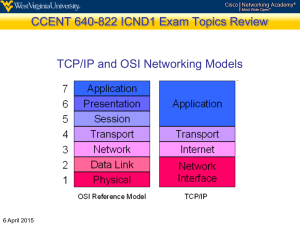
Chapter 5
advertisement

Trojans, Backdoors, Rootkits Viruses, and Worms Trojans: Programs that hide malicious code Backdoor: Way of accessing a computer without the security and authentication procedures that are normally required Rootkit: Modify the OS to conceal malicious programs while they run Virus: self-replicating (within a machine) by producing its own code; attach copies of itself to other executable code Worm: infects local and remote machines; spread automatically Example: Melisa “Virus” (1999) Trojan: entered computers by masquerading as an email Virus: infected word processing files when opened Worm: used Outlook to spread itself to user’s personal address book Trojan: Malicious program disguised as something benign Often delivered as part of a “wrapper” process Examples: BackOrifice: 31337 or 31338 – “Cult of the Dead Cow” NetBus: 12345, 12346, 20034 Whack-a-mole: 12361 or 12362 Delivered via: NetBIOS remote install Fake executables ActiveX controls, VBScript, Java scripts Spyware / Adware Backdoor Allows access to the system Often delivered via a Trojan May install a new service, or use an unused existing service Remote Access Trojan (RAT) Overt: normal and legitimate use Covert: using programs in unintended way Tunneling is a good way for Trojans to bypass IDS Port redirectors: modify which ports are used Datapipe (Linux) Fpipe (Windows) Port analyzing Fport: Identify unknown open ports and their associated applications Remote Access Trojans (RATs) Data-Sending Trojans Collect passwords & other confidential data Eg: eBlaster Destructive Trojans: destroy files or OS DoS Trojans: cause DoS attack Proxy Trojans: help hacker hide FTP Trojans: connect via port 21 Security Software Disabler Trojans FireKiller 2000 External attacker accesses internal systems QAZ: 7597 Replaces Notepad.exe with Note.com Tini: 7777; Windows Backdoor trojan allowing command prompt to anyone who connects Donald Dick: 23476 or 23477 NetBus: 12345, 12346, 20034, 23476 Netcat: allows telnet session Sample command: nc –L –p 5000 –t –e cmd.exe SubSeven BackOrifice 2000: 31337 Firekiller 2000 Programs auto starting and running Screen flips Sudden reduction in system resources Corrupt or missing files CD-ROM drawer opens and closes Wallpaper, background, etc changes Unexpected/suspicious Web sites Mouse moves by itself or pointer disappears Taskbar disappears Task Manager is disabled netstat –an Back Orifice Deep Throat NetBus Whack-a-Mole TCP NetBus 2 GirlFriend Sockets de Troie Masters Paradise UDP 31337, 31338 UDP 2140, 3150 TCP 12345, 12346 12361, 12362 TCP 20034 TCP 21544 TCP 5000, 5001, 50505 TCP 3129, 40421, 40422 40423, 40426 Devil Evil Doly Trojan Chargen Stealth Spy Phaze NetBIOS datagram Sub Seven ICQ Trojan MStream TCP 65000 TCP 23456 TCP 1011, 1012, 1015 UDP 9, 19 TCP 555 TCP, UDP 138 TCP 6711, 6712, 6713 TCP 1033 UDP 9325 The Prayer 1.0 – 2.0 TCP Online KeyLogger UDP Portal of Doom TCP,UDP Senna Spy TCP Trojan Cow TCP 9999 49301 10067, 10167 13000 2001 Features: Firewall testing, port scanning, create backdoor, identify services Command line interface opens TCP and UDP -d: detach from the console -l –p [port]: creates a listening TCP port -z: port scanning -v: verbose mode -e: run at any time -L: auto restart after dropped connection -u: switches to UDP Three things needed: Legitimate Program Trojan Program Wrapper Program Bundle Trojans with legitimate software Trojan Man Yet Another Binder Predator Wrapper Graffiti EXE Maker Restorator Spyware detectors Malwarebytes Norton Internet Security Fport Tripwire Check file signature, size, integrity Dsniff: contains Trojans, collection of hacking tools Windows Built-in Commands Sigverif SFC (system file checker): sfc /scannow “What’s Running” or “What’s on My Computer?” Be wary of free cleaning applications International Computer Security Association (ICSA) Sets standards for AV software Virus: infects another file and spreads Worm: Does not need a carrier program Often exists inside other files (like Word or Excel) Examples: Nimda, I Love You Polymorphic: change signature to avoid detection – eg: Virut (requires reformat) Stealth: hide File: infects files that can load/execute (.exe, .com, .bin, .sys) Armored: encrypted Boot Sector: modifies master boot files System Sector: affect the executable code of the disk Program: infect .BIN, .COM, .EXE, .SYS files Macro: perform a sequence of actions when a particular app is triggered; eg: Excel Tunneling: tunnel under antivirus software and hide Multipartite: affects multiple targets Dual Payload: Eg: Chernobyl: changes 1st MB of HD to zero; replaces code of BIOS to garbage Network: run code on remote systems Source Code: not common, very hard to write due to different compilers and languages Example: Batch file called Game.bat text @ echo off delete c:\windows\system32\*.* delete c:\windows\*.* Convert Game.bat to Game.com with ‘bat2com’ utility Assign an icon with Windows file properties screen Send as email attachment Kefi’s HTML Virus Construction Kit Virus Creation Laboratory v1.0 The Smeg Virus Construction Kit Rajaat’s Tiny Flexible Mutator v1.1 Windows Virus Creation Kit v1.00 Scanning with UP TO DATE scanner Use Sheep Dip or SocketShield Integrity checking Isolate one computer from the network and run downloaded software there first Tripwire With MD5 Downside: can’t detect differences made by virus versus a bug Testing antivirus software EICAR.com X5O!P%@AP[4\PZX54(P^)7CC)7}$EICAR-STANDARD-ANTIVIRUS-TEST- FILE!$H+H*