Relational Notation
advertisement

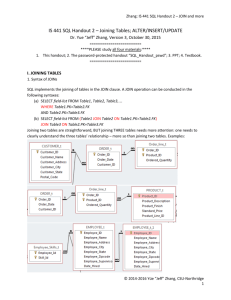
BACS 485 Translating E/R to Relational Notation BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation 1 Relational Notation Relational Notation is a shorthand way to represent E/R diagrams. It is a half-way step between an abstract tool (i.e., E/R diagrams) and an implementation specific tool (i.e., SQL Create Table commands). The format is as follows: Table-name(key-attribute, attribute-1,… attribute-N) BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation 2 Relational Notation The basic rules of translating E/R diagrams to Relational Notation are given below: Each entity becomes a table Each attribute on the table becomes an attribute on the table Primary keys are underlined Foreign keys are underlined with a dashed line In 1:1, the foreign key can be on either side of the relation (context dependent) In 1:N, the foreign key goes on the ‘N’ side In M:N, the relation becomes a table and the key for the new table is the concatenated primary keys of the original tables In sub-type/super-type, the primary key of the sub-type(s) is the same as the super-type (thus, no “foreign key”) BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation 3 1:1 E/R to Relational Notation A B Table1 D C Rel Translates to 2 tables: Table1 (A,B,C,D) OR Table2 (D,E,F) E F Table2 Table1 (A,B,C) Table2 (D,E,F,A) pick one depending upon context, red letter is foreign key BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation 4 1:1 Relational Notation to E/R Translate from 2 tables: Table1 (X,Y,Z) OR Table2 (L,M,N,X) Table1 (X,Y,Z,L) Table2 (L,M,N) pick one depending upon context, red letter is foreign key X Y L Z Table1 BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation Rel M N Table2 5 1:N E/R to Relational Notation A B Table1 D C Rel E F Table2 Translates to 2 tables: Table1 (A,B,C) Table2 (D,E,F,A) red letter is foreign key BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation 6 1:N Relational Notation to E/R Translate from 2 tables: Table1 (X,Y,Z,L) Table2 (L,M,N) red letter is foreign key X Y L Z Table1 BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation Rel M N Table2 7 Simple M:N E/R to Relational Notation A B Table1 D C Rel E F Table2 Translates to 3 tables: Table1 (A,B,C) Table2 (D,E,F) Table3 (A,D) Notice that there is no foreign key BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation 8 Simple M:N Relational Notation to E/R Translate from 3 tables: Table1 (X,Y,Z) Table2 (L,M,N) Table3 (X,L) X Y L Z Table1 BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation Rel M N Table2 9 More Complex M:N E/R to Relational Notation A B D C E F X Table1 Rel Table2 Translates to 3 tables: Table1 (A,B,C) Table2 (D,E,F) Table3 (A,D,X) Notice that relationship attribute is attached to new table BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation 10 More Complex M:N Relational Notation to E/R Translate from 3 tables: Table1 (X,Y,Z) Table2 (L,M,N) Table3 (X,L,P) X Y L Z M N P Table1 BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation Rel Table2 11 More Complex M:N E/R to Relational Notation A B D C E F X Table1 Rel Table2 Translates to 3 tables: Table1 (A,B,C) Table2 (D,E,F) Table3 (A,D,X) Notice that relationship attribute is attached to new table BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation 12 More Complex M:N E/R to Relational Notation H I J Table3 A B Table1 C D Rel E F Translates to 4 tables: Table1 (A,B,C) Table2 (D,E,F) Table3 (H,I,J) Table4 (A,D,H,K) Table2 K BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation 13 Sub-Type / Super-Type E/R to Relational Notation A B C Table1 (A,B,C) Table2 (A,D,E,F) Table3 (A,H,I,J) Table1 E Notice that Table2 and Table3 do not have a key in the E/R. Table3 Table2 D F BACS485 – E/R to Relational Notation Translates to 3 tables: H I J 14