Instrument Systems

Instrument Systems
Instrument Systems
• Vacuum System
• Pitot-static system
• Magnetic System
Pitot-Static System
• Types of Pressure
• System components
Two types of Pressure
• Dynamic Air
Pressure
• Pitot or ram pressure
• Supplied by pitot tube
• Location varies
• Needs to face directly into the relative wind
• Pressure caused by moving air
• Only linked to airspeed indicator
• Static Air Pressure
• Also, ambient static air pressure
• Supplied by static port
• Location varies
• Needs to be in undisturbed air
• Pressure just outside of the airplane
• Linked to all Pitot
Static instruments
Components of system
• Pitot Pressure Lines
• Connects pitot tube to airspeed indicator
• Needs to run direct
• Sump in lowest point collects moisture
• Static Pressure Lines
• Connect to all three
• Has sump in lowest lines
Pitot-Static System
Pitot Static Flight Instruments
Pitot-Static Instruments
• Airspeed Indicator
• Altimeter
• Vertical Speed Indicator
Airspeed Indicator
Airspeed Indicator
• Displays the speed of the aircraft through the air
• Only instrument that uses both types of pressure
• Measures the difference between the two pressures
• Greater the difference the greater the airspeed
Airspeed Indicator Operation
• Instrument is contained within a sealed case
• Pressure sensitive diaphragm
• Ram pressure line is connected directly to one side of the diaphragm
• Diaphragm expands and contracts due to ram pressure
• Inside of the case is vented to the static port
Inside airspeed indicator
Airspeed Indicator Operation
• Diaphragm expands and contracts in proportion to the difference between the two pressures
• Measured by mechanical linkage
• Linkage is displayed by the hands on the face of airspeed indicator
Airspeed Indicator
Airspeed Definitions
• Indicated Airspeed
• Value read from the indicator
• indicated stall speeds remain constant
• Uncorrected for installation(position) and instrument error
Airspeed Definitions
• Calibrated Airspeed
• Indicated Airspeed corrected for installation and instrument error
• Determine from looking in the POH
• True Airspeed
• True speed of aircraft through the air
• Calibrated corrected for altitude and nonstandard temperature
Airspeed Definitions
• Ground Speed
• Actual speed of the aircraft over the ground
• True airspeed adjusted for the wind
• Found using the E6B
Airspeed Definitions
Airspeed Indicator
• White Arc
• Green Arc
• Yellow Arc
• Red Line
Airspeed Errors
• Position Error
• Occurs when the static port sense an erroneous static pressure
• Mainly caused by slipstream
• Error may be determined by using the airspeed calibration chart
• Instrument Error
• Errors due to imperfections in the instrument itself, imperfections with manufacturing
Altimeter
Altimeter
• System Operation
• Types of Altitude
• Markings
• Errors
Altimeter
• Simply a barometer that measures static pressure of the air around the aircraft.
• Uses only the static pressure
• Operates by the changes in pressure
• Standard pressure at Mean Sea Level in
29.92 inches of mercury
• Atmosphere declines 1 inch of mercury every thousand feet
Altimeter Operation
• Aneroid wafer
• Stack of hollow, elastic metal wafers
• Expand and contract as pressure changes
• This is shown through mechanical linkage
• Each pressure setting is a definite size on window
Altimeter Operation
• Pressure Window
• Kollsman window
• Small adjustable subscale that allows the current altimeter setting to be set in
• Important to reset with current
• Above 18,000’ always set at 29.92
Altimeter Operations
Altimeter Functions
Air moves out
8
9
7
6
0 1
2
5
4
3
Wafers expand
8
9
7
6
0 1
2
5
4
3
Air moves in
8
9
7
6
0 1
2
5
4
3
Wafers contract
© UND Aerospace, 1994
Types of Altitude
• Indicated Altitude
• Read from Indicator
• Pressure Altitude
• Height above standard datum
• Density Altitude
• Pressure corrected for nonstandard temperatures
Types of Altitude
• True Altitude
• True height above sea level
• Airports and obstruction are based on
• Absolute Altitude
• Actual height above surface
True
Altitude
Absolute
Altitude
Pressure
Altitude
Indicated
Altitude
Standard
Datum Plane
© UND Aerospace, 1994
Pressure = 29.92" Hg
Altimeter
Altimeter Errors
• Pressure Error
• High to Low-Look out below, low to high plenty of sky
• Need to set in current altimeter setting
Vertical Speed Indicator
VSI
• System Operation
• Markings
• Errors
Vertical Speed Indicator
• Provides reference to rate of change
• Will show trend away from level quickly
• Responds faster then the altimeter
• Shows both rate and trend
• Uses only static pressure
VSI Operations
• Expandable Capsule
• Directly connected to static port
• Connected through mechanical linkage
• Calibrated Leak
• Instrument Case’s connection to the static port
• Allows capsule to change pressure more gradually
VSI Operation
• Pressure inside of capsule changes the same as the outside air
• Pressure in instrument case changes slower because of calibrated leak.
