1.4 Measure and Classify Angles
advertisement

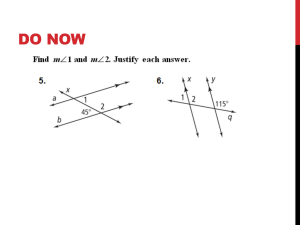
1.4 Measure and Classify Angles An angle consists of two different rays with the same endpoint. The rays are the sides of the angle. The endpoint is the vertex of the angle. The angle with sides (ray) AB and (ray) AC can be named <BAC , <CAB, or <A. 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles Example 1: Name Angles Name three angles is the diagram: 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles Example 2: Name Angles Name three angles in the diagram: 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles Angles can be classified as acute, right, obtuse, and straight. Draw an example: Acute Right Obtuse Straight 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles Example 3: Use the diagram to find the measure of the indicated angle. Then classify the angle. a. <KHJ b. <GHK c. <GHJ d. <GHL 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles Angle Addition Postulate 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles Example 4: Given the <LKN = 145 degrees, find m<LKM and m<MKN 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles Example 5: Given the <XYZ = 72 degrees, find m<XYW and m<ZYW 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles Congruent Angles: Two angles are congruent angles if they have the exact same measure. 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles