OpenGL Basics
advertisement

OpenGL Basics
OpenGL – Open Graphics Library
What it is
a s/w interface to graphics h/w
mid-level, device-independent, portable graphics
subroutine package
developed primarily by SGI
2D/3D graphics, lower-level primitives (polygons)
does not include low-level I/O management
basis for higher-level libraries/toolkits
The camera analogy
OpenGL libraries
GL – gl.h – Opengl32.lib
Provides basic commands for graphics drawing
GLU (OpenGL Utility Library) – glu.h – glu32.lib
Uses GL commands for performing compound graphics like
viewing orientation and projection specification
polygon tessellations, surface rendering etc.
GLUT (OpenGL Utility Toolkit) – glut.h – glut.lib
is a window system-independent toolkit for user interaction built on top
of OpenGL and WGL (Windows) or GLX (Linux).
System-specific OpenGl extensions
GLX : for X window system (Linux/Unix)
WGL: for Windows 95/98/2000/NT
AGL : Apple Macintosh system
OpenGL conventions
Functions in OpenGL start with gl
Most functions use just gl (e.g., glColor())
Functions starting with glu are utility
functions (e.g., gluLookAt())
Note that GLU functions can always be composed
entirely from core GL functions
Functions starting with glut are from the
GLUT library.
OpenGL conventions
Function names indicate argument type
and number
Functions ending with f take floats
Functions ending with i take ints
Functions ending with b take bytes
Functions ending with ub take unsigned bytes
Functions that end with v take an array.
Examples
glColor3f() takes 3 floats
glColor4fv() takes an array of 4 floats
Graphics Pipeline
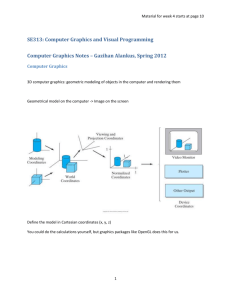
Step 1: Modeling Transform
Vertices of an object are define in it’s own co-ordinate
system (Object Space)
A scene is composed of different objects and some times
multiple copy of the same object
Modeling transforms places all the objects in a world coordinate system (World Space)
Model Transforms must be specified before specifying the
vertices of an object
glRotatef(30, 1, 0, 0);
glVertex3d(20, 30, 10);
Instantiate &
Modeling
Transform
Basic Modeling Transforms are:
Translate : glTranslate{f|d}(x,y,z)
Rotate : glRotate{f|d}(,x,y,z)
Scale : glScale{f|d}(x,y,z)
Object
Space
World Space
Step 2: Viewing Transform
A model can be viewed from different angles.
Viewing Transform specify following information about the
viewer:
eye position
head up
Look at direction
Eye Space
Step 2: Viewing Transform
void gluLookAt(GLdouble eyex, GLdouble eyey,
GLdouble eyez, GLdouble centerx, GLdouble
centery, GLdouble centerz, GLdouble upx,
GLdouble upy, GLdouble upz);
Step 3: Normalize & Clip
Normalize View volume within an unit cube.
