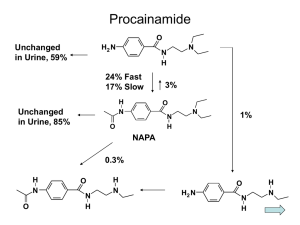
PXR
advertisement

Role of PXR Signaling in Mediating the Cardioprotective Effects of -3 Fatty Acids Saraswathi Viswanathan, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Internal Medicine/DEM University of Nebraska Medical Center-Omaha Metabolic Syndrome and CVD • • • • • Abdominal obesity Atherogenic dyslipidemia Insulin resistance Elevated blood pressure Pro-inflammatory state Fish and PUFAs Fish OilOil and -3-3 Fatty Acids EPA-Eicosapentaenoic acid DHA-Docosahexaenoic acid Clinical Evidence for the Beneficial Effects of Fish Oil • 30 g of fish per week reduced caronary artery disease (Kromhout DBE, 1985). • EPA&DHA reduced plasma TG and nonHDL cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia (De Luis, DA 2009). • -3 fatty acids reduced plasma TG, total cholesterol without altering glycemic index (Sirtori CR, 1998). Mechanisms TG-Lowering Effect • • • Reduced TG secretion Increased TG clearance Increased -oxidation Mechanisms Mediating the Cholesterol-Lowering Effects Cholesterol CYP 7A1 CYP 27A1 CYP 11A CYP 3A Cholesterol hydroxylation Bile acid Sulfotransferases Glutathione S transferases CYP3A Sult1e1 Sult2a1 Sult3e1 Gsta1 Gsta2 Bile acid Detoxification PXR Mechanisms Mediating the AntiInflammatory Effects of -3s • • • • Interference with arachidonic acid metabolism COX-derived 3-series eicosanoids LOX-derived resolvins Cytochrome P450-derived epoxides PXR and Inflammation PXR CYP 2C and CYP 3A -3 FAs -3 epoxides Antiinflammatory PXR •Drug detoxification •Bile acid homeostasis •Cholesterol metabolism •Reduce inflammation Preliminary Data Effect of Fish Oil on Plasma Lipids 1.0 250 500 ^ 400 300 200 100 OO FO 200 150 ^ 100 50 0 OO FO n=13-15 per group; ^P<0.001 vs OO OO-Olive Oil, FO-Fish Oil Free Fatty Acids (mEq/L) 600 0 FFA-Plasma TG-Plasma Triglycerides (mg/dL) Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) TC-Plasma 0.8 0.6 ^ 0.4 0.2 0.0 OO FO Effect of Fish Oil on Hepatic Steatosis B CE 25 20 15 ^ 10 5 0 75 60 45 ^ 30 15 FO O O FO 0 D Free fatty acids (mg/g) 3 2 1 FO O O 0 FFA 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 n=4-10 per group; ^P<0.001 vs OO OO-Olive Oil, FO-Fish Oil FO FC 4 O O C Free cholesterol (mg/g) TG 90 Triglycerides (mg/g) 30 O O Cholesterol ester (mg/g) A Effect of Fish Oil on Inflammatory Genes in Liver 0.0 OO 1.0 ^ 0.5 0.0 FO OO IL-1 1.0 ^ 0.5 0.0 OO FO MMP-12 1.5 1.0 0.5 ^ 0.0 FO E 1.5 MMP-12 mRNA (Relative Expression) ^ 0.5 MIP-1 1.5 OO FO F TNF 2.0 1.5 1.0 # 0.5 0.0 OO FO SAA-1 mRNA (Relative Expression) 1.0 MIP-1 mRNA (Relative Expression) MCP-1 1.5 D IL-1 mRNA (Relative Expression) C B TNF mRNA (Relative Expression) MCP-1 mRNA (Relative Expression) A SAA-1 1.2 0.8 # 0.4 0.0 OO n=5-6 per group; ^P<0.001 and #P<0.01 vs OO OO-Olive Oil, FO-Fish Oil FO Genes Upregulated in Liver upon Fish Oil Feeding-Microarray Analysis Genes CYP3A44 CYP2C68 Sult 1e1 Sult 1b1 Sult 3a1 GSTA1 GSTA2 Fold Increase 1.6 