593 - Sir Richard Hawkins
recommended the following
treatment for scurvy: "That which
I have seen most fruitful for this
sickness, is sour oranges and
lemons."
• 1601- Lancaster shows that
lemon juice supplement
eliminates scurvy among sailors
(non-randomized controlled trial)
• 1747- Lind shows that citrus juice
supplement eliminates scurvy
• 1795- (194 years after Level 2
evidence) British Navy
implements citrus juice
supplement
The Translational Research Continuum at UF:
An Expansion of T3 and T4 Research
What works under
controlled conditions?
“Bench”
Basic
Biomedical
Discovery
Clinical
Efficacy
T1
16%
What is the effect
on population
health
“Bedside”
(Translation to Humans)
18% 14%
20%
21%
T4
(Translation to
Population Health)
37%
27%
48%
2008
Community
Practices
•
•
•
(Translation to
Patients)
2011
(n= 862)
Clinical Practice
T2
What works in
real world
settings
(n=912)
T3
How can we
change practice?
(Translation to Practice)
Clinical
Effectiveness
Community
Practices
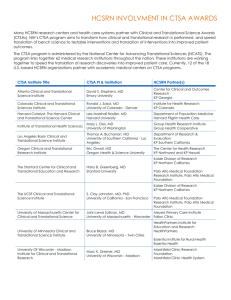
CTSI Study Registry includes 9,401 human subject research protocols across four IRBs (medical and non-medical)
4,497 / 9,401 are considered medical and/or health related protocols
3,422 / 4,229 are categorized as translational research (T1 – T4)
UF VIVO Map of Science
13 Disciplines
National Institutes of Health
Clinical and Translational Science Awards
• In 2006, NIH developed the Clinical and Translational Science Award
(CTSA) as a program of the National Center for Research Resources
• The CTSA consortium works together as a national resource sharing
a common vision to improve human health by helping scientists
bridge laboratory discoveries to patient treatments
• National Strategic Goals:
•
•
•
•
Improve the way biomedical research is conducted
Reduce time it takes for discoveries to become treatments
Engage communities in clinical research
Train the next generation of clinical and translational researchers
• The 61 CTSA institutions are linked together to transform the local,
regional, and national environment to increase the efficiency and
speed of clinical and translational research
CTSA: The National Consortium
A Catalyst for Collaboration
CTSA
consortium
Corporate
Partners
16 UF
Colleges
UF
CTSI
UF
Health Care
Systems
Institutes
Community
Partners
UF CTSI Organization
What Resources Are Available at CTSI?
Successful development and implementation of a project
• Regulatory and submission help
– Online irb submission (Click Commerce)
– Budget and pricing tool, fixed medicare rates for research
– Irb navigators, Clinical Trials.gov support
• Database development and support
– REDCap or custom
• Research design and analysis support
– Biostatistics, qualitative/quantitative analysis, informatics
• Communications research consulting (College of Journalism)
• Recruitment and retention services
– StudyConnect, HealthStreet, ResearchMatch
– IDR project: universal consent and cohort discovery
– Community engagement coordinators
What Other Resources Are Available at
CTSI?
• Clinical trial staff and facilities (inpatient/outpatient)
– CRC and disease-specific research units
– CTRB, Jax, and Lake Nona
• Pilot awards
• Education and Training programs for CTS
• VIVO: semantic approach to scholarly networking and discovery
• Core services
• Metabolomics (Tim Garrett, Dave Powell)
• Biorepository (Mike Clare-Salzler)
• Biobehavioral Core (Sara Joe Nixon)
• Genotyping Core (Julie Johnson)
• Human Imaging Core (Song Lai)
• Simulation (under development)
UF-Affiliated Research Networks
•
•
•
Local/ Regional
– North Florida Pediatric Community Research Network (Jacksonville area)
– Jacksonville Health Equity Research Organization Practice-Based Research
Network (JaxHERO)
Statewide
– Health IMPACTS for Florida (UF-FSU statewide research network)
– Florida Neonatal Neurologic Network
National
– NHLBI Cardiovascular Cell Therapy Research Network (Carl Pepine)
– NIDCR Dental Practice-Based Research Network (Valeria Gordan)
– Hepatitis C Therapeutic Registry and Research Network (HCV-TARGET, Nelson)
– Network for Pancreatic Organ Donors with Diabetes (nPOD)
– NIH Pharmacogenomics Research Network (Julie Johnson)
– Sentinel Network for Community-Based Participatory Research (Linda Cottler)
UF-FSU Community Research Program
Goal:
•
•
•
Test interventions in physician
practices;
Translate research findings into
improved health care quality; and
Mentor medical students and
trainees in conducting research
and implementing research
findings in practice.
Two pilot projects:
• Sports related concussion surveillance
and management (PI: Bauer)
• Health risk assessment among
adolescents in primary care (PI:
Shenkman)
Funding:
• UF/FSU($500,000)
• State of Florida ($600,000)
• NIH ($ 473,000)
Implementation Science
UF&Shands Personalized Medicine Program
• Background
– Human genome project completed in 2001
– Collins (NIH): expectation that an individual’s personal genome will be
part of their medical record, from which information can be pulled to
determine disease risk or guide treatment decisions
• Challenge
– Despite the substantial number of important genetic discoveries
made, there are limited examples of clinical translation to practice
• UF Objectives for Personalized Medicine Program
– Engage UF&Shands Health System as leaders in genetic-guided care
– Pre-emptively genotype on broad panel (256 SNPs) to mimic eventual
reality of genomic data in EMR
• Prepare health informatics systems to handle increasing amounts
of genetic data linked into EMR
• Define when and how to use genetic data in patient care
Personalized Medicine ProgramLaunched June 25, 2012
https://ufandshands.org/news/2012/uf-delivers-promise-personalized-medicine-heartpatients#!/-1/
Clinical Translation in Genomics and Pharmacogenomics
UF&Shands Personalized Medicine Initiative
Clopidogrel (Plavix): genetic polymorphism of CYP2C19 leads to reduced
ability to activate clopidigrel and increased risk of cardiovascular complication
CER, Economic Impact
“Front door” consent;
Bioethics; Communications
Research
Biorepository
BMI; Hospital IT; Epic
Genotyping Core
IDR; Bioinformatics; Research IT
NHGRI Genomic Medicine Proposal
Implementation Science
UF CTSI’s Vision
Improving the health of Florida’s communities with a focus
on prevention and an emphasis on team science
• Learning Health System
– “one which progress in science, informatics, and care culture align to generate
new knowledge as an ongoing, natural by-product of the care experience, and
seamlessly refine and deliver best practices for continuous improvement in
health and health care” (IOM, 2007)
– Put CTS research to work on health system priorities: quality, effectiveness,
safety
• Linkage as “One Florida”
– Cultivating an ability to work together with public and private partners to
develop statewide collaborations and networks
• UM CTSA award and statewide initiatives
• Human Investment-Team Science
– Develop and sustain current and future translational researchers and
strengthen the research workforce
– Team science approach as basis for both patient care and research