File - MrsBlochScience
advertisement

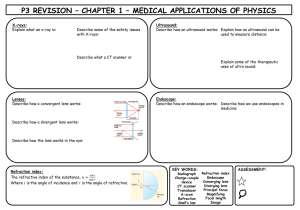
Waves and Light – Course 2 CGPA – Mrs. Bloch 9-3 Refraction and Lenses Vocabulary 9.3 1. Index of Refraction- A measure of the amount of ray of light bends when it passes one medium to another. 2. Mirage- An image of a distant object caused by refraction of light as it travels through air of varying temperatures. 3. Lens- A flexible structure that focuses light that has entered the eye. A curved piece of glass or other transparent material that is used to refract light. 4. Concave Lens- A lens that is thinner in the center than at the edges. 5. Convex Lens- A lens that is thicker in the center than at the edges. What Happens When Light Hits an Object? Pg. 328 When light hits an object= it can be reflected, refracted, and/or absorbed. • The more transparent/see-through an object is, the less light it will absorb. • An opaque/solid not clear object will both reflect and absorb light. Reflected Refraction Refraction (bent) can cause you to see something that may not actually be there. When light rays enter a medium at an angle, the change in speed causes the rays to bend. Some mediums cause light to bend more than others. The index of refraction of a medium is a measure of how much a light ray bends when it enters that medium. Pencil Animation The refraction occurs only at the boundary. Once the light has crossed the boundary between the two media, it continues to travel in a straight line. Only now, the direction of that line is different than it was in the former medium. Refraction and Lenses pg. 329 Optical Illusion In a Fish Tank There is only one fish in the tank, but refraction makes it look as though there are two. Refraction and Lenses pg. 330 Refraction is the bending of a wave when it enters a medium where it's speed (frequency speed) is different. Refraction of Light The light ray bends as it passes through different mediums. Refraction in Different Mediums pg. 330 Some mediums causes light to bend more than others. • Fig. 2 light ray travels faster _____ P1 • When light passes from air into water the light slows down. • Then the light slows down again and bends more when it passes from the water into the glass. • When light passes back from glass to air, the light speeds up. Refraction and Lenses pg. 330 Bending Light The table shows the index of refraction of some common mediums. What Happens When Light Hits an Object? Prisms and rainbows pg. 331 When white light enters a prism, each wavelength is refracted (bend) by a different amount. The longer the wavelength= wave is less bent by a prism . Prisms and Rainbows pg. 331 Which color has the longest wavelength? = _____is refracted the least Which color has the shortest wavelength?= _____is refracted the most • This difference in refraction causes white light to spread out into the colors of the spectrum. • When white light from sun shines through water droplets, the droplets act like prisms, refracting and reflecting the light and separating the colors to appear as a rainbow Brainpop Rainbow Refraction and Lenses Rainbow A rainbow forms when light is reflected and refracted by water droplets suspended in the air. Did You Know? • You can see the effects of refraction even more in a diamond. • Light rays slow down and bend considerably when they enter a diamond. • These light rays eventually exit the diamond as bright bursts of light. • The bursts of light give diamonds their characteristic sparkle. Quick Quiz Check your understanding of these principles by determining which color(s) of light are reflected by the paper and what color the paper will appear to an observer. Color virtual lab What Happens When Light Hits an Object? Mirages Pg. 332 A mirage is an image of a distant object caused by the refraction of light. When light moves from hot air near the ground to cooler air above, it refracts. You may see a mirage on a road. What Determines the Type of Image Formed by a Lens? pg. 333 Binoculars Eyeglasses Cameras A lens is a curved piece of glass or other transparent material that refracts/bend light. • A lens forms an image by refracting light waves that pass through it. • Lenses can have different shapes. The type of image formed by a lens depends on: the shape of the lens and the position of the object. What Determines the Type of Image Formed by a lens? Pg. 333 Characteristics of a concave lens and images: • Thinner in the center than at the edges. • A concave lens can produce only virtual images because parallel light rays passing through it never meet. • The virtual images are always upright and smaller than the object. • The image is located where the light rays appear to come from. Refraction and Lenses pg. 333 Concave Lens A concave lens produces a virtual image that is upright and smaller than the object. In the second diagram, where would the image be when the two light rays are extended back to the same side of the lens as the object? What Determines the Type of Image Formed by a Lens? A convex lens is thicker in the center than at the edges. It acts like a concave mirror because it focuses rays of light. An object’s position relative to the focal point determines whether a convex lens forms a real or virtual image. When an object is between the lens and the focal point, a virtual image forms. The image forms on the same side of the lens as the object. If the image is outside of the focal point, a real image forms on the other side of the lens. The real image can be smaller, larger, or the same size as the object. Refraction and Lenses pg. 333 How a Convex Lens Works The type of image formed by a convex lens depends on the object’s position. Which image is virtual and which is real? Refraction and Lenses Lenses and Mirrors These photos show parallel rays of light passing through a convex lens and a concave lens. Complete the Lenses and Mirrors table. What Factors Affect the Speed of a Wave? pg.336 Light waves, sounds waves, and other waves move at different speed in different materials. The speed of a wave through a substance is determined by the substance’s physical properties. Light, like all E.W, consists of: vibrating electric fields magnetic fields The speed of light through a substance depends on how that substance interacts with electric and magnetic fields. What Factors Affect the Speed of a Wave? Pg. 337 The speed of sound waves is affected by three factors— temperature, compressibility and density • As temperature of a medium (way) increases = the speed of sound also increases. • As for solids, a temperature increase = causes wave speeds to decrease. What Factors Affect the Speed of a Wave? pg.337 Two other factors that determine the speed of sound through a substance are: the compressibility and density of that substance. Compressibility is a measure of how hard a substance is to compress, or squeeze. Density is a measure of how much mass a given volume of a substance has. Refraction and Lenses The Changing Speed of Sound Sound travels faster through steel than air, even though steel is denser, because steel is also less compressible. Resources Pearson Art in Motion (Refraction, Reflection, and Rainbows) http://www.pearsonsuccessnet.com/snpapp/learn/navigateIDP.do?method=vlo&internalId=140711110000083# Light Absorption, Reflection, and Transmission http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/light/u12l2c.cfm http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:rM-LG-4ua3gJ:hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/geoopt/refr.html+&cd=2&hl=en&ct=clnk&gl=us&client=firefox-a Color virtual lab++++++++ http://water.me.vccs.edu/courses/env211/lesson15_print.htm