Compound Angle Formulae: Trig Cheat Sheet
advertisement

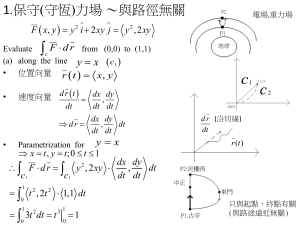
Compound Angle Formulae 1. Addition Formulae cos( A B) cos A cos B sin A sin B cos( A B) cos A cos B sin A sin B sin( A B) sin A cos B cos A sin B cos( A B) sin A cos B cos A sin B Example: sin( x 30)o sin x cos30 cos x sin 30 3 sin x cos x 2 2. Formulae Involving Double Angle (2A) sin 2 A 2sin Acos A cos 2 A cos 2 A sin 2 A 2cos 2 A 1 1 2sin 2 A Two further formulae derived from the cos2 A formulae. cos 2 A 12 (1 cos 2 A) sin 2 A 12 (1 cos 2 A) Mixed Examples: 4 Given that A is an acute angle and tan A , calculate sin 2 A and cos 2 A. 3 sin A 4 cos A 3 sin 2 A cos 2 A 1 sin 2 A ( 43 sin A)2 1 sin A Similarly: sin 2 A 2sin A cos A cos A 16 25 3 5 4 5 Substitute form the tan (sin/cos) equation +ve because A is acute 3-4-5 triangle !!! 24 25 cos 2 A cos2 A sin 2 A 9 16 25 7 25 A is greater than 45 degrees – hence 2A is greater than 90 degrees. Find the exact value of sin 75o. 2 sin(75o ) sin(45 30) sin(75o ) sin 45cos30 cos 45sin30 45 1 o 1 Prove that sin( ) tan tan cos cos sin cos cos sin cos cos sin sin cos cos tan tan 30 o 1 1 3 1 1 1 3 2 2 22 2 2 sin( ) cos cos 2 Q.E.D. 3 For the diagram opposite show that cos LMN 5 . 5 M cos LMN cos( ) 3 2 Length of LM 18 3 2 Length of MN 10 1 3 1 1 2 10 2 10 2 2 20 4 5 5 5 10 3 3 cos( ) cos cos sin sin 1 5 L 1 N (A Higher Question) Show that, for the triangle ABC in the diagram, a a b c sin a sin b sin c b sin . cos( ) The sine rule b From the diagram: C a b sin sin( [ 2 ]) a b sin( 2 [ ]) The sum of the angles of a triangle=180 sin( 2 ) cos b cos( ) b sin cos( ) As required A 2 c a B Prove that, cos 4 sin 4 cos 2 . x 2 y 2 ( x y)( x y ) cos4 sin 4 (cos2 )2 (sin 2 )2 (cos2 sin 2 )(cos2 sin 2 ) cos 2 sin 2 1 cos 2 sin 2 cos( ) cos cos sin sin cos2 TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS Double angle formulae (like cos2A or sin2A) often occur in trig equations. We can solve these equations by substituting the expressions derived in the previous sections. Use sin2A = 2sinAcosA when replacing sin2A cos2A = 2cos2A – 1 cos2A = 1 – 2sin2A if cosA is also in the equation if sinA is also in the equation when replacing cos2A Solve: cos 2 x o 4sin x o 5 0 for 0 x 360o. cos2x and sin x, so substitute 1-2sin2 (1 2sin 2 x) 4sin x 5 0 6 4sin x 2sin 2 x 0 cp. w. 6 4 z 2 z 2 0 (6 2sin x)(1 sin x) 0 sin x 1 or sin x 3 x 90o 0 sin x 1 for all real angles Solve: 5cos 2 x o cos x o 2 for 0 x 360o. cos 2x and cos x, so substitute 2cos2 -1 5(2cos2 x 1) cos x 2 10cos 2 x cos x 3 0 (5cos x 3)(2cos x 1) 0 3 1 cos x or cos x 5 2 s a t c All S_ Talk C*&p ?? x 51.3 or x 90 60 150o or x 360 51.3 x 270 60 210 o 308.7 o o 2 y 0.6 y0 y 0.5 3 2 The diagram shows the graphs of f ( x) a sin bx o and g ( x) c sin x o for 0 x 360o. yy 4 y f ( x) 2 360o 0 -2 xx y g ( x) -4 Three problems concerning this graph follow. i) State the values of a, b and c. yy 4 f ( x) a sin bxo The max & min values of asinbx are 3 and -3 resp. The max & min values of sinbx are 1 and -1 resp. a3 2 g ( x) c sin x o The max & min values of csinx are 2 and -2 resp. c2 360o 0 -2 -4 f(x) goes through 2 complete cycles from 0 – 360o b2 y f ( x) y g ( x) xx ii) Solve the equation f ( x) g ( x) algebraically. From the previous problem we now have: f ( x) 3sin 2 x and g ( x) 2sin x Hence, the equation to solve is: 3sin 2 x 2sin x Expand sin 2x 3(2sin x cos x) 2sin x 6sin x cos x 2sin x 0 Divide both sides by 2 3sin x cos x sin x 0 Spot the common factor in the terms? sin x(3cos x 1) 0 Is satisfied by all values of x for which: sin x 0 or cos x 1 3 iii) find the coordinates of the points of intersection of the graphs for 0 x 360o. From the previous problem we have: sin x 0 or sin x 0 cos x cos x 1 3 Hence: x 0o or x 70.5o x x 180o 360o or x x (360 70.5)o 289.5o or 1 3