• Gives us the rate
• When pressure is equal straight and level
VSI Operations
Types of Information Portrayed
• Trend Information
• Immediate indication of an increase or decrease
• First Indication
• Rate Information
• Shows the stabilized rate of change
• Take 6-9 seconds
Markings
VSI Errors
• Abrupt changes cause errors
• Rough control and turbulent air cause error
Vacuum System
System Operation
• Vacuum System
• Draws air through the filter system
• Moves through Attitude and Heading indicator where it spins gyros
•Spins at 18,000 RPM
• Air continues into engine driven vacuum pump
System Operation
Gyroscopic Principles
• Rigidity in Space
• Remains in a fixed plane when spinning
• Gimbal instrument around gyro to allow it remain in plane able to show changes in pitch and attitude
Gyroscopic Principals
• Precession
• When outside force is applied to gyro it will be felt 90 degrees in rotation of spinning
• Includes friction
Gyroscopic Instruments
• Heading Indicator
• Attitude Indicator
• Turn Cordinator
Heading Indicator
Heading Indicator
• Operation
• Markings and Use
• Limitations and Errors
Heading Indicator Operation
• Relies on Rigidity on Space
• Primary source of Heading information
• Senses rotation along the vertical axis
• Gyro spins in the horizontal axis
• Support gimbals drive the compass card
• Works through gears and linkage
• Setting knob
Heading Indicator Operation
Markings & Use
Limitations
• Reset every 15 minutes
• Pitch - 55 degrees
• Bank - 55 degrees
Heading Errors
• Precession
• Can be a negative in Heading indicator
• Causes the heading to drift
• Should check every 15 minutes
• Make sure you are in straight and level, unaccelerated flight
• Tumbling
• Occurs after excessive pitch and roll
Attitude Indicator
• Operation
• Markings and Use
• Limitations and Errors
Attitude Indicator Operations
• Mechanical Substitute for the natural horizon
• Gives immediate and direct information of plane’s pitch and bank
• Gyro spins in the horizontal plane
• Self erecting mechanisms
• Vacuum Driven, normally
Attitude Indicator Operations
Markings & Use
Climb
Climb and
Left Bank
Level Flight
Glide
Glide and
Left Bank
Level Flight and Left Bank
Attitude Indicator Errors
• Usually very minor
• Minor on acceleration and deceleration
• Somewhat precesses on turns
• Errors are maximum when rolling out of a 180 degree or 360 degree turn
• Instrument Tumbling (older AI)
• Caging mechanism
• May take awhile for it to re-erect itself
• After 100 degrees of bank and 60 degrees of pitch
Turn Indicators
• Two Types
• Turn and Slip
• Operation
• Markings
• Turn Coordinator
• Operation
• Markings
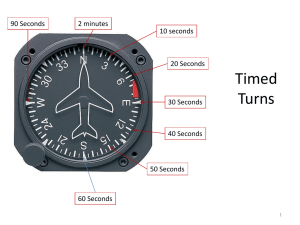
Turn & Slip Indicator
L R
L
TURN
2 MIN
R
BANK
Turn Coordinator
• Operation
• Like the Turn and Slip
• But shows both rate of turn and rate of roll
• Gimbal is set at a 30 degree angle
• Allows force to be felt
• Allows gyro more movement
Turn Coordinator
Gyro gimble
(mount not shown)
Gyroscope rotor
Index marks
Aircraft silhouette
Inclinometer
Canted gyro axis
Parallel to longitudinal axis of a/c
Turn Coordinator
Operation
Inclinometer
• Contains fluid and ball
• Kerosene type fluid
• Steel ball
• Shows the quality of the turn
(Coordination)
• Shows forces acting ball in the turns
Quality of Turn
Skid Turn Coordinator
Slip Turn Coordinator
Magnetic Compass
Magnetic Compass
• Construction
• Diagram and function
• Markings and use
• Compass Errors
• Use of compass
Magnetic Compass Construction
The Earth’s Magnetic Field
The Earth's Magnetic Field
Geographic Pole
Magnetic Pole
Magnet aligns itself with magnetic force
Lines of magnetic force
Compass Errors
• Variation
• Deviation
• Magnetic Dip
• Northerly Turning Error
• Acceleration/Deceleration Error
• Oscillation Error
Variation
• Variation - Angular difference between true north and magnetic north.
• Agonic line - The line where there is no angular difference.
• Isogonic - Lines showing the angular lines difference.
Variation
Geographic
North Pole o
13
20 o 10 o
North
Magnetic
Pole o
0 10 o
20 o
15 o
Isogonic lines 5 o
15 o o
5
Agonic line
Compass Card
• Deviation
• Error due to magnetic interference within the aircraft
• Compensating magnets in compass help to counteract
• Called Swinging
• Error on compass correction card
Compass Card
For N 30 60 E 120 150
Steer 357 023 050 080 111 145
For S 210 240 W 300 330
Steer 178 213 246 278 307 333
Magnetic Dip
• How it works
• Errors it causes
Magnetic Dip
• Most significant error
• Difficult to get actual readings
• Magnet in compass tries to point 3Ds to pole
• Causes errors in turns and acceleration
How it Works
Magnetic flux lines point downward at the poles, compass magnets dip to low side of turn
Dip
North Pole
No Dip
Magnetic
Dip
Aircraft
Flight Path
Errors it Causes
• Acceleration error - ANDS
• Northerly turning error
• North lags
• SOS - south over shoot
Acceleration Error
• Accelerate
• Will show a turn to the North
• When speed stabilizes compass returns to accurate
• Error greatest on headings of West and
East
• Deceleration
• Will show a turn to the South
• Use ANDS
• Accelerate North
Decelerate South
Acceleration & Deceleration Errors ~
ANDS
N N
N
• 01-185
S
15
12
E
E
6 3 N
Deceleration
Accleration
Constant Airspeed
Turning Errors
• Northerly Error
• Initially indicate turn to opposite direction
• Southerly Error
• Heading will lead the turn