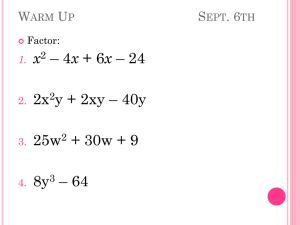Document
advertisement

Chapter 11 Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume Click the mouse or press the space bar to continue. Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 Lesson 11-1 Perimeter Lesson 11-2 Area of Parallelograms Lesson 11-3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Make a Model Lesson 11-4 Area of Triangles Lesson 11-5 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Lesson 11-6 Volume of Rectangular Prisms Lesson 11-7 Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms 11-1 Perimeter Five-Minute Check (over Chapter 10) Main Idea and Vocabulary California Standards Key Concept: Perimeter of a Square Key Concept: Perimeter of a Rectangle Example 1 Example 2 11-1 Perimeter • I will find the perimeters of squares and rectangles. • perimeter 11-1 Perimeter Standard 5MG1.4 Differentiate between, and use appropriate units of measures for twoand three-dimensional objects (i.e., find the perimeter, area, volume). 11-1 Perimeter 11-1 Perimeter 11-1 Perimeter The base of the Eiffel Tower is shaped like a square with each side measuring 125 meters. What is the perimeter of the base? P = 4s P = 4(125) P = 500 Perimeter of a square Replace s with 125. Multiply. Answer: The perimeter of the base of the Eiffel Tower is 500 meters. 11-1 Perimeter The park is shaped like a square with each side measuring 100 yards. What is the perimeter of the park? A. 400 feet B. 400 yards C. 200 yards D. 100 yards 11-1 Perimeter Find the perimeter of the rectangle. 7m 4m P = 2 + 2w P = 2(7) + 2(4) P = 14 + 8 Write the formula. Replace with 7 and w with 4. Multiply. P = 22 Add. Answer: The perimeter is 22 meters. 11-1 Perimeter Find the perimeter of the rectangle. A. 7 cm B. 6 cm 3 cm 1 cm C. 8 cm D. 10 cm 11-2 Area of Parallelograms Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 11-1) Main Idea California Standards Key Concept: Area of a Parallelogram Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 11-2 Area of Parallelograms • I will find the areas of parallelograms. • base • height 11-2 Area of Parallelograms Standard 5MG1.1 Derive and use the formula for the area of a triangle and of a parallelogram by comparing it with the formula for the area of a rectangle. Standard 5MG1.4 Differentiate between, and use appropriate units of measures for two- and threedimensional objects. 11-2 Area of Parallelograms 11-2 Area of Parallelograms Find the area of the parallelogram. The base is 3 and the height is 10. A = bh A = 3 • 10 A = 30 Area of parallelogram Replace b with 3 and h with 10. Multiply. Answer: The area is 30 square units or 30 units2. 11-2 Area of Parallelograms Find the area of the parallelogram. A. 35 units2 B. 28 units2 C. 49 units2 D. 64 units2 11-2 Area of Parallelograms Find the area of the parallelogram. A = bh A = 8.2 • 4.5 A = 36.9 Area of parallelogram Replace b with 8.2 and h with 4.5. Multiply. Answer: The area is 36.9 square centimeters or 36.9 cm2. 11-2 Area of Parallelograms Find the area of the parallelogram. A. 68 mm2 B. 70 mm2 C. 68.64 mm2 D. 70.42 mm2 11-2 Area of Parallelograms A particular area rug is shaped like a parallelogram. Estimate the area of the floor it will cover. Estimate 6 1 is about 6 and 10 1 is about 11. 4 2 A = bh Area of parallelogram A = 11 • 6 Replace b with 11 and h with 6. A = 66 Multiply. Answer: The area of the rug is about 66 ft2. 11-2 Area of Parallelograms A parking lot is shaped like a parallelogram. Estimate the area of ground it will cover. A. 7,000 sq. yds. B. 7,200 sq. yds. C. 7,140 sq. yds. D. 7,080 sq. yds. 11-3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Make a Model Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 11-2) Main Idea California Standards Example 1: Problem-Solving Strategy 11-3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Make a Model • I will solve problems by making a model. 11-3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Make a Model Standard 5MR2.3 Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Standard 5MG1.4 Differentiate between, and use appropriate units of measures for two- and threedimensional objects. 11-3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Make a Model While volunteering at the local farm market, Julia was asked to make a display for the oranges. She needs to stack the oranges in the shape of a square pyramid. The base should have 100 oranges and one orange needs to be on top. There are 400 oranges total. Are 400 oranges enough to make a square pyramid with a base of 100 oranges? 11-3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Make a Model Understand What facts do you know? • The oranges need to be in the shape of a square pyramid with 100 oranges in the base and 1 orange on top. • There are 400 oranges altogether. What do you need to find? • Are 400 oranges enough to make a square pyramid with a base of 100 oranges? 11-3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Make a Model Plan Make a model using pennies to find the number of oranges needed. 11-3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Make a Model Solve Begin with 100 pennies. For each consecutive layer, place 1 penny where 4 meet. bottom layer second layer third layer fourth layer 100 81 64 49 11-3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Make a Model Solve Answer: By continuing this pattern, 100 + 81 + 64 + 49 + 36 + 25 + 16 + 9 + 4 + 1 or 385 oranges will be needed. Since 385 < 400, 400 oranges are enough to make a square pyramid. 