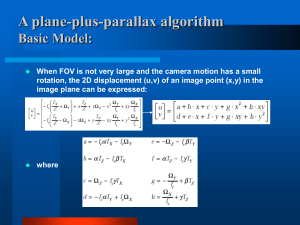
Engineering
advertisement

Engineering Creating objects that use verified technological principles to help humans meet their needs. Kinds? Mechanical, Chemical, Biomedical, Electrical, Computer, and Civil Engineering. What is Mechanical Engineering? It is a branch of engineering that deals with the design, construction, operation and improvement of systems or technical objects. → What is a mechanical function? It is defined as the role played by a mechanism* inside a more or less complex object. * A mechanism is a part of substance having a specific function. YouTube - mechanical engineering The Five basic Mechanical Functions? Typical Function Description Link 2 or more parts are connected together. Guiding Control One or more parts allows a part to rotate, translate or both together. Lubrication A substance that reduces friction between two or more parts. Seal A mechanism that prevents leaks of gases, liquids, or solids from an object Support Part that is used to hold up another corresponding part. LINKS How objects are “connected together”. Guiding Control “allows a part to rotate, translate or both” Lubrication “reduces friction” Seal “prevents leaks” Support “hold up other corresponding parts” A Mechanical Object Link Support Guide Control Seal Lubrication How to Describe Links The link function is the connections between two parts or more. They exist when an object is composed of more than a single part. Kinds of Links Direct Link Connects parts with no other device being used. Lego Indirect Link Connects parts by using another device to hold them together. Nail Bolt Screw Removable Link Non-removable Link Link can be removed without damaging anything on the object. Connected parts can not be removed without damaging the object. Nut and Bolt separates the seat from the post. Welded frame can’t be separated. Rigid Link Elastic Link Pieces of the object can not be interchanged when assembled. Allows for parts to change position. Table pieces. Shocks or Springs. Complete Link Partial Link No parts move independently of each other. All move together. Parts can move independently to each other. Hammer C-Clamp A link always has 4 of the 8 properties; they have one from each pair of properties: Direct or Indirect; Removable or Non-Removable Rigid or Elastic Complete or Partial Example: A Door, its Hinge, and the Door Frame. Link Property Direct or Indirect? The door & its frame are held by hinges which need screws. INDIRECT LINK Removable or Non-removable? The door and hinges can be removed by unscrewing them. REMOVABLE LINK Rigid or Elastic? Neither the door’s wood or hinges metal can be stretched. RIGID LINK Complete or Partial The door can move freely without causing the door frame to move. PARTIAL LINK Your Turn Describe the four characteristics of the links in each of the following examples: Create a basic design plan using a ruler, BUT ONLY SYMBOL THE LINKS AND WHAT 4 PROPERTIES THEY HAVE. a) A table and its four legs connected with screws. b) A pair of scissors. c) A pen and its cap. Motion Transmission Systems Is defined as a system’s ability to transmit the same motion from one part of an object to another. When we pedal a bicycle, we transmit a force into the peddles, which then transmits the motion into the bike’s wheels via the chain and gears. Question? Does it always have to move in the same way? Bidirectional Spiral Motion transmits into Bidirectional Rectilinear Translation. Egg Beater Hand Out Antique Egg Beater Motion Transmission System ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ _________________________________ Link Indirect Non-removable Rigid Complete Support Guide Control Seals? Lubrication? Keep this sheet handy, you will need it later. Do Motion Systems need… Lubrication*? Guiding Control*? Seals*? Support*? Not all of them, but where there is motion, usually lubrication* is needed for limiting friction….which means there should be seals* keeping the lubricant stored or inside the mechanism. Most movements require a guide control* so the “pieces don’t fly” as well as giving support* frames where the mechanisms won’t interfere with each other. Plus it depends on what the object is used for. YouTube - ENGINE ANIMATION.... From the Video, did you see evidence of each of the following Mechanical Functions? Lubrication. Oil for the pistons, and gears. Guiding Control: The Cylinders the pistons move through. The Gears proper rotation. Seals: Keep the lubricants and gas from leaving the engine. Support: All the nuts and bolts, molded frame. Types of Transmission Systems: Mechanisms Motor Mechanism Definition Mechanism of a system on which force is applied. Bike: Pedals transmit leg energy. Intermediate Mechanism Mechanism of a system that transfers the action of a motor mechanism (driving force) to a receiving mechanism Chain on a Bike Receiving Mechanism Mechanism of a system that receives the motion through an intermediate mechanism. Rear Wheel in a bike. Chain and Sprocket System Back Wheel Chain Pedal (Receiving Mechanism) (Intermediate Mechanism) (Motor Mechanism) If any of the pieces of the mechanism fail, what would the possible result be? Antique Egg Beater Motion Transmission System ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ _________________________________ Link Indirect Non-removable Rigid Complete Motor Mechanism Intermediate Mechanism Support Guide Control Receiving Mechanism Different Types of Motion Transmission Systems Chain and Sprockets Belt and Pulley Gears Friction Gears Wheel and Worm Gear Simple Machines Antique Egg Beater Motion Transmission System Changed rotation direction 90o. Twice the energy, with the same energy output. Transformation Systems The ability of one mechanism to CHANGE the nature of motion in another mechanism. Options: 1. Rotation into Translation; 2. Rotation into Rotation; 3. Translation into Rotation; 4. Translation into Translation. Rotation: Translation: A B B Examples Extraordinaire! B Motion Transformation of a Bicycle Rotation Motion Translation Motion Therefore, a bicycle transforms its motion from: Rotation Motion into Translation Motion. Different Types of Motion Transmission Systems Name of System Screw and Gear System Ex: ________________ Wheel and Worm Gear Ex: ________________ Cam and Follower Ex: ________________ Diagram of System Motion Transformation Systems Is the The ability of one mechanism to CHANGE the nature of motion in another mechanism. Example: C-Clamp Rotation Motion Translation Motion Rack and Pinion Steering Rack and Pinion: Rotation Motion Translation Motion Cam and Follower Rotational Motion Alternating Translation Motion Major Examples of Motion Transmission Systems Clock Towers have 4 types of motion transmission systems in use. Belt and Pulley Gears Friction Gears Wheel and Worm Gear Any Mechanical Functions? Links? Guiding Controls? Lubrication? Seals? Supports? Type of Motion Transformation? Translation Motion Rotational Motion Personal Questions Pg. 371 Synergy; Questions: 1-7, 10-12.