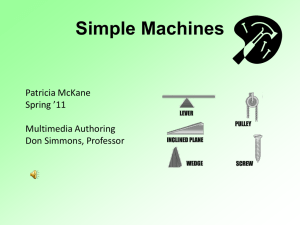
Input Force - Central Lyon CSD
advertisement

“Work and Power” CHAPTER 14 LESSON 1 I. WORK A. Books in hand Demo B. Def – the product of force and distance 1. Not…a job, chores, school. 2. Formula: Work = Force x Distance 3. Force is in Newtons 4. Distance is in meters 5. Work is in Joules 6. Ex: Your backpack is full and weighs 30 Newtons. You lift it from the floor to the shelf, a distance of 1.5 meters. How much work is done on the backpack? W=FxD 30 N x 1.5 m = ? 45 Joules 7. A backpack has a weight of 35 N and a student who is 1.8 meters tall has it on her back. How much work is the student doing on the backpack? W=FxD 35 N x 0 meters = 0 Joules 8. A carpenter lifts a 45-kg beam 1.2 meters. Approximately how much work is done on the beam? (be careful!!! Look at your units) Hint … 1 kg = 9.8 N 45 kg x 9.8 N/kg = 441 Newtons 441 N x 1.2 meters = =529.2 Joules II. POWER A. Def – Rate of doing work. 1. 2 variables a. Work and Time B. Formula 1. Power = Work (J) / Time (s) a. Unit is the Watt (W) b. A 60-watt light bulb requires 60 J per second. C. Ex: A machine puts forth 400 J of work in 0.25 seconds. What is the amount of power of the machine? P=W/T P = 400 J 0.25 Sec = 1600 Watts D. A similar machine exerts 500 J of work with 1400 Watts of power. What is the time it takes this machine to do its job? T=W/P T = 500 J 1400 Watts = 0.36 sec CHAPTER 14 LESSON 2 “Work and Machines” I. WHY WE USE MACHINES A. What are Machines? 1. Machine – a device that changes a force. makes work easier change the size of a force needed change the direction of a force B. Advantages of a Machine 1. Increasing force… tradeoff is you put in greater distance -”easier” Ex. Pg. 418 – changing a tire with a jack 2. Increasing distance… tradeoff is you put in less distance -”harder / more difficult” Ex. Pg. 419 – rowing a boat with oars 3. Changing Direction… movement in one direction causes movement in the opposite direction Ex. Pg. 419 rowing a boat with oars II. WORK INPUT AND WORK OUTPUT A. Work Input to a machine 1. Formula… Fi x Di a. Input Force – the force you exert to the machine. -Fi -Ex. Pushing on a crowbar b. Input Distance –the distance the input force acts through. -Di -Ex. The length of a crowbar B. Work Output of a machine 1. Formula… Fo x Do 1. Output force – the force exerted by the machine. Fo 2. Output distance – the distance the output force is exerted through. Do **Work output is always less than work input** Why??? Friction (pg. 420 p. 1 end) In-class Assignment… 1. Pg. 420 #’s 1-6 2. Read 14.3 CHAPTER 14 LESSON 3 “Mechanical Advantage and Efficiency” I. Mechanical Advantage A. Def – the # of times a machine multiplies the input force. (MA) B. Pg. 421 – nut cracker C. MA of Force = Output force Input force D. Ideal – MA w/o friction E. MA of Distance = Input Distance Output Distance F. Ex. A carpenter uses a claw hammer to pull a nail from a board. The nail has a resistance of 2500 N. The carpenter applies an input force of 125 N. What is the mechanical advantage of the hammer? MA = Output force Input force so… 2500 N 125 N = 20 MA G. Ex. A worker applies an input force of 20 N to pry open a window that has a output force of 500 N. What is the mechanical advantage of the crowbar? 500 / 20 = 25 H. Find the input force needed to lift a 2000 N rock, using a jack with a mechanical advantage of 10. Fi = Fo / MA =2000 / 10 =200 N II. EFFICIENCY B. Def – How much work put into the machine is changed to useful work put out by the machine. 1. Formula Efficiency = Woutput Winput X 100 2. Why doesn’t Wout = Win? -friction -dirt -age -bad parts -improper use 3. Ex: A sofa weighing 1000 N must be placed in a truck bed 1.2 m off of the ground. A worker uses a force of 500 N to push the sofa up the inclined plane that has a slope of 3.5 m. What is the efficiency of the inclined plane? Fo = Fi = Do = Di = 1000 N 500 N 1.2 m 3.5 m 1000 N x 1.2 m 500 N x 3.5 m = 68.6 % efficient A record setting buck weighing 1205 N is pulled up a ramp to the back of a pick-up with a force of 600 N by a hunter. If the back end of the pick up is 1.2 meters high and the length of the ramp is 3.2 meters, what is the efficiency of the ramp? 75.3% The Simple Machine CHAPTER 14 LESSON 4 I. LEVER SYSTEM A. Def – A lever is a bar that is free to pivot or turn about a fixed point. B. Parts of a lever 1. Fulcrum – fixed point of the lever 2. Effort arm – part where force is applied to the lever. 3. Resistance arm – part where the resistance is found on the lever. C. Ideal Mechanical Advantage 1. IMA = Length of effort arm Length of resistance arm or Le Lr 2. Ex: A worker uses an iron bar to raise a manhole cover weighing 65 N. The effort arm of the lever is 60 cm long. The resistance arm is 10 cm long. What is the ideal mechanical advantage of the bar? 60 cm Le = 10 cm Lr = = 6 (IMA) D. Types of Levers 1. 1st Class -E – F – R -Common Ex: teeter totter scissors pliers claw of hammer 2. 2nd Class -F–R–E - Common Ex: stapler bottle opener wheelbarrow nut cracker 3. 3rd Class (increase speed) -F–E–R - Common Ex: fishing rod tweezers mousetrap baseball bat softball bat II. PULLEYS A. Def – a grooved wheel with a rope or chain running along the groove. 1. similar to 1st class lever 2. uses rope instead of bar 3. has effort arm and resistance arm. B. Types of Pulleys 1. Fixed -Fixed – pulley does not move -MA = 1 2. Movable -Movable – pulley is movable -MA = 2 (can vary) 3. Block and Tackle -uses fixed and movable -Large Mechanical advantage -MA = # of ropes in the pulley system -MA = 2 WHAT IS THE MA? =4 III. WHEEL AND AXLE A. Def – a simple machine consisting of 2 different sized wheels that rotate together. 1. Parts -small wheel = axle 2. Effort force is applied to large wheel 3. Large wheel turns the axle 4. IMA = rw / ra 5. Ex: Bike, doorknobs, ice cream makers, cars… 6. Ex: An ice cream maker has a wheel radius of 20cm. The axle has a radius of 15 cm. What is the ideal mechanical advantage of the wheel and axle? 20 / 15 =1.3 IMA IV. INCLINED PLANE, WEDGE, SCREW A. Inclined Plane 1. Def – a sloped surface used to raise objects 2. IMA = length of slope / height of slope 3. Ex: any ramp 4. Remember** Force is smaller but distance is greater. B. Screw 1. Def – Inclined plane wrapped in a spiral cylindrical post. 2. Ex: screws, lids, drill bits C. Wedge 1. Def – Inclined plane with 1 or 2 sloping sides 2. Used to cut or split 3. Ex: knives, ax blades, chisels…