Remove Primitives that are not in Normalized view volume
Eye Space
Clipping Space
• After clipping lighting effects and textures are applied to the
primitives
Step 4: Projection
Maps 3D-coordinates to 2D-image coordinates
Image Space
Perspective
Projection
Types
Parallel
Projection
Clipping Space
Step 4: Projection
Perspective Projection
Step 4: Projection
Perspective Projection
Step 4: Projection
Parallel Projection
Step 5: Rasterization
Projected image (vertices) in image space
has fractional x and y co-ordinates values
But raster scan device can only display
pixels at integer co-ordinates
• Some Algorithms:
Image
Space
Rasterization
– DDA (Digital Differential Analyzer
– Brasenham’s Algorithm
– Midpoint Algorithm
Screen
Space
Step 6: Viewport Transformation
Maps rasterized 2D images onto graphical
device
Screen Space
Device Space
Step 6: Viewport Transformation
void glViewport(GLint x, GLint y, GLsizei width, GLsizei height);
gluPerspective(fovy, 1.0, near, far);
glViewport(0, 0, 400, 400);
gluPerspective(fovy, 1.0, near, far);
glViewport(0, 0, 400, 200);
Graphics Pipeline
Graphics
Primitives
Modeling
Transform
transform
matrix
Object
Space
World
Space
Viewing
Transform
Eye, lookat,
headup
Eye Clipping Image
Space
Space
Space
Screen
Space
Normalize
& Clip
Parallel or
material,
Perspectiv
lights, color
e
volume
Shading &
Texture
projection
matrix
Device
Space
Projection
viewport
location
Image on
Screen
Viewport
Transform
Image in
Internal Buffer
Scan
conversio
Rasteri-n
zation
Primitives
Primitives: Points, Lines & Polygons
Each object is specified by a set Vertices
• Grouped together by glBegin & glEnd
glBegin(type)
glVertex*( )
glVertex*( )
…
glEnd( );
• type can have 10
possible values
Primitive Types
V0
V4
V3
V0
V4
V0
V2
V1
GL_LINE
V0
V2
V1
V4
V4
V3
V3
V1
GL_POINTS
V0
V3
V1
GL_LINE_STRIP
V5
V5
V5
V5
V2
V4
V3
V2
GL_LINE_LOOP
Polygon must be:
• Simple
• No-holes inside
• Convex
V2
V1
GL_POLYGON
Simple
Non-convex
P1
P2
Convex
Complex
Primitive Types
V8
V1
V7
V6
V2
V2
V1
V1
GL_TRIANGLE
V5
V3
V5
V3
V4
V0
V5
GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP
GL_TRIANGLE_FAN
Order of Vertex rendering
V0
V3
V0
V2
V4
V6
V7
V1
V6
V2
V3
V4
V4
V2
V0
V0
V1
V4
V5
GL_QUAD
V3
V5
V7
GL_QUAD_STRIP
GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP
012, 213, 234, 435
GL_QUAD_STRIP
0132, 2354, 4576
GL_TRIANGLE_FAN
012, 023 , 034, 045
Configuring OpenGL in Visual C++
Files Required for GLUT:
glut32.dll
glut.h
glut32.lib
Sample Program
Specify Canvas Color
Must always remember to clear canvas before
drawing
glClearColor( r , g , b , α )
specify the color to clear the canvas to
should generally set α to be 0 (i. e., fully transparent)
this is a state variable, and can be done only once
glClear( GL_ COLOR_ BUFFER_ BIT)
actually clears the screen
glClear clears
such as the depth buffer GL_ DEPTH_ BUFFER_ BIT
but we’re not using it right now
Redrawing Window
void glFlush(void);
Forces previously issued OpenGL commands to begin execution
It returns before the execution ends.
glutSwapBuffers() automatically calls glFlush()
For single buffer display function should end with this command
void glFinish(void);
Forces previously issued OpenGL commands to complete
This command doesn’t return until all effects from previous commands
are fully realized.
void glutPostRedisplay(void);
Causes the currently registered display function to be called at the
next available opportunity.
Initializing GLUT
Void glutInit( int argc, char **argv)
initialize glut, process command line arguments such as
-geometry, -display etc.
void glutInitDisplayMode(unsigned int mode)
Mode for later glutCreateWindow() call
mode is a bit-wised Ored combination of
Either GLUT_RGBA or GLUT_INDEX
Either GLUT_SINGLE or GLUT_DOUBLE
One or more GLUT_DEPTH, GLUT_STENCIL, GLUT_ACCUM
buffers
default:RGBA & SINGLE
Initializing GLUT
void glutInitWindowPosition(int x, int y)
Initial location of window
void glutInitWindowSize(int width, int height)
Initial size of window
int glutCreateWindow(char *name)
Called after Init, Displaymode, Position and Size calls
Window will not appear until glutMainLoop is called
Return value is a unique identifier for the window
Event driven approach
void glutMainLoop(void);
enters the GLUT event processing
loop.
should be called at most once in a
GLUT program.