1.6 2.2 2.0 1.8 2.2 1.6 Effect of Fish Oil on PXR and CYP3A in Liver OO PXR CYP3A GAPDH GAPDH PXR/GAPDH CYP3A/GAPDH # 0.4 0.2 0.0 OO FO 0.8 CYP3A/GAPDH (Arbitrary Units) PXR/GAPDH (Arbitrary Units) 0.6 FO OO FO # 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 OO FO OO,Olive Oil; FO, Fish Oil, n=5-6 samples per group, #P<0.01 vs OO Hypothesis Cholesterollowering Effects -3 Fatty Acids (EPA & DHA) PXR Cardioprotective Effects Anti-inflammatory Effects Overall Hypothesis: The cholesterol-lowering and antiinflammatory effects of -3 fatty acids are mediated via PXR. Specific Aims Specific Aim 1: To determine the role of PXR in mediating the cholesterol-lowering and anti-inflammatory effects of -3 fatty acids in a model of diet-induced obesity and dyslipidemia. Specific Aim 2: To determine the role of PXR in mediating the cholesterol-lowering and anti-atherosclerotic effects of -3 fatty acids in a model of genetic dyslipidemia. Specific Aim 3: To determine whether the -3 fatty acids modulate PXR signaling in cultured hepatocytes. Experimental Design-Specific Aim 1 Experimental Diets High Fat Diet 45% Fat (energy) 1% Cholesterol Chow Diet Study Groups Mutant-PXR-/- WT-PXR+/+ Chow Diet 0.56% Oleic Acid 0.56% -3s Chow Diet 0.56% Oleic Acid 0.56% -3s Proposed Experiments-Specific Aim 1 • • • • Lipid profiles in plasma and liver Expression of genes/proteins involved in cholesterol/bile acid metabolism and inflammatory response Analysis of gall bladder bile for cholesterol and phospholipids Levels of -3 epoxide metabolites in liver Experimental Design-Specific Aim 2 Experimental Diets High Fat Diet 40% Fat (energy) 0.5% Cholesterol Chow Diet Study Groups LDLR;PXR-/- LDLR-/- Chow Diet 0.56% Oleic Acid 0.56% -3s Chow Diet 0.56% Oleic Acid 0.56% -3s Proposed Experiments-Specific Aim 2 • Lipid profiles in plasma and liver • Genes involved in cholesterol/bile acid metabolism and inflammatory response • Analysis of gall bladder bile for cholesterol and phospholipids • Atherosclerotic lesion area Experimental Design-Specific Aim 3 Primary Hepatocytes from WT and PXR-/- Mice PXR Signaling LCA Bile Acid Detoxification Inflammation Apoptosis LCA+ -3s Bile Acid Detoxification Inflammation Apoptosis Experimental Design-Specific Aim 3 Human HepG2 Cell Line Scrambled siRNA for PXR siRNA for PXR Inflammation Inflammation -3s -3s LCA Apoptosis Apoptosis Summary Dyslipidemia in Obesity Genetic Dyslipidemia -3 Fatty Acids (EPA & DHA) SA2 SA1 Hepatocyte Inflammation & Apoptosis PXR Signaling SA3 CYP 2C & CYP 3A Cholesterol & Bile Acid Metabolism 3-Epoxides Liver Lipid-lowering Effects Anti-inflammatory Effects Anti-atherosclerotic Effects Impact • Identification of novel molecular mechanisms by which 3 fatty acids mediate their cholesterol-lowering and antiinflammatory effects. • The findings will be critical to target PXR using dietary factors to efficiently prevent/treat dyslipidemia in humans without adverse side effects.