Optics Review
advertisement

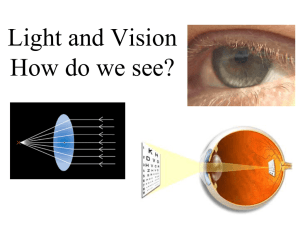
Optics Review Exam Review 2009 Optics Review: Types of Light Sources • INCANDESCENT • FLUORESCENT • PHOSPHORESCENT • CHEMILUMINESCENT • BIOLUMINESCENT – – – – Created by glowing objects Give off lots of heat Inefficient – cost more to operate Cheap to make – – – – Created by UV emission from mercury source Less heat produced Less expensive to run More expensive to make – – – Glow in the dark stickers, clocks etc. Absorb light and then re-emit it later Usually a greeny-yellow colour – – – Chemical reaction causes light No heat Glow sticks – – Chemiluminescence in living organisms Fire flies, some deep sea fish Optics Review: Properties of Light • Light travels in straight lines called RAYS • Light is a form of energy and travels in WAVES • “White” Light can be refracted into the VISIBLE SPECTRUM ROY G. BIV Optics Review: Primary Colours of Light • Primary Additive Colours • All colours can be made from 3 primary additive colours of LIGHT RED + BLUE + GREEN → WHITE RED + BLUE → MAGENTA RED + GREEN → YELLOW GREEN + BLUE → CYAN Technologies that use this: TV’s, spotlights, movie theatres THE HUMAN EYE! Optics Review Primary Colours of Light • Primary Subtractive Colours of Light • Take White light and subtract one primary colour and we have a Subtractive Colour Ex: White – blue = yellow magenta + cyan → blue magenta + yellow → red yellow + cyan → green magenta + cyan + yellow → black • These are used in pigments (paints, ink jet printer cartridges) • Coloured filters pull (subtract) colours to produce desired results Optics Review Example White R+G+B – Primary Colours of Light blue – B yellow + cyan R + G + G +B = = yellow R+G → green → Green *Green dominates the combination Optics Review: EMR • Electromagnetic Radiation is a spectrum of wave energies and includes VISIBLE light • Waves have WAVELENGTH (), FREQUENCY(), and AMPLITUDE (A) • From shortest to greatest frequency (least energy --------------------------------------------------------- most energy) Radio – Micro – Infrared – VIS – UV – X-Rays – Gamma Rays Longest ----------------------------------------------- shortest Optics Review: Uses of EMR • RadioWaves – TV, radio, cell phones • Microwaves – Microwave ovens – cooking food – Telecommunications • Infrared – Remote controls – Thermal imaging • UV – Tanning (also causes sun burns and skin damage) – Heating lamps – fast food, spas • X-Rays – Doctors and dentists use to see bones/teeth • Gamma Rays – Doctors use to target and kill cancer cells Optics Review: Laws of Reflection • Light travels in straight lines called RAYS • Light bounces or reflects off of hard, shiny surfaces like a mirror • Law 1: The Angle of Incidence (i) = the Angle of Reflection (r) • Law 2: The Incident Ray (IR), Reflected Ray (RR), and the Normal (N) are in the same plane N IR i r RR Reflecting Surface Optics Review: Laws of Reflection • Example: If the angle of incidence is 45o, what is the angle of reflection? N IR 45 r RR Mirror • Law of Reflection states that i = r so both equal 45o • NOTE: i is between the Incident Ray and the Normal Laws of Refraction • Light “bends” or refracts when light moves at an angle from one medium to another • Law 1: The refracted ray bends towards the normal if light enters a denser medium (air → water) • Law 2: The refracted ray bends away from the normal if light enters a less dens medium (water → air) IR N Optics Review: Optics Review: • • • • Refraction When light enters water, light is “bent” This causes optical illusions Double images Images of objects where they are not • REFRACTION and REFLECTION ALSO CAUSE: • Rainbows • Sun dogs (rainbow like circles around the sun on the very cold days) • Sunsets and Sunrises – dust and oxygen and nitrogen particles in the air reflect and refract light • BLUE SKY – oxygen and nitrogen scatter (reflect) light filtering out colours other than blue Optics Review: • Lenses are shaped pieces of plastic or glass that refract light • Convex Lenses: thicker in middle – converge or focus light • Concave Lenses: thicker on edge – diverge or spread light Properties of Lenses Optics Review: • • • • • • • Properties of Lenses Convex lenses can Magnify Invert Form real images Concave lenses can: Minimize Create inverted or upright images Optics Review: Properties of Mirrors • Lenses are shaped pieces of plastic or glass that refract light • Convex Mirrors (fisheye): Create virtual, upright, smaller images • Used in side mirrors, security mirrors • Concave Lenses: can create many different types of images depending upon placement • Used for vanity/makeup mirrors - magnifying Optics Review: The EYE • The eye is the organ responsible for sight • The retina has two types of cells: • RODS – sensitive to light • See in shades of gray • CONES – sensitive to colour • RED, GREEN & BLUE (the three primary colours) Optics Review: The EYE Optics Review: The EYE Optics Review: • The EYE • • • • • • Eyelash Retina Lens iris Ciliary muscles Optic Nerve The EYE • • • • • • • The Camera Lens cap Film / chip Lens Diaphragm Focus ring USB cable Optics Review: • Farsightedness – lens too flat, the image produced by the lens is too far past the retina • Correction – use a convex lens to converge the image on the retina The EYE and Lenses Optics Review: • Nearsightedness – lens too curved; the image produced by the lens is too far forward of the retina • Correction – use a concave lens to diverge the image on the retina The EYE and Lenses Optics Review: The EYE and Lenses