Once called, this routine will never
return.
It will call as necessary any callbacks
that have been registered.
While (TRUE) {
e=getNextEvent();
switch (e) {
case (MOUSE_EVENT):
call registered MouseFunc
break;
case (RESIZE_EVENT):
call registered ReshapeFunc
break;
…
}
Keyboard
Callback
Keyboard
Mouse
Display
OS
Event
Queue
MainLoop
Each application has its
Own event queue
Mouse
Callback
Display
Callback
Callback Functions
void glutDisplayFunc(void (*func) (void))
Specifies the function that’s called whenever
the window is initially opened
The content of the window is needed to be redrawn
glutPostRedisplay() is explicitly called.
void glutReshapeFunc(
void (*func)(int width, int height));
Specifies the function that’s called whenever
The window is resized or moved
The function should perform following tasks
Call glViewPort(0,0,width, height); // default behavior
Redefine projection matrix to match aspect ratio of image &
view port
Callback Functions
void glutKeyboardFunc(
void (* func)(unsigned int key, int x, int y) );
Specifies the function that’s called whenever
a key that generates an ASCII character is pressed.
The key callback parameter is the generated ASCII
value.
The x and y callback parameters indicate the location
of the mouse when the key was pressed.
Callback Functions
void glutMouseFunc(
void (* func)(int button, int state, int x, int y));
Specifies the function that’s called whenever a mouse
button is pressed or released.
button callback parameter is one of
GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON
GLUT_MIDDLE_BUTTON
GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON
state callback parameter is either
GLUT_UP
GLUT_DOWN
The x and y callback parameters indicate the location of
the mouse when the event occurred.
Animation( Motion = Redraw+Swap )
Animation( Motion = Redraw+Swap )
Animation( Motion = Redraw+Swap )
Transformation in OpenGL
OpenGL uses 3 stacks to maintain
transformation matrices:
Model & View transformation matrix stack
Projection matrix stack
Texture matrix stack
You can load, push and pop the stack
The top most matrix from each stack is
applied to all graphics primitive until it is
changed
Graphics
Primitives
(P)
M
Model-View
Matrix Stack
N
Projection
Matrix Stack
Output
N•M•P
Translation – 2D
Y
Y
(4,5)
(7,5)
(7,1)
Before Translation
x’ = x + dx
y’ = y + dy
x
P
y
X
Translation by (3,-4)
d x
x
P T
y
d y
Homogeniou s Form
x 1 0 d x x
y 0 1 d * y
y
1 0 0 1 1
(10,1)
X
P P T
Transformations and OpenGL®
Each time an OpenGL transformation M is
called the current MODELVIEW matrix C is
altered:
v Cv
v CMv
glTranslatef(1.5, 0.0, 0.0);
glRotatef(45.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
v CTRv
Note: v is any vertex placed in rendering pipeline v’ is the transformed
vertex from v.
Matrix Operation
Thinking About Transformations
There is a World Coordinate System where:
All objects are defined
Transformations are in World Coordinate space
Two Different Views
As a Global System
Objects moves but
coordinates stay the
same
Think of transformation
in reverse order as
they appear in code
As a Local System
Objects moves and
coordinates move with
it
Think of transformation
in same order as they
appear in code
Order of Transformation T•R
Global View
Rotate Object
Then Translate
glLoadIdentity();
Local View
glMultiMatrixf( T);
Translate Object
glMultiMatrixf( R);
draw_ the_ object( v); Then Rotate
v’ = ITRv
Effect is same, but perception is different
Order of Transformation R•T
Global View
Translate Object
Then Rotate
glLoadIdentity();
Local View
glMultiMatrixf( R);
Rotate Object
glMultiMatrixf( T);
draw_ the_ object( v); Then Translate
v’ = ITRv
Effect is same, but perception is different
Thank You