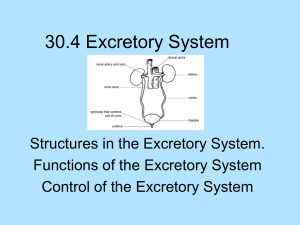
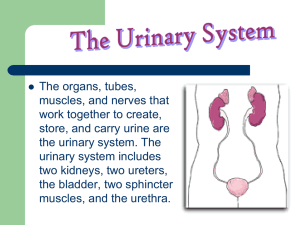
What happened with SLE Kidney disease ( lupus nephritis )in the past
advertisement

SLE and Kidney Disease in 2014 GERALD APPEL, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Columbia University –College of Physicians and Surgeons NY-Presbyterian Hospital New York, New York Lupus and Kidney Disease • What are the kidneys – how do they work? ( what is a nephrologist?) • How does SLE involve the kidneys? • How do you know if you have kidney involvement? • Are there different patterns of Kidney disease with SLE? • What happened with SLE Kidney disease ( lupus nephritis )in the past ? • Can we treat kidney disease due to LN today? • How successful are we? • Will there be new ways to treat it tomorrow. Lupus and Kidney Disease • What are the kidneys – how do they work? ( what is a nephrologist?) • How does SLE involve the kidneys? • How do you know if you have kidney involvement? • Are there different patterns of Kidney disease with SLE? • What happened with SLE Kidney disease ( lupus nephritis )in the past ? • Can we treat kidney disease due to LN today? • How successful are we? • Will there be new ways to treat it tomorrow. Where can one find a kidney? Lupus and Kidney Disease • What are the kidneys – how do they work? ( what is a nephrologist?) • How does SLE involve the kidneys? • How do you know if you have kidney involvement? • Are there different patterns of Kidney disease with SLE? • What happened with SLE Kidney disease ( lupus nephritis )in the past ? • Can we treat kidney disease due to LN today? • How successful are we? • Will there be new ways to treat it tomorrow. ISN/RPS Classification of LN • Class I Minimal mesangial LN • Class II Mesangial proliferative LN • Class III Focal LN III (A): Active lesions: focal proliferative LN III (A/C): Active and chronic lesions III (C): Chronic inactive lesions with scars • Class IV Diffuse LN IV-S (A): Active lesions: diffuse segmental proliferative LN IV-G (A): Active lesions: diffuse global proliferative LN IV-S (A/C): Active and chronic lesions IV-G (A/C): Active and chronic lesions IV-S (C): Chronic inactive lesions with scars IV-G (C): Chronic inactive lesions with scars • Class V Membranous LN • Class VI Advanced sclerotic LN ISN = International Society of Nephrology; RPS = Renal Pathology Society Lupus Nephritis Class I Lupus Nephritis Class II Lupus Nephritis Class III Histology WHO Class IV: Diffuse Endocapillary Proliferation With Karyorrhexis and Focal Necrosis Focal Necrosis Endocapillary Proliferation Lupus Nephritis Class IV Pre-Rx Post-Rx Lupus Nephritis Class IV Lupus Nephritis Class V End stage kidney due to chronic GN: Diffuse and global glomerulosclerosis, tubular atrophy & interstitial fibrosis Lupus and Kidney Disease • What are the kidneys – how do they work? ( what is a nephrologist?) • How does SLE involve the kidneys? • How do you know if you have kidney involvement? • Are there different patterns of Kidney disease with SLE? • What happened with SLE Kidney disease ( lupus nephritis )in the past ? • Can we treat kidney disease due to LN today? • How successful are we? • Will there be new ways to treat it tomorrow. Case 3: Saleswoman with rash and arthritis •A 29 year old saleswoman develops arthritis multiple joints, fever •Exam: Lymphadenopathy, and a malar rash. •Labs: –Urinalysis 3+ protein, 18-20 rbc’s –Creatinine 1.2 mg/dl –24 hr. protein 1.8 g per day –Complement 18% (normal 50-150%) –ANA positive, Anti-DNA antibody positive KIDNEY BIOPSY PERFORMED RBC cast forms a mold of tubular lumen Diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis: Diffuse and global mesangial and glomerular capillary wall positivity for IgG Full house IF staining: IgG, IgM, IgA, C3, C1q Lupus and Kidney Disease • What are