File - Ms. Robinson
advertisement

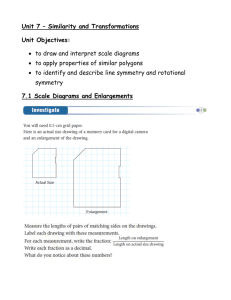
Translations in the Coordinate Plane Symmetry in Reflections Reflections in the Coordinate Plane Rotational Symmetry Rotations in the Coordinate Plane Dilations Translations in the Coordinate Plane Symmetry in Reflections Reflections in the Coordinate Plane Rotational Symmetry Rotations in the Coordinate Plane Dilations $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 Which Graph shows the translation of the letter Z? If point A is translated 4 units left and 3 units up, what will be the coordinates of point A in its new position? G. (-5, 5) Identify the transformation that is not the same as the other three. Explain your reasoning. The transformation A is not a translation; the others are translations. Triangle PQR has vertices P(0, 0), Q(5, -2), and R(-3, 6). Predict the vertices of P’Q’R’ after the translation 8 units left, and 1 unit down. P’(-8, -1) Q’(-3, -3) R’(-11, 5) What are the coordinates of the point (x,y) after being translated m units left and n units up? (x – m, y + n) Determine whether the figure has line symmetry. If so, copy the figure and draw all lines of symmetry. Yes, 6 lines of symmetry Determine whether the figure has line symmetry. If so, copy the figure and draw all lines of symmetry. No, it does not have line symmetry. Describe the ways the symmetry of the Fogong Monastery, show below at the left, if similar to that of the Eiffel Tower in Paris, France, shown below at the right. Both structures will look the same after reflected over a vertical line and will not look the same after reflected over a horizontal line. Flags of some countries have line symmetry. Of the flags shown below, which flags have line symmetry? Copy and draw all lines of symmetry. The drawing shows a car. Copy the drawing on grid paper. Then draw the right side of the car so that the completed drawing has a vertical line of symmetry. Copy the figure onto graph paper. Then draw the image of the figure after a reflection over the given line. Predict the coordinates of the image’s vertices after triangle FGH is reflected over the x-axis. F (1, -1) G (5, -3) H (2, -4) F’(1, 1) G’(5, 3) H’(2, 4) Which of the following is the reflection of triangle ABC with vertices A(1, -1), B(4, -1), and C(2, -4) over the x-axis. Marisol found the results of a reflections over the y-axis. They should be A’(1, -1), B’(4, -1), and C’(1, -5). Suppose point K with coordinates (7, -2) is reflected so that the coordinates of its image are (7,2). Without graphing, which axis was the point reflected over? Explain your reasoning. The x-axis. The xcoordinates are the same, but the y-coordinates are opposites. Determine whether the figure has rotational symmetry. If it does, name the angle(s) of rotation. Yes, 180 degrees. Determine whether the figure has rotational symmetry. If it does, name the angle(s) of rotation. No, it does not have rotational symmetry. Show the figure after a clockwise turn of 90, 180, and 270 degrees. Show the figure after a clockwise turn of 90, 180, and 270 degrees. Which figure show the letter F after a rotation 270 degrees clockwise? Triangle XYZ has vertices X(2, -2), Y(5, 0), and Z(3, -4). What are the coordinates of point Y’ after a clockwise rotation of 180 degrees? (-5, 0) Triangle XYZ has vertices X(2, -2), Y(5, 0), and Z(3, -4). What are the coordinates of point Y’ after a counterclockwise rotation of 90 degrees? (0, 5) Describe what information is needed to rotate a figure. To rotate a figure, you need to know the number of degrees it is going to be rotated, the direction of rotation, and about what point the figure is being rotated. Draw a figure that has line symmetry but not rotational symmetry. Draw and find the new vertices of the following triangle after a counterclockwise rotation of 270 degrees about the origin. Quadrilateral LMNP was dilated to form quadrilateral WXYZ. Which number best represents the scale factor used to change quadrilateral LMNP into quadrilateral WXYZ? A. 3 B. 2 C. ½ D. 1/3 C. ½ Square A is similar to square B. What scale factor was used to dilate square A to square B? 3/5 Copy the figure shown. Then draw the figure centered on X with a scale factor of 7/3. Copy the figure shown. Then draw the figure centered on Z with a scale factor of 2/3. Write a general rule for finding the new coordinates of any ordered pair (x, y) after a dilation with a scale factor of k. Multiply each member of the ordered pair (x, y) by the scale factor k. The new coordinates are (kx, ky). Multiple Transformations Describe the image after a dilation with a scale factor of -2.