circulartrigfunctions
advertisement

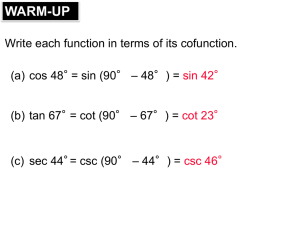
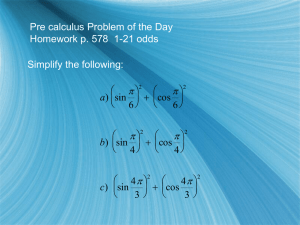
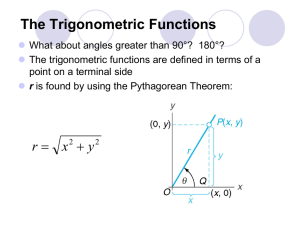
Circular Trigonometric Functions Y • circle…center at (0,0) r θ •radius r…vector with length/direction X • angle θ… determines direction Y-axis 90º Quadrant II Quadrant I r 180º Terminal side r θ 0º X-axis Initial side Quadrant III 360º Quadrant IV 270º Y-axis -270º Quadrant II -180º Terminal side r Quadrant I Initial side θ Quadrant III -360º X-axis 0º Quadrant IV -90º • angle θ…measured from positive x-axis, or initial side, to terminal side counterclockwise: positive direction clockwise: negative direction • four quadrants…numbered I, II, III, IV counterclockwise • six trigonometric functions for angle θ whose terminal side passes thru point (x, y) on circle of radius r sin θ = y / r csc θ = r / y cos θ = x / r sec θ = r / x tan θ = y / x cot θ = x / y These apply to any angle in any quadrant. For any angle in any quadrant x2 + y2 = r2 … So, r is positive by Pythagorean theorem. (x,y) r θ x y Y r θ x (x,y) y X NOTE: right-triangle definitions are special case of circular functions when θ is in quadrant I *Reciprocal Identities sin θ = y / r and csc θ = r / y cos θ = x / r and sec θ = r / x tan θ = y / x and cot θ = x / y *Ratio Identities sinθ tanθ = cosθ cosθ cot θ = sinθ *Both sets of identities are useful to determine trigonometric functions of any angle. Positive trig values in each quadrant: Y Students All sin positive (csc) all six positive (-, +) (+, +) II I Take tan positive (cot) III IV (-, -) (+, -) X Classes cos positive (sec) Y REMEMBER: In the ordered pair (x, y), x represents cosine and y represents sine. (-, +) (+, +) II I III IV (-, -) (+, -) X #1 Draw each angle whose terminal side passes through the given point, and find all trigonometric functions of each angle. θ1: (4, 3) θ2: (- 4, 3) θ3: (- 4, -3) θ4: (4, -3) SOLUTION I (4,3) θ1 SOLUTION x= y= r= sin θ = cos θ = tan θ = csc θ = sec θ = cot θ = II (-4,3) θ2 x= y= r= sin θ = cos θ = tan θ = csc θ = sec θ = cot θ = SOLUTION x= y= r= sin θ = cos θ = tan θ = csc θ = sec θ = cot θ = θ3 (-4,-3) III SOLUTION x= y= r= θ4 (4,-3) IV SOLUTION sin θ = cos θ = tan θ = csc θ = sec θ = cot θ = Y II ref θ2 ref θ3 III I θ1 ref θ4 IV Perpendicular line from point on circle always drawn X to the x-axis forming a reference triangle Y II ref θ2 ref θ3 III I θ1 ref θ4 IV Value of trig function of angle in any quadrant is equal to trig X function of its reference angle, or it differs only in sign. #2 Given: tan θ = -1 and cos θ is positive: • Draw θ. Show the values for x, y, and r. SOLUTION Given: tan θ = -1 and cos θ is positive: • Find the six trigonometric functions of θ. SOLUTION # 1 Find the value of sin 110º. (First determine the reference angle.) SOLUTION #2 Find the value of tan 315º. (First determine the reference angle.) SOLUTION #3 Find the value of cos 230º. (First determine the reference angle.) SOLUTION #1 Draw the angle whose terminal side passes through the given point 1, 3 . SOLUTION Find all trigonometric functions for angle whose terminal side passes thru 1, 3 . SOLUTION #2 Draw angle: sin θ = 0.6, cos θ is negative. SOLUTION Find all six trigonometric functions: sin θ = 0.6, cos θ is negative. SOLUTION #3 Find remaining trigonometric functions: sin θ = - 0.7071, tan θ = 1.000 SOLUTION Find remaining trigonometric functions: sin θ = - 0.7071, tan θ = 1.000 SOLUTION #1 Express as a function of a reference angle and find the value: cot 306º . SOLUTION #2 Express as a function of a reference angle and find the value: sec (-153º) . SOLUTION #3 Find each value on your calculator. (Key in exact angle measure.) sin 260.5º tan 150º 10’ SOLUTION cot (-240º) csc 450º SOLUTION cos 5.41 sec (7/4) SOLUTION π/2 = 1.57 0 2π = 6.28 π = 3.14 3π/2 = 4.71 # 1 The refraction of a certain prism is sin 100° n= sin 47° Calculate the value of n. SOLUTION #2 A force vector F has components Fx = - 4.5 lb and Fy = 8.5 lb. Find sin θ and cos θ. Fy = 8.5 lb θ Fx=-4.5 lb SOLUTION Fy = 8.5 lb θ Fx=-4.5 lb SOLUTION