Curved Mirrors
advertisement

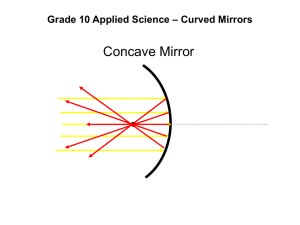
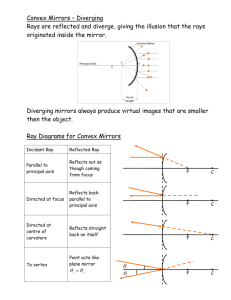
Curved Mirrors Curved Mirror Terminology Like plane mirrors, curved mirrors still follow the law of reflection, but, because of their curvature, the rays are reflected at slightly different positions. Vertex – The middle point of a curved mirror. Focal Point – The point where light rays meet or appear to meet. Focal Length – The distance from the vertex to the focal point. Curved Mirror Terminology Concave Mirrors A concave mirror has a reflecting surface that curves inward like a bowl. AKA: Converging Mirror The image formed by a concave mirror depends on how far away the object is away from the focal point of the mirror. Concave Mirror Diagram What happens to light rays that strike a concave mirror? Focal Point Vertex Uses for Concave Mirrors Flashlight Telescope Car Headlight Solar Oven Image Terminology When it comes to describing an image in a mirror – we have to be able to describe it on several levels… 1. 2. 3. 4. Location – Where is the image? Orientation – Upright or Inverted? Size – Larger or Smaller? Type – Real or Virtual? The characteristics spell out the word LOST!!! You will need to get LOST for each ray diagram you do for a mirror!!! Virtual vs. Real Images Virtual images are formed from diverging light rays. • Virtual images are tricky because are eyes believe the image is being made from light rays. • Virtual images can not be projected on to a screen. Real images are formed from the convergence of light rays – the image is made when light rays intersect each other. • Real images can be projected on to a screen. Images in Concave Mirrors This gets tricky…it all depends on how far away the object is away from the mirror itself. There are four different outcomes for the image type, position and orientation based on each of the following: 1. Object more than two focal lengths away from vertex. 2. Object is between 1 and 2 focal lengths away from mirror. 3. Object is at focal point. 4. Object is between focal point and vertex. Images in Concave Mirrors Convex Mirrors A convex mirror is a reflecting surface that curves outward. AKA: Diverging Mirror A convex mirror produces a virtual image that is upright and smaller that the object. Convex Mirror Diagram What will happen to the light rays as they strike a convex mirror? Can we relate the reflected rays in some manner? Uses for Convex Mirrors Store Security Side-view Mirrors Images in Convex Mirrors What image of the candle will appear in the mirror? The Image is: • Upright • Smaller • Virtual Images in Convex Mirrors Magnification Magnification is the measure of how much larger or smaller the image is compared with the object itself. Magnification is expressed as a ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object. Magnification = Image height Object height Magnification can also be determined using the ratio of the distance from image to mirror and distance from object to mirror. Magnification = Image distance Object distance M = hi ho M = di do Make sure to use proper formulas and units when doing your calculations. THE END!!!