the kidneys – how do they work? ( what is a nephrologist?) • How does SLE involve the kidneys? • How do you know if you have kidney involvement? • What happened with SLE Kidney disease ( lupus nephritis )in the past ? • Can we treat kidney disease due to LN today? • How successful are we? • Will there be new ways to treat it tomorrow. Side Effects of Cyclophosphamide in the past Event Cy Therapy (n = 21) Combination Therapy (n = 20) n/n n/n Hypertension 10/20 10/20 Ischemic heart disease 1/19 4/19 Hyperlipidemia 7/20 8/19 Valvular heart disease 9/19 7/21 Avascular necrosis 6/21 6/20 Osteoporosis 4/18 3/19 Premature menopause 9/16 10/18 Major infections 7/21 9/20 Herpes zoster infection 6/21 5/20 Lupus and Kidney Disease • What are the kidneys – how do they work? ( what is a nephrologist?) • How does SLE involve the kidneys? • How do you know if you have kidney involvement? • Are there different patterns of Kidney disease with SLE? • What happened with SLE Kidney disease ( lupus nephritis )in the past ? • Can we treat kidney disease due to LN today? • How successful are we? • Will there be new ways to treat it tomorrow. Proliferative LN ACR- KDIGO Treatment guidelines – INDUCTION MMF + glucocorticoids (e.g. pulse methylprednisolone) or CYC + Glucocorticoids (e.g. pulse methylprednisolone) EURO LUPUS Low-dose CYC 6 months Anti-MIF & LN Ad Board, July 13, 2011 or NIH study Hi-dose CYC 6 months CONFIDENTIAL Proliferative Lupus Nephritis – Maintenance Treatment ACR – KDIGO Treatment guidelines CYC induction NOT IMPROVED IMPROVED NOT IMPROVED MMF1-2g/d or AZA 2 mg/kg/d ± lo dose daily GC CYC (lo- or hidose) + pulse GC then daily GC MMF1-2g/d or AZA 2 mg/kg/d ± lo dose daily GC MMF 2-3g/d x 6 months + pulse GC then daily GC 6 months IMPROVED 6 months MMF induction Lupus and Kidney Disease • What are the kidneys – how do they work? ( what is a nephrologist?) • How does SLE involve the kidneys? • How do you know if you have kidney involvement? • Are there different patterns of Kidney disease with SLE? • What happened with SLE Kidney disease ( lupus nephritis )in the past ? • Can we treat kidney disease due to LN today? • How successful are we? • Will there be new ways to treat it tomorrow. ELNT - 10 year FU - ESRD Houssiau FA et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2009, ELNT - 10 year FU Houssiau FA et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2009, Jan 20 (Epub ahead of print) Response judged by blinded Clinical Endpoint Committee: Decrease in proteinuria to <3g if baseline nephrotic (≥3g/d) , or by ≥50% in patients ith subnephrotic (<3g/d) proteinuria and Stabilization of serum creatinine level (24-week level ± 25% of baseline), or improvement Proportion of patients reponding (%) ALMS TRIAL Primary Endpoint: Responders at Month 6 100 80 60 56.2% 53.0% 40 20 MMF IVC 0 MMF was not superior to IVC (p = 0.575) Appel , Contreras, Dooley et al JASN 2009 24 hour urine protein (g/day, SD) Serum creatinine (μmol/L, SD) ALMS Trial - Renal Variables 160 140 120 100 IVC MMF 80 60 40 20 0 9 8 Serum creatinine and urine protein levels improved in both the MMF and IVC groups 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Baseline 4 8 12 16 Week 20 24 Endpoint Lupus and Kidney Disease • What are the kidneys – how do they work? ( what is a nephrologist?) • How does SLE involve the kidneys? • How do you know if you have kidney involvement? • Are there different patterns of Kidney disease with SLE? • What happened with SLE Kidney disease ( lupus nephritis )in the past ? • Can we treat kidney disease due to LN today? • How successful are we? • Will there be new ways to treat it tomorrow. Rituximab: Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody Rituximab - FDA approved for the treatment of relapsed or refractory, CD20-positive B-cell NHLymphomas • Approved for Rheumatoid Arthritis – used in 240,000 patients > 10 yrs • Approved for ANCA+ glomerulonephritis since 2010 • Chimeric murine/human monoclonal antibody Davies B, Shaw T. Presented at EULAR 2004. Maloney DG, et al. