Refraction
advertisement

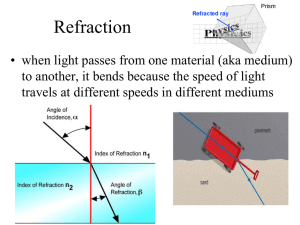
Topic Displacement Vectors 2 3 Kinematics 4 Graphs 5 Energy 6 Power 7 Springs 8 Shadows 9 Field of Vision 10 Colors 11 Concave mirrors 12 Convex mirrors 13 Refraction 14 Lenses 15 Optical Power 1 Slides Minutes 9 27 13 39 13 39 10 30 10 30 5 15 4 12 3 9 7 21 3 9 7 21 4 12 5 15 10 30 6 18 Refraction is the bending of light rays as they pass from one medium into another medium of different optical density. The index of refraction of a transparent medium is a ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the medium: n = c/v where n = is the index of refraction (no units) c = 3 x 108 m/s v = speed of light in the medium (in m/s) Note : The greater the index of refraction of a medium, the slower light travels in that medium. The index of refraction for a vacuum is 1, for water it is 1.33, for diamond it is 2.42, etc. The highest of any natural material Click When refraction occurs, light bends away from the normal when the optical density (index of refraction) is less dense (and vice versa). The following illustration demonstrates this fact: n1 = 1 Normal n2 = 1.5 n1 < n2 n1 = 1.5 Normal n2 = 1 n1 > n2 Click Refraction Slide: 13. 1 A light ray passes from air into a liquid as illustrated below. Determine the index of refraction for this liquid. Step-1: Determine the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction. i r Step-2: Calculate the index of refraction using Snell’s Law. A) 1.5 B) 1.4 C) 0.72 D) 0.65 Click Refraction Slide: 13. 2 Click Refraction Slide: 13. 3 Click Refraction Slide: 13. 4 Away from normal Away from normal Towards normal Away from normal Because n 1is greater than n2 , the refracted ray bends AWAY from the normal. Click Refraction Slide: 13. 5 REMEMBER Critical angle means the angle of refraction is 90o. Click … and good luck!