The Role of the Physician Associate
advertisement
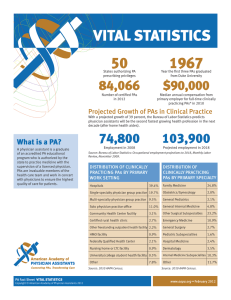
OUTLINE OF SESSION Definition of the Physician Associate Development of the Profession PA Responsibilities and Attributes Employment Professional Issues Training Programmes WHAT IS A PHYSICIAN ASSOCIATE? “…a new healthcare professional who, while not a doctor, works to the medical model, with the attitudes, skills and knowledge base to deliver holistic care and treatment within the general medical and /or general practice team under defined levels of supervision.” (The Competence and Curriculum Framework for the Physician Assistant, Dept. of Health, Sept 2006) Note: CCF updated in 2012. http://www.ukapa.co.uk/files/CCF-27-03-12-forPAMVR.pdf DEVELOPMENT OF THE PROFESSION Developed by doctors Need for primary care services Medical Education Model Increased capacity and access PHYSICIAN ASSOCIATE RESPONSIBILITIES The PA is trained to: Take Patient History Perform Physical Exam Formulate Differential Diagnosis Create Treatment and Management Plans Perform Procedures Select/Recommend Medications Request and Interpret Diagnostic studies … All with doctor supervision (the PA works to the scope of practice of the supervising doctor) PHYSICIAN ASSOCIATE ATTRIBUTES PAs are trained to be: Aware of the limits of their competence Team players Lifelong learners Autonomous decision makers within their scope of practice and level of experience HOW DOES A PHYSICIAN ASSOCIATE WORK? To the medical model With doctor supervision Within the scope of practice of the supervisor As a dependent clinician In a relationship between doctor and PA which is based on mutual trust and respect From within the Doctor-PA relationship, the PA exercises autonomous medical decision-making, to extend healthcare to the doctor’s patients PHYSICIAN ASSISTANTS GLOBALLY USA – 47 year history with > 100,000 qualified UK – 220 PAs, growing demand (outpacing supply) The Netherlands – ~1000 PAs from 5 programmes Canada – >300 PAs Sub-Saharan Africa – similar models; various titles; unknown numbers Australia – now training PAs Germany – training in progress RATIONALE: UK ROLE The PA profession helps to meet UK health care needs by: Building capacity Expanding skills mix Redistributing doctor workload Developing a defined health profession to expand midlevel staff without depleting current roles Help meet demand for increased quality of care PHYSICIAN ASSOCIATE EMPLOYMENT IN THE UK ~220 trained PAs working in: A&E Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery ENT Paediatric Intensive Care Paediatric Surgery GI Acute Medicine Haematology Derm/Lymphoedema Infectious Disease General Practice Cardiology Respiratory Oncology Urology Psychiatry Vascular Surgery Plastic Surgery GUM (Sexual Health) Geriatrics DH SPECIFICATION FOR PA EDUCATION Competence and Curriculum Framework Updated 2012 Competencies Procedural Skills Matrix of Conditions 2006 Programme Specification ~ 3200 hours over 2 years ~ 50% clinical (incl. 200 simulation hours) ~ 50% theory http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Pu http://www.ukapa.co.uk/files/CCF-2703-12-for-PAMVR.pdf blicationsandstatistics/Publi cations/PublicationsPolicyA ndGuidance/DH_4139317 PGDip PA STUDIES - CLINICAL PLACEMENTS General Practice Acute Medicine A&E Obs/Gynae Paediatrics Mental Health Surgery Electives: Cardiology, Gastroenterology, Dermatology, Neurology etc. NATIONAL EXAM Taken after completing university course Required to practise as PA SBA + OSCE Ensures minimum standards across UK PA programmes Re-certification exam EVERY 6 YEARS CURRENT ISSUES Registration & prescribing Voluntary list √ → voluntary register √ → statutory register Prescribing as integral to role rather than extension UKAPA - Leading Organisation (www.ukapa.co.uk) Registering Body Salary Band 7 (£30-39k) to 8a (£38-45k) Occasional Band 6 internship job post PA MVR PA TRAINING PROGRAMMES Current programmes Aberdeen Birmingham St George’s, University of London Worcester Wolverhampton (Oct 2014 Coming soon Plymouth (Jan 2015) In development or interested ~20 other universities GENERAL REQUIREMENTS Excellent interpersonal skills Motivated Self-directed learner Professionalism Maturity Strong communication skills (verbal & written) FINAL THOUGHTS Newly qualified PAs will still function as beginners Can make a substantial contribution in continuity for Patients Health care teams Pioneering as a Physician Associate Still relatively new role to the UK Opportunity to participate in change/creation Not THE solution, but PART of the solution! SUMMARY Intense Training Student Enthusiasm & Dedication Demand for PA role Opportunity to be part of a profession in the making