Walking pneumonia - The Cabrini Code
advertisement

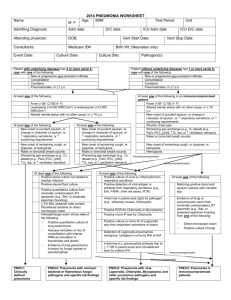
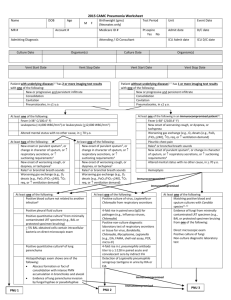
Pneumonia 101 Armaan Khalid What the... Definition of Pneumonia An acute or chronic disease marked by inflammation of the lung parenchyma, that causes consolidation of inflammatory exudates Main causes Bacteria Virus Fungal & etc Classification Anatomical/Radiological Lobar Multi-focal/lobular (bronchopneumonia) Interstitial (focal diffuse) Location of Contraction Community Institutional (nursing home) Nosocomial (hospital) Precipitating Factors Smoking (Smokers in household) Previous lung pathology (COPD, CF) EToH abuse Immunosuppresion Recent hospital admission IVDU (S Aureus haematogenous spread) Recent exposure to pneumonia pts Preceding viral infection HIV Causative Organisms Atypical Pneumonia Assoc w a milder form of pneumonia Walking pneumonia Considered atypical because Inability to detect on gram stain Inability to be cultivated in normal media Examples Mycoplasma Chlamydophila species Legionella Coxiella burnetii (Q fever) Bordetella pertussis (Whooping cough) Clinical Presentation Preceding Hx of viral illness On Hx/Ex Febrile/Pleuritic Pain/Dry cough Sputum production Malaise/Rigors/Chills Tachypnoea/cardia ↓ chest movements Use of accessory chest muscles Sg of consolidation +/- pleural rub History Taking Impt to review pt’s: Potential exposure Envt/Work/Social factors Aspiration risks Seizure/EToH/GORD Host factors COPD/IVDU/Smoking/HIV Sputum Characteristics S Pneumoniae Rust coloured sputum Pseudomonas/Haemophilus & Pneumococcal Green sputum Klebsiella species Red currant jelly sputum Anaerobic species Foul smelling/Bad tasting sputum Risk Stratification How do you make the decision to Rx the pt in a out/in-patient setting? CURB-65 criteria Pneumonia Severity Index (PSI) PSI calculator online http://pda.ahrq.gov/clinic/psi/psicalc.asp CURB-65 criteria C – Confusion U – Uraemia, BUN > 20 mg/dL R – Respiratory Rate > 30 bpm B – Blood pressure < 90/60 mm Hg 65 – Age > 65 years old Score 0-1: Score 2: Score 3-4: Outpatient treatment Admit to the wards Admit to ICU PSI Calculator Differential Diagnosis Asthma Atelectasis Bronchiectasis COPD Lung Abscess Viral infection Influenza Workup FBE/UNE/BUN/LFT/CRP/ESR Blood cultures Impt to get them before initiating empirical therapy Sputum (microscopy & culture) ABG ? Pleural fluid tap CXR (frontal & lateral) Further Workup Pneumococcal antigen Counter-immunoelectrophoresis of sputum, urine & serum Mycoplasma antibodies Legionella & Chlamydia antibodies Immunoflurorescent tests Legionella antigen Urinary antigen test Radiological Findings General Characteristics Affected tissue will appear denser May contain air bronchogram(s) Visibility of air in the bronchi Sign of airway disease, not pathognomonic for pneumonia Airspace pneumonia appears fluffy & their margins are indistinct If it abuts a pleural surface, there will be a sharp demarcation of the margins Patterns of Appearance Lobar Segmental (Bronchopneumonia) Interstitial Round Cavitary I Spy With My Little Eye Lobar Pneumonia Patterns on CXR Lobar Pneumonia Common organism: S Pneumoniae Homogenous consolidation w air bronchogram Silhouette sign present when in contact with the heart, aorta or diaphragm Segmental Pneumonia Patterns on CXR Segmental (Bronchopneumonia) Common organisms: S Aureus & gramnegative bacteria Affects the walls of the bronchioles Spread centrifugally via tracheobronchial tree to many foci @ the same time Margins are fluffy & indistinct Produces exudate that fills the bronchi No air bronchograms present May be assoc w atelectasis Interstitial Pneumonia Patterns on CXR Interstitial Pneumonia Common organisms: Mycoplasma, viral pneumonia & PCP Reticular interstitial disease w diffuse spread throughout lungs in early disease process Frequently progresses to airspace disease Round Pneumonia Patterns on CXR Round Pneumonia Common organisms: H influenzae, Strep & Pneumococcus Spherical pneumonia usually seen in the lower lobes of children May resemble a mass Clinical presentation does not match w that of a mass Cavitary Pneumonia Patterns on CXR Cavitary Pneumonia Common organism: M tuberculosis Primary TB < Reactivation TB Primary TB Upper lobes > lower lobes Assoc w ipsilateral hilar adenopathy & large unilateral pleural effusions Reactivation TB Cavities are thin-walled, smooth inner margin & usually no air-fluid level Localised Lower Lobe Pathology Spine Sign On Lateral CXR, thoracic spine vertebra are darker in diaphragm than in shoulder girdle CXR needs to penetrate more tissue in the shoulder girdle than in diaphragm With interstitial/airspace disease in posterior lower lobe, vertebra would be more opaque (brighter) than usual Spine Sign! Silhouette Sign If 2 objects of the same radiographic density touch each other, then their edges disappear Silhouette Sign Valuable in localising lung pathology Silhouette Sign Helpful Hints Structure That Isn’t Visible Disease Location Ascending Aorta Right Upper Lobe Right Heart Border Right Middle Lobe Right Hemidiaphragm Right Lower Lobe Descending Aorta Left Upper/Lower Lobe Left Heart Border Lingula of Left Upper Lobe Left Hemidiaphragm Left Lower Lobe Management Respiratory Support O2 +/- bronchodilators Fluid resuscitation Empiric Abx Rx Empiric Rx should initially be broad Each hospital has it’s own guidelines Empirical Rx of Pneumonia Supportive Measures Analgesia & anti-pyretics Chest physiotherapy IV fluids or diuretics Positioning of patient (Aspiration risk) Suctioning & bronchial hygiene Clinical Resolution Clinical response to Abx Rx Improvement seen in 48-72 hrs Abx shouldn’t be changed w/in 72hrs Time required for Abx to act Change if marked deterioration Radiological resolution takes longer than clinical resolution Clinical Resolution (or lack thereof) No resolution Resistant to Abx 2° to complications (empyema/abscess) Non-infectious cause (CHF/malignancy) Viral aetiology Consider CT/MRI Bronchoscopy Lung biopsy Consult ID physician Viral Pneumonia Common in children & the elderly Prevalent in the immunosuppressed Uncommon in adults 13-50% of all CAP Influenza virus main offender (>50%) Clinical findings similar to bacteria May predispose & superimpose on a bacterial pneumonia Common during winter Rx Supportive Rx Antiviral Immunisations References Kumar & Clark, Clinical Medicine, 6th edn, Chapter 14, Pneumonia, pp 922929 W Herring, Learning Radiology: Recognizing The Basics, 1st edn, Chapter 8 Recognizing Pneumonia, pp 60-67 Longmore et al, OHCM, 7th edn , Chapter 5, Chest Medicine, pp 152-153