Radiosity - TAMU Computer Science Faculty Pages

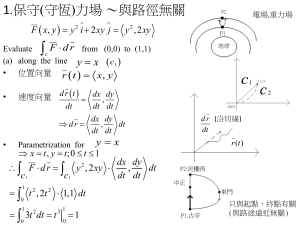
Radiosity
Dr. Scott Schaefer
1
Radiosity
2/38
Radiosity
Physically based model for light interaction
View independent lighting
Accounts for indirect illumination
Color bleeding
Soft shadows
3/38
The Rendering Equation
L o
( p , v )
L e
( p , v )
f ( l , v ) L o
( r ( p , l ),
l ) cos
i d
i
4/38
The Rendering Equation
L o
( p , v )
L e
( p , v )
f ( l , v ) L o
( r ( p , l ),
l ) cos
i d
i
Outgoing radiance from surface at p in the direction v
5/38
The Rendering Equation
L o
( p , v )
L e
( p , v )
f ( l , v ) L o
( r ( p , l ),
l ) cos
i d
i
Emitted radiance from surface at p in the direction v
6/38
The Rendering Equation
L o
( p , v )
L e
( p , v )
f ( l , v ) L o
( r ( p , l ),
l ) cos
i d
i
BRDF of surface at p
7/38
The Rendering Equation
L o
( p , v )
L e
( p , v )
f ( l , v ) L o
( r ( p , l ),
l ) cos
i d
i
Ray cast from p in the direction of l
8/38
The Rendering Equation
L o
( p , v )
L e
( p , v )
f ( l , v ) L o
( r ( p , l ),
l ) cos
i d
i
Output radiance of intersected surface in the direction of l
9/38
The Rendering Equation
L o
( p , v )
L e
( p , v )
f ( l , v ) L o
( r ( p , l ),
l ) cos
i d
i
Angle between l and n
10/38
The Rendering Equation
L o
( p , v )
L e
( p , v )
f ( l , v ) L o
( r ( p , l ),
l ) cos
i d
i
Integral about hemisphere centered at p
11/38
BRDF’s
B idirectional R eflectance D istribution F unction
Determines amount of incoming light from direction l reflected from surface in the direction of v v l
Image taken from “A Data-Driven Reflectance Model”
12/38
Discretizing the Rendering Equation
Assume perfectly diffuse surfaces f ( l , v )
c
Discretize space into patches
Color is constant per patch
Image taken from “Radiosity on Graphics Hardware”
13/38
Discretizing the Rendering Equation
L o
( p , v )
L e
( p , v )
f ( l , v ) L o
( r ( p , l ),
l ) cos
i d
i
14/38
Discretizing the Rendering Equation
L i
L i , e
c i
L j h i , j cos
i d
i h i , j
1
0 patch i is visible to patch j along l patch i is not visibl e to patch j along l
15/38
Geometric Computation of Form Factors
L i
L i , e
c i
L j h i , j cos
i d
i
N
16/38
Geometric Computation of Form Factors
L i
L i , e
c i
L j h i , j cos
i d
i
N
17/38
Geometric Computation of Form Factors
L i
L i , e
2
1 c i
L j cos
d
2
1
N
18/38
Geometric Computation of Form Factors
L i
L i , e
c i
L j
sin
2 sin
1
2
1
N
19/38
Geometric Computation of Form Factors
L i
L i , e
c i
L j
sin
2 sin
1
1
2 sin(
)
2 sin(
1
)
N
20/38
Geometric Computation of Form Factors
N
21/38
Geometric Computation of Form Factors
Project patches onto hemisphere
N
22/38
Geometric Computation of Form Factors
N
Project spherical patches onto tangent plane
23/38
Geometric Computation of Form Factors
N
Divide by area of disc in tangent plane ( for surfaces)
24/38
Geometric Computation of Form Factors
L i
L i , e
j c i
L j
F i , j
Divide by area of disc in tangent plane ( for surfaces)
N
F i , j
= form factor
25/38
Matrix Computation of Radiosity
L i
L i , e
j c i
L j
F i , j
1
c c
2 c n
1
F
1 , 1
F
2 , 1
F n , 1
1
c
1
F
1 , 2 c
2
F
2 , 2
c n
F n , 2
c c
1
F
1 , n
2
F
2 , n
1
c n
F n , n
L
L
2
L n
1
L
L e e
, 1
, 2
L e , n
26/38
Matrix Computation of Radiosity
L i
L i , e
j c i
L j
F i , j
L
L
L n
1
2
L
L e , 2
L e e
, 1
, n
c c c n
1
2
F
1 , 1
F
2
F n
, 1
, 1 c
1
F
1 , 2 c
2
F
2 , 2
c n
F n , 2
c c
1
2
F
F
2
1 , n
, n c n
F n , n
L
L
2
L n
1
27/38
Matrix Computation of Radiosity
L i
L i , e
j c i
L j
F i , j
L
L i i
L i n
1
2
L
L e e
,
, 1
L e , n
2
c c c n
1
2
F
1 , 1
F
2
F n
, 1
, 1 c c c
2
1 n
F
1 , 2
F
2 , 2
F n , 2
Jacobi iteration
c
1
F
1 , n c
2
F
2 , n
c n
F n , n
L
L i
1
2
L i i
1
1
1 n
28/38
Matrix Computation of Radiosity
L i
L i , e
j c i
L j
F i , j
L i
L e
K L i
1
29/38
Matrix Computation of Radiosity
L e
30/38
Matrix Computation of Radiosity
L
e
K L e
31/38
Matrix Computation of Radiosity
L e
K L e
K
2
L e
32/38
Matrix Computation of Radiosity
L e
K L e
K
2
L e
K
3
L e
33/38
Radiosity Examples
Image taken from http://www.9jcg.com/tutorials/jason_jacobs/radiosity_01.jpg
34/38
Radiosity Examples
35/38
Radiosity Examples
Image taken from www.cs.dartmouth.edu/~spl/Academic/ComputerGraphics/Fall2004/radiosityExample.jpg
36/38
Advantages of Radiosity
Global illumination method: modeling diffuse inter-reflection
Color bleeding: a red wall next to a white one casts a reddish glow on the white wall
Soft shadows: an area light source casts a soft shadow from a polygon
No ambient hack
View independent: assigns a brightness to every surface
37/38
Disadvantages of Radiosity
Radiation is uniform in all directions
Radiosity is piecewise constant
No surface is transparent or translucent
Must determine how to subdivide shapes into small enough patches
38/38