PPT - Animated Science
advertisement

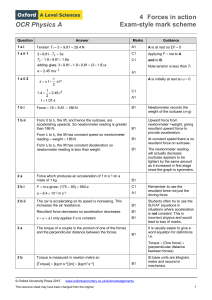
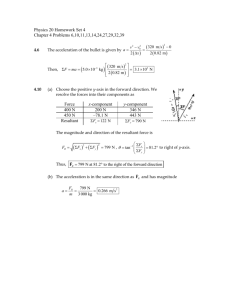
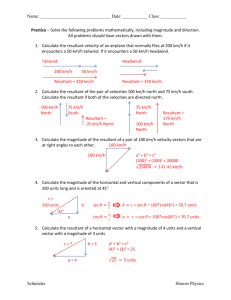
Quick Tests Physics – Module 2 Abstract Maths 2 1) 2) Simplify? Make the square the subject? 2 3) Find the triangle? Maths Rearrange the following 10 equations to find “a” for each equation; ab c ab c Maths rules Do the same to both sides i.e. add and divide Separate terms on one side must be put in brackets so each is dealt with the same Functions like cos, sin, tan, squares can be cancelled by their inverse. This is not the same as 1/x function Sqrt applies to everything not just the term you fancy sin 1 ( a ) d tan(a ) b c 1 5 2 2 a b Go one step at a time and write our your working, less chance of going wrong then! See if it is true for numbers at the start and end of your rearranging. a b c 2 2 2 2 a b2 c c 2 2 a b c2 5c 5( a 1) c 2 sin(a ) x Vectors I 1) What is the result distance and angle (from vertical); 2) What is the result force and angle (from horizontal); NB. Ignore air resistance in all cases 3) What are the resultant forces. 4) What is the resultant force NS and EW directions. Then resultant and angle? 4.123N Vectors II NB. Ignore air resistance in all cases 1) vector or scalar? – force, temperature, acceleration, weight, displacement 2) When a ball is thrown vertically into the air what are the accelerating forces on it? 3) When a ball is thrown horizontally off a cliff what are the accelerating forces on it? 4) Draw a diagram and use Pythagoras rules involving cos & sin etc.. to explain how to resolve a resultant force into two forces at 90 degrees. 5) When dealing with a problem involving a picture frame hanging from a single wire under tension what can we say about the vertical or horizontal forces to help us solve the problem? 6) Explain the difference between displacement and distance travelled using the idea of a circular running track? Uniformly Accelerated Motion 1. What does u stand for? 2. What does v stand for? 3. Which equation is wrong; 4. What does a constant downwards slope on a ST graph show? s 5. What does a constant upwards slope on a V-T graph show? 6. What does the area under a V-T graph represent? 7. When throwing a ball up into the air vertically or horizontally describe how the accelerating forces on it change in detail for the entire journey (ignore drag) 8. Draw out the graphs and add the Y-axes to each one… s = 0.5gt2 t v v = gt a t a=g t (down is positive) Gas Laws 1. What is an experimental equation which links pressure to temperature Pressure 2. What is a derived equation which links pressure to c 2 3. How many atoms in a mole? 4. What does “p” stand for and what are the common units used? Charles 5. What can I substitute Nm/V for? 6. Name each graph law to the right; 7. What does “n” stand for? 2 8. What does c represent 9. How many litres is a 10. True or false m3 c2 T Boyles What are the standard units… 1) Internal Energy 1) J 2) Avogadro's constant 2) particles / mole 3) Boltzmann constant 3) J K-1 4) Molar gas constant 4) J K-1 mol-1 5) Acceleration 5) ms-2 6) Acceleration (another form) 6) Nkg-1 7) Momentum 7) kgms-1 8) Kinetic Energy 8) J 9) Kinetic Energy (another form) 9) kg m2 s-2 10) Density 10) kgm-3