Agar_starch_prac
advertisement

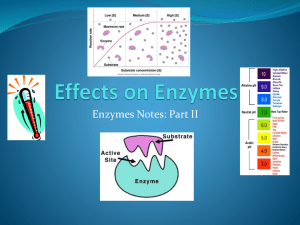
• Understand techniques used for measuring enzyme activity • Explain the principles of using of starch - agar plates for assaying carbohydrase activity •Use precise experimental techniques in assaying enzyme actiivity •To interpret enzyme activity graphs •To complete serial dilutions using precise measurements •To set up starch agar plates with amylase Here are some answers to enzyme related questions Can you write a question for each? Answer - Lock and key, induced fit Answer - Ionic, disulphide (bridges) and hydrogen bonds Answer - Increased (kinetic) energy enzyme/substrate moves faster, including collisions Answer - Denatured Answer - Amylase Enzyme Kinetics - measuring the rate of enzyme reactions. To measure an enzyme catalysed reaction you need a signal to measure that shows the progress of the reaction. The signal should change with either substrate or product concentration, and it should preferably be something that can be measured continuously. Can you think of possible signals? Typical signals include colour changes, pH changes, mass changes, gas production, volume changes or turbidity changes. If the reaction has none of these properties, it can sometimes be linked to a second reaction, which does generate one of these changes. One useful method is to dissolve the substrate in agar in an agar plate. If a source of enzyme is placed in the agar plate, the enzyme will diffuse out through the agar, turning the substrate into product as it goes. Well containing enzyme There must be a way to distinguish the substrate from the product, and the reaction will then show up as a ring around the enzyme source. What signal could be used to show the digestion of starch? The higher the concentration of enzyme, the higher the diffusion gradient, so the faster the enzyme diffuses through the agar, so the larger the ring in a given time. The diameter of the ring is therefore proportional to the enzyme concentration. This can be done for many enzymes, e.g. a protein agar plate can be used for a protease enzyme, or a starch agar plate can be used for the enzyme amylase. Starch Agar Plate You are now going to set up an agar plate to assay the activity of amylase (a) Name the part of the enzyme labelled D. Active site; 1 ........................................................................................................ .............................................. (1 mark) (b) Explain how substrate C is broken down by the enzyme. Substrate enters active site; Complimentary shapes / Lock and ........................................................................................................ Key; (Binding) to form enzyme-substrate complex; Lowering of ........................................................................................................ activation energy; Conformational / shape change; ........................................................................................................ Breaking of bonds in substrate; Products no longer fit active site and so are released; (c) Molecules A and B inhibit the enzyme in different ways. Explain how each molecule inhibits the enzyme. Molecule A Molecule A binds at site away from active site / allosteric site; ........................................................................................................ Causes enzyme / active site to change shape; ........................................................................................................ ....................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................... Molecule B Prevents substrate from entering / no ....................................................................................................... enzyme-substrate ....................................................................................................... complex formed / active site blocked; ....................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................ (4 marks) (i) Describe how a saprophytic fungus obtains its food. Secretes enzymes (for extra-cellular digestion); ...................................................................................................... Absorbs products; ...................................... ...................................................................................................... (2 marks) (ii) What conclusion can be drawn from the results? ii) Optimum pH is 7 / neutral / between 6 and 8 / between 7 ................................................................................................. and 8; ................................................................................................ (1 mark) (iii) Use an appropriate method to estimate the maximum rate of reaction that was observed in this investigation. Show your working. Maximum rate of reaction Max rate = Distance 11 × 60 ................................................................................................. ................................................................................................. Time 4 ................................................................................................. 2.75 mm / hour, 0.046mm/min, 4.6 x 10-3 mm/min ................................................................................................. 1 mm/ 21.8 mins, 23.76mm2/hour]