Nicotine and pregnancy
advertisement

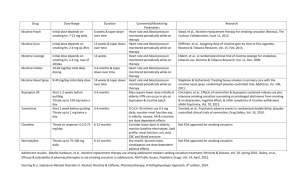
Nicotine Use in Pregnant Women and its Effect on Offspring Jessica Kozlowski, Pak Kei Chan Alan Lu, Shunzhi Chang 2014 Nov 25 PHM142 Fall 2014 Coordinator: Dr. Jeffrey Henderson Instructor: Dr. David Hampson 1. Introduction Negative effects of smoking on mother and fetus: Neurobehavioral effects Cardiovascular effects Reduced infant birth weight Premature delivery Infant death 1. Introduction 15-25% of mothers smoking during pregnancy Majority of women who quit for pregnancy start again after their child’s birth 45% of fathers smoking at the time of their child’s birth Why not quit? Start smoking cessation? - nicotine addiction Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) better alternative for the fetus. Is it safe? Minimal human data about effect of direct nicotine exposure in pregnant women, but a lot about tobacco smoke exposure. 2. Pharmacokinetics of Nicotine Clear liquid b.p.247 °C Small molecule Mw = 162 Miscible in water logP = 1.2, amphiphilic Fast absorption Cross Blood-brain barrier (10~20s) and placenta barrier 2. Pharmacokinetics of Nicotine 3. Cigarette Smoking during Pregnancy - Effects on offspring Few studies to accurately evaluate effects in pregnant women using nicotine replacement therapy (NRT). Most effects studied in rodents. Short term effects: low birth weight and sudden infant death syndrome. Long-term effects: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Neurobehavioral problems. Hypertension. Obesity and type 2 diabetes. Respiratory dysfunction. Childhood cancers (leukemia/lymphoma). Impaired fertility. 3. Cigarette Smoking during Pregnancy - Neurobehavioural problems Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, learning disabilities, behavioral problems, increased anxiety. In rats, nicotine is a neuroteratogen, which compromises development of critical neural pathways. 10 uM 100 uM 3. Cigarette Smoking during Pregnancy - Hypertension Associated with in utero exposure to cigarette smoking. Perinatal nicotine In rats, perinatal nicotine exposure exposure: Enhances AT1 and attenuates AT2 gene expression. Increases Ca2+ sensitivity of myofilaments leading to vasoconstriction and development of hypertensive phenotype in adulthood. AT1: Angiotensin II receptor type 1. AT2: Angiotensin II receptor type 2. AT1/AT2 ratio ↑ ↑ Ca2+ sensitivity of myofilaments ↑ Vasoconstriction Hypertension 4. Methods of Smoking Cessation Bupropion (Zyban) Nicotine Replacement Therapy Other (Hypnosis, acupuncture, quitting gradually, quitting “Cold Turkey”) 4. Preventative Methods - Bupropion Initially prescribed to treat various forms of depression. It was discovered that smoking cravings and withdrawal effects were reduced. Inhibition of neurotransmitter uptake Study conducted showed no increased risk of congenital malformation in fetal development. Summary Slide Nicotine can readily cross the blood-brain barrier and the placental barrier. It is also an ingredient found in tobacco and it’s primary responsible for sustaining addictive effects. Smoking during pregnancy has been shown to cause neurobehavioral and cardiovascular abnormalities. Nicotine acts as a neuroteratogen and induce neurobehavioral problems which include: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), learning disabilities, or increased risk of nicotine addiction. An example of a cardiovascular problem is hypertension. Studies conducted in rats have shown that perinatal nicotine exposure : - Alters the gene expression of AT1 and AT2 - Myofilaments are more sensitive to Ca2+ - Vasoconstriction occurs easily, thus causing hypertension The bottom line: Absentia > Bupropion > NRT > cigarette smoking, with the best alternative to smoking being quitting prior to pregnancy. Thank You Very Much! References Bruin JE, Gerstein HC, Holloway AC (2010) Long-term consequences of fetal and neonatal nicotine exposure: a critical review. Toxicol Sci 116: 364-74. Ho MK, Tyndale RF (2007) Overview of the pharmacogenomics of cigarette smoking. Pharmacogenomics J 7: 81-98. Horst WD, Preskorn SH (1998) Mechanisms of action and clinical characteristics of three atypical antidepressants: venlafaxine, nefazodone, bupropion. J Affect Disord 51: 237-54. Rose JE, Behm FM, Westman EC, Coleman RE (1999) Arterial nicotine kinetics during cigarette smoking and intravenous nicotine administration: implications for addiction. Drug Alcohol Depend 56: 99-107. Slotkin TA (2004) Cholinergic systems in brain development and disruption by neurotoxicants: nicotine, environmental tobacco smoke, organophosphates. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198: 132-51. Wickstrom R (2007) Effects of nicotine during pregnancy: human and experimental evidence. Curr Neuropharmacol 5: 213-22. Wu P, Wilson K, Dimoulas P, Mills EJ (2006) Effectiveness of smoking cessation therapies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 6: 300. Xiao D, Dasgupta C, Li Y, Huang X, Zhang L (2014) Perinatal nicotine exposure increases Angiotensin II receptor-mediated vascular contractility in adult offspring. PLoS One 9: e108161. Zyban 150 mg prolonged release film-coated tablets – Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC)". electronic Medicines Compendium. GlaxoSmithKline UK. 1 August 2013. Retrieved 22 October 2013.