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15(10):3266-3274. Rituxilup Trial • MPred + MMF + Rituximab vs MP + MMF + steroids ( ALMS regimen ) • 19 Adult + 4 Peds Centers in UK; Europe 12 Centers in 3 networks; US Centers. • Non-inferiority Trial of 252 LN patients • Primary endpoint complete remission at 1 yr. • Secondary Endpoints – Time to CR, Partial remissions, PR with histologic response, serious infections, SAEs, SRI score etc. IMNL-SCT-019799 Belimumab – FDA Approved for SLE Placebo 1 mg/kg belimumab * p<0.05 + + + * * + + p<0.05 + * + * + * + * + * 40 % SRI Responders SRI Responders (%) 60 10 mg/kg belimumab 20 0 p<0.05 50 * 40 30 20 10 0 0 4 8 0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 16 32 24 32 40 48 52 Week 44 36Visit 40 60 68 48 76 52 Visit Week Navarra, et al. Lancet. 2011;377(9767):721-31 Furie, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(12):3918-30 SRI, SLE Responder Index Abatacept ( CTLA4Ig Co-Stimulatory Blocker ) Study in 300 LN PTS Abatacept 30/10 30 mg/kg x4, then 10 mg/kg Q 28 days Randomization 1:1:1 Abatacept 10/10 10 mg/kg days 1,15, 29, then Q 28 days Placebo Days 1 and 15 (1st and 2nd dose) Dose every 28 days Day 337 Final dose Background Rx: MMF up to 3 g/day plus corticosteroids Primary Outcome Measure: Time to complete response Courtesy of D Wofsy Treatment of LN with Abatacept and Low-Dose Pulse Cyclophosphamide: The ACCESS Trial Brad H. Rovin on behalf of the ACCESS Trial Group • EuroLupus Low dose Cyclophosphamide and prednisone starting at 60 mg (tapering to 10 mg by week 12 ) • Azathioprine 2 mg/kg/day PO maintenance • Abatacept 500 mg or 1000 mg at 0, 2, 4, then Q4 wk until week 24 vs Placebo Proteasome Inhibitors N N O N H O OH H N B OH Bortezomib Carfilzomib ( Velcade™) (Kyprolis) Manufacturer Takeda Onyx/Amgen Status Approved Approved Indications Myeloma & Mantle Cell Lymphoma Myeloma & Solid Tumors Class Boronic Acid Ketoepoxide Active Sites Targeted b5/LMP7/LMP2 b5/LMP7 Bortezomib for NZB/W F1: Kidney Disease Neubert Nat. Med. 2008 An Open Label Randomized Phase IV Study of the Safety and Efficacy of ACTHAR GEL in Patients with Membranous (Class V) Lupus Nephritis Principal Investigator: Brad H. Rovin MD, Ohio State University Primary Objectives: • To determine the safety and tolerability of Acthar Gel in patients with Class V lupus nephritis • To determine the efficacy of Acthar Gel in patients with Class V lupus nephritis as CRR+PRR Administration of Acthar SCRN 0 1 2 3 4 5 Follow-Up 6 9 12 Study Month ARM 1. Acthar Gel 80 IU administered subcutaneously 2 times per week, 12 patients ARM 2. Acthar Gel 80 IU administered subcutaneously 3 times per week, 13 patients Treatment of Severe LN in the Future • Treatment will still be divided into an induction and maintenance phase. • Induction therapy will consist of Cyclophosphamide (usually IV ) or MMF or Newer regimens e.g. older drugs combined with CNI’s, ACTH, proteosome inhibitors, or corticosteroid free Rituximab regimens. • Maintenance therapy will consist of MMF or AZA or rituximab or other newer agents . • Use of combinations of immunosuppressives will increase. • One Regimen Will Not Fit All Lupus and Kidney Disease • What are the kidneys – how do they work? ( what is a nephrologist?) • How does SLE involve the kidneys? • How do you know if you have kidney involvement? • Are there different patterns of Kidney disease with SLE? • What happened with SLE Kidney disease ( lupus nephritis )in the past ? • Can we treat kidney disease due to LN today? • How successful are we? • Will there be new ways to treat it tomorrow.