Quick Condition - spin.mohawkc.on.ca
advertisement

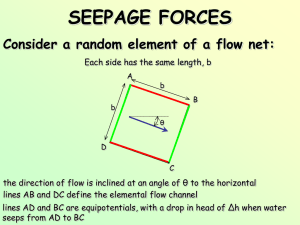
Quick Study What happens if the direction if the upward of the seepage seepage force force is was equal vertically in up? magnitude to the effective weight of the soil? the force Instead ofvector θ being diagram as shown would θbefore: = look 90° something like this: θ Resultant Body Force or Stress, σ’ θ =Effective 90° Seepage So instead of Craig’s vector diagram looking like Force this: iwV : Effective Weight ’b2 : It’s alive! This is known as a QUICK condition. The effective stress drops to 0 and the soil In old English, quick means alive. cannot support anything that won’t float on The soil looks like its boiling and appears to be water! “alive”. IT’S ALIVE!! Quick Study If a quick condition develops, the resultant Where would you expect to see seepage body force = 0 and iwV = ’V vertically upwards? the hydraulic The Near seepage the downstream forces gradient to the surface soil that right produces of the the a quick sheet pile wall (downstream seepage condition vectors is calledare the side) will almost critical completely hydraulic all have upward vertical vertical gradient, (no ic: horizontal components component) γ' Gs 1 ic γw 1e check out eqn. 1.21 on pg 20 in Craig Quick Study d 2 d This depth The Model mass studies has of embedment ahave volume shown of:of a sheetthe that pilesoil wall mass extends extending from downstream over this depth, soil d surface and half to the bottom this distanceoffrom the sheet the piling piling. is most prone to the quick condition. It is designated, d as shown. d 1 2 V d 1 2 d 2 Quick Study d 2 h = 0 ∆s d hm Δh ie Δs For At Hence, A Factor surface sands, the ofaDC, average Safety factor the average of hydraulic against Safety head, hmboiling gradient heaving against (quick is forestimated seepage condition) at the from surface at theDC midpoint to adjacent can AB beis: expressed of to line the DC sheet using from piling the theis flow hydraulic expressed exit net. as the gradient, average ie hm gradient, critical over thehydraulic last element (AEFG): ic i At surface mAB the excess d divided by this average total head has been gradient, im: dissipated (h = 0). ic ic Fheave boil ie im Quick Study The Consider elevation the head equilibrium at DC is of –d the if forces the downstream acting on the freesoil water mass surface ABCD with is at unit ABweight sat. zm - d d 2 d γ d 2 1 2 sat The average poreof water total weight ABCD is pressure on CD is: sat x the Volume of (h ABCD m+d)w The boundary water force on CD is the area of the PWP distribution on CD: 1 2 d(hm d) γw ½d(hm+d)w Quick Study To find the Resultant Body Force of ABCD: d 2 if γ' γsat - γw , then γsat γ'γw 1 d 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 ( γ ' γ )d γ ' d γ d γ d w 2 2 2 w 2 sat 3 1 2 d(hm d)γw 1 h 2 d wd m w 2 1 2 ' γ' d γwd hmγwd γwd 1 2 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 ' γ' d 21 hmγwd 1 2 2 2 or Quick Study The average hydraulic Now, consider the equilibrium gradient for seepage of the forces acting from on the DC AB is: ABCD hm with soiltoskeleton i m bouyant unit weight d ’. d 2 d 1 2 γ' d2 Jm hm wd 1 2 The seepage on of ABCD effectiveforce weight is: ABCD is ’ x the Volume of 2 h d m ABCD Jm w 1 hm w d d 2 2 The resultant body force of ABCD is: ' γ' d 21 hmγwd Look familiar? 1 2 2 Quick Study So, if σ’ = 0 as with a quick condition, then 0 γ' d 21 hmγwd 1 2 1 2 2 γ' d 21 hmγwd 2 A Factor of Safety against heaving (quick condition) can then be expressed. γ' Generally, The stabilizing a 1factor force ofissafety the effective is the ratio weight of 2 γforce icforces γdestabilizing 'd stabilizing of theFsoil forces mass. over seepage w 2 γ'd The 1 is the destabilizinghforce. h γ d h γ im m m w m w 2 d Quick Study dfilt ’filt Well, If the you factor unit could weight of increase safety of thethe is effective makingmaterial the weight engineer the nervous, filter is of ’filt andsoil it is adjacent you could placed toto aalways depth the sheet redesign of dpile the filt, then wall structure the by extra adding and effective arepeat filterweight the is material process... density). w’ = ’filt x(high dfilt and the new factor of safety would be: Not an option? γ'd w' F 1 2 hm γw d 1 2 2