Document
advertisement

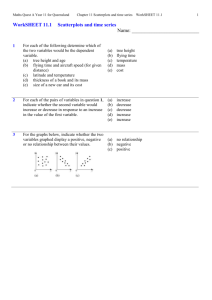
The FlowVizMenu and Parallel Scatterplot Matrix: Hybrid Multidimensional Visualizations for Network Exploration Christophe Viau, École de technologie supérieure, Montreal Michael J. McGuffin, École de technologie supérieure, Montreal Yves Chiricota, Université du Québec à Chicoutimi, Chicoutimi Igor Jurisica, Ontario Cancer Institute, Toronto Network exploration by graph metrics ? Network exploration by graph metrics Computed metrics: • Degree Network exploration by graph metrics Computed metrics: • Degree • Closeness centrality • Clustering coefficient • K-core decomposition • ... Network exploration by graph metrics Computed metrics: • Degree • Closeness centrality • Clustering coefficient • K-core decomposition • ... Multi-dimensional visualizations Scatterplot Matrix (SPLOM) Parallel Coordinates Related work Using a Scatterplot Matrix (SPLOM) and Node-Link Diagram to visualize a graph GraphDice [Bezerianos et al., 2010] Related work Integration of scatterplots and parallel coordinates Yuan et al., 2009 Steed et al., 2009 Holten and van Wijk, 2010 Our proposed interface Our proposed interface Parallel Scatterplot Matrix Our proposed interface FlowVizMenu Parallel Scatterplot Matrix Our proposed interface Attribute-Driven Layout FlowVizMenu Parallel Scatterplot Matrix A sequence of scatterplots A sequence of scatterplots Rotating scatterplots around the y-axis Rotating scatterplots around the y-axis Rotating scatterplots around the y-axis Parallel Scatterplot Matrix (P-SPLOM) Rotating around x- or y-axes causes a transition from Scatterplot Matrix (SPLOM) to stacked Parallel Coordinates. Scatterplot Matrix (SPLOM) Parallel Coordinates Ordering of axes within P-SPLOM Problem: traditional SPLOM ordering doesn’t yield useful parallel coordinates. Axes are repeated in each row and column Repeated axes: useless for parallel coordinates Ordering of axes within P-SPLOM Solution: order the axes according to a Latin square. Each row and column contains each axis once. Useful parallel coordinates Scatterplot Staircase (SPLOS) Inspired partly by quilts [Watson et al. 2008] Sequence of scatterplots: treats one dimension differently. Scatterplot Staircase (SPLOS): all dimensions treated uniformly; every adjacent pair of plots share an axis. Parallel coordinates: more difficult to judge correlations than in scatterplots [Li et al., 2010] FlowVizMenu • Variant of a FlowMenu with embedded visualization • Smoothly animated transitions • Brushing and linking • More than two dimensions possible with PCA FlowVizMenu In-out gesture to quickly select axes of scatterplot Attribute-Driven Layout (ADL) ADL: Layout based on a scatterplot selected in the FlowVizMenu. The network layout can be a mixture of • Attribute-Driven Layout (ADL) • Manual layout • Force-directed layout Demo Initial user feedback Five bioinformaticians used our prototype and gave feedback. All had experience working with network data. Results: Pros: • Exploring along multiple metrics, smooth transitions, and integration of views were judged useful • All participants stated they would use the interface if it were made available to them Cons: • Some pairings of metrics within the scatterplots may not be useful • Too many hotkeys + button combinations in the current prototype Contributions: Three hybrid multidimensional visualization techniques for visualizing networks Contributions: Three hybrid multidimensional visualization techniques for visualizing networks • A Parallel Scatterplot Matrix (P-SPLOM) that transitions between a scatterplot matrix and parallel coordinates Contributions: Three hybrid multidimensional visualization techniques for visualizing networks • A Parallel Scatterplot Matrix (P-SPLOM) that transitions between a scatterplot matrix and parallel coordinates Contributions: Three hybrid multidimensional visualization techniques for visualizing networks • A Parallel Scatterplot Matrix (P-SPLOM) that transitions between a scatterplot matrix and parallel coordinates • A FlowVizMenu to quickly select the dimensions for an embedded scatterplot Contributions: Three hybrid multidimensional visualization techniques for visualizing networks • A Parallel Scatterplot Matrix (P-SPLOM) that transitions between a scatterplot matrix and parallel coordinates • A FlowVizMenu to quickly select the dimensions for an embedded scatterplot Contributions: Three hybrid multidimensional visualization techniques for visualizing networks • A Parallel Scatterplot Matrix (P-SPLOM) that transitions between a scatterplot matrix and parallel coordinates • A FlowVizMenu to quickly select the dimensions for an embedded scatterplot • An Attribute-Driven Layout to configure the graph according to a scatterplot of graph metrics Future directions • Application to other domains • Evaluation of performance and usability • Exploration of the design space of each visualization (e.g., on a small screen) Acknowledgments We thank our collaborators for their feedback: • SAP Business Objects • Members of Jurisica Lab at OCI • Members of the Multimedia Lab at ETS This research was funded by an SAP Business Objects ARC Fellowship, NSERC, and the FQRNT. Thank you P-SPLOM: variants P-SPLOM: Pearson correlation coefficient P-SPLOM: Latin square P-SPLOM: another latin square Scatterplot Staircase Parallel Scatterplot Matrix (P-SPLOM) • Rotating around x- or y-axes causes a transition from Scatterplot Matrix (SPLOM) to stacked Parallel Coordinates Ordering of axes within P-SPLOM The traditional SPLOM ordering doesn’t produce interesting parallel coordinates Repeated axes: useless for parallel coordinates P-SPLOM ordering • We explored variants of latin square