Lab 3: Earth Sun-Geometry
advertisement

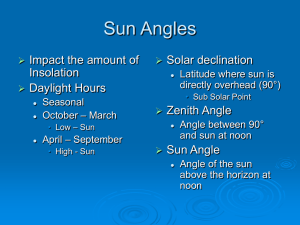
Lab 3: Earth Sun-Geometry • Earth’s axis is tilted 23½° (from the perpendicular to the plane of the ecliptic) • Primary cause for Earth’s seasons! • Tilt is oriented in the same direction all year: • North Pole points towards Polaris Earth-Sun Geometry • Solstices: – Summer (June 21 or 22) • Northern Hemisphere is tilted 23½° toward the sun – Sun’s rays are directly over head at 23½° N (Tropic of Cancer) – Winter (December 21 or 22) • Northern Hemisphere is tilted 23½° away from the sun – Sun’s rays are directly over head at 23½° S (Tropic of Capricorn) Solar Noon = Sun at highest point in the sky Earth-Sun Geometry http://www.geography.hunter.cuny.edu/~tbw/wc.notes/2.heating.earth.su rface/01_EarthSun.html Equinoxes: – Midway between solstices • Autumnal equinox – September 22 or 23 • Vernal equinox – March 21 or 22 Rotation Animation Sun angles vary with latitude: – High sun angles in the tropics – Medium sun angles at mid-latitude – Low sun angles in the arctic Sun Angle by Season • Solar declination: latitude at which the sun is directly above at solar noon (only between 23 ½ N-S) • Zenith angle (ZA): the angle between a point directly overhead & the sun at solar noon (related to the 90 degrees) • Solar elevation angle (SA): the angle of the sun above the horizon at solar noon (relates to 0 degrees) Finding Zenith 1. Know where the sun is directly overhead + or – 2. Latitude of location HINTS: •Locations in same hemisphere = SUBTRACT! •Locations in different hemispheres = ADD! • Solar Declination is 0° = SUBTRACT! Formulas: • Location gives you Zenith Angle • Date gives you Solar Declination 1. Zenith Angle = 90 – Sun Angle 2. Solar Elevation Angle = 90 – Zenith Angle Calculating Solar Declination • Use formula: 23.5 * sine (n) OR • Use an Analemma! 1. June 21: summer solstice (23½ °N) 2. NH tilted towards the sun SD = 23½°N 47 ° 1. 66.5 – 23.5°(SD) = 43°(ZA) 2. 90° – 43°(ZA) = 47°(SA) SUN ANGLE: 36½° 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 0.00 1.75 3.49 5.23 6.98 8.72 10.45 12.19 13.92 15.64 10 17.36 19.08 20.79 22.50 24.19 25.88 27.56 29.24 30.90 32.56 20 34.20 35.84 37.46 39.07 40.67 42.26 43.84 45.40 46.95 48.48 30 50.00 51.5 52.99 54.46 55.92 57.36 58.78 60.18 61.57 62.93 40 64.28 65.61 66.91 68.20 69.47 70.71 71.93 73.14 74.31 75.47 50 76.60 77.71 78.80 79.86 80.90 81.92 82.90 83.87 84.80 85.72 60 86.60 87.46 88.29 89.10 89.88 90.63 91.36 92.05 92.72 93.36 70 93.97 94.55 95.11 95.63 96.13 96.59 97.03 97.44 97.81 98.16 80 98.48 98.77 99.03 99.25 99.45 99.62 99.76 99.86 99.94 99.98 8.834 units 1. Note your latitude! 2. Determine – a. Sun at 90° b. ZA (difference between your locations) c. SA (90° – ZA) a. Sun at 90°: 23½° S b. ZA: 23½° + 60° = 83½° c. SA: 90° – 83½° = 6½° **units determined by 1/sin(SA) The larger the unit, the cooler the temperature. WHY?