Velocity and Speed - Western Reserve Public Media
advertisement

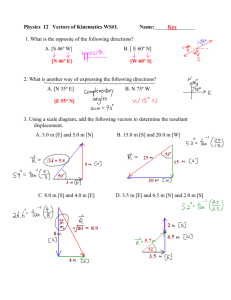
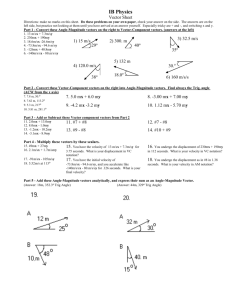
What is speed? Speed: how fast something is moving or how much distance is covered in a certain amount of time. We will discuss two types of speed: • Instantaneous speed: An object’s speed at any given instant. • Average speed: An average of all instantaneous speeds. To calculate average speed • average speed = total distance/time s = d/t If you cover 75 m in 3 sec, how fast are you going? Answer: 25 m/s If you travel 20 m/s for 10 m, how long did it take you? Answer: .5 s Velocity • Velocity is the same as speed, but it has a direction associated. • Speed has no specific direction. Question • Can something have a constant speed but a changing velocity? • Yes. All it has to do is turn. • Remember: Velocity includes direction; speed does not. Negative velocity and speed Is it possible for something to have a negative velocity? • Yes, it means it is going backward. Is it possible for something to have a negative speed? • No, there is no specific direction. Backward is arbitrary. You pick which way you want to be positive in any given problem. Combining vectors in 1-D • First, simply add them together. • If you walk 5 miles north, 2 miles south and 3 miles north, what distance have you walked? What is your displacement? – Distance: 10 m – Displacement: 6 m N • If you are walking toward the back at 1 m/s on a bus that is moving 10 m/s … – You are moving 9 m/s (forward) Note: You cannot combine speeds. Vectors • Vectors are units with a direction associated with them. – Distance: no direction – Displacement: distance with a direction • If you walk 5 m north and 2 m south, what distance have you walked? What is your displacement? • Distance 7 m; displacement 3 m N