11-3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Make a Model Check Look back at the problem. 400 – 100 – 81 – 64 – 49 – 36 – 25 – 16 – 9 – 4 – 1 leaves 15 oranges. 11-4 Area of Triangles Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 11-3) Main Idea California Standards Key Concept: Area of a Triangle Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 Area of Triangles 11-4 Area of Triangles • I will find the areas of triangles. 11-4 Area of Triangles Standard 5MG1.1 Derive and use the formula for the area of a triangle and of a parallelogram by comparing it with the formula for the area of a rectangle. Standard 5MG1.4 Differentiate between, and use appropriate units of measures for two- and threedimensional objects. 11-4 Area of Triangles 11-4 Area of Triangles Find the area of the triangle. By counting, you find that the measure of the base of the triangle is 5 and the height is 8. A= 1 bh 2 1 A = (5) • (8) 2 Area of a triangle Replace b with 5 and h with 8. 11-4 Area of Triangles A= 1 (40) 2 A = 20 Multiply. Multiply. Answer: The area of the triangle is 20 square units. 11-4 Area of Triangles Find the area of the triangle. A. 25 sq. units B. 16 sq. units C. 12 1 sq. units 2 D. 20 sq. units 11-4 Area of Triangles Find the area of the triangle. A= 1 bh 2 1 A = (16.4) • (7.9) 2 Area of a triangle Replace b with 16.4 and h with 7.9. 11-4 Area of Triangles A= 1 (129.56) 2 A = 64.78 Multiply. Divide. 129.56 ÷ 2 = 64.78 Answer: The area of the triangle is 64.78 square meters. 11-4 Area of Triangles Clio cut out a banner in the shape of a triangle. What is the area of the banner? A. 99 sq. cm B. 99 cm C. 49 1 cm 2 1 D. 49 sq. cm 2 11-4 Area of Triangles Find the area of the triangle. A= 1 bh 2 1 A = (12) • (6) 2 Area of a triangle Replace b with 12 and h with 6. 11-4 Area of Triangles A= 1 (72) 2 A = 36.5 Multiply. Divide. 72 ÷ 2 = 36.5 Answer: The area of the triangle is 36.5 square inches. 11-4 Area of Triangles Kira drew a triangle on the sidewalk with chalk. What is the area of her triangle? A. 21 sq. ft B. 10.5 sq. ft C. 20 sq. ft D. 11 sq. ft 11-5 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 11-4) Main Idea California Standards Example 1: Problem-Solving Investigation 11-5 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy • I will choose the best strategy to solve a problem. 11-5 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Standard 5MR2.3 Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Standard 5MG1.4 Differentiate between, and use appropriate units of measures for two- and threedimensional objects. 11-5 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy ROSS: I want people to find out about a party I’m having, so I will tell Jamie and Cara and have each of them tell two friends, and so on. I wonder how many people would be invited to the party in three minutes if two friends tell another two friends each minute? YOUR MISSION: Find the number of people who would be invited to the party in three minutes. 11-5 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Understand What facts do you know? • You know that Ross tells Jamie and Cara about the party, and then each friend tells two other friends each minute. What do you need to find? • You need to find the number of people who would be invited to the party in three minutes. 11-5 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Plan Draw a diagram to show the number of people who would be invited to the party. 11-5 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Solve Answer: So, 14 people would be invited to the party. 11-5 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Check Look back at the problem to see if the diagram meets all of the requirements. Since the diagram is correct, the answer is correct. 11-6 Volume of Rectangular Prisms Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 11-5) Main Idea and Vocabulary California Standards Key Concept: Volume of a Rectangular Prism Example 1 Example 2 11-6 Volume of Rectangular Prisms • I will find the volume of rectangular prisms. • rectangular prism • volume • cubic units 11-6 Volume of Rectangular Prisms Standard 5MG1.3 Understand the concept of volume and use the appropriate units in common measuring systems to compute the volume of rectangular solids. Standard 5MG1.4 Differentiate between, and use appropriate units of measures for two- and three-dimensional objects (i.e., find the perimeter, area, volume). 11-6 Volume of Rectangular Prisms 11-6 Volume of Rectangular Prisms Find the volume of the rectangular prism. Estimate V ≈ 10 m × 10 m × 5 m or 500 m3 In the figure, the length is 10 meters, the width is 8 meters, and the height is 5 meters. Use V = wh. 11-6 Volume of Rectangular Prisms V = wh Volume of rectangular prism V = 10 • 8 • 5 Replace with 10, w with 8, and h with 5. V = 400 Multiply. Answer: The volume is 400 cubic meters. 11-6 Volume of Rectangular Prisms Check for Reasonableness Since we overestimated, the answer should be less than the estimate. 400 < 500. 11-6 Volume of Rectangular Prisms Find the volume of a rectangular prism with a length of 14 mm, a width of 6 mm, and a height of 3 mm. A. 250 mm3 B. 300 mm3 C. 252 mm3 D. 254 mm3 11-6 Volume of Rectangular Prisms A closet is 6.2 feet long, 2.8 feet wide, and 8.1 feet high. Find the amount of space contained within the closet for storage. Round to the nearest foot. Estimate V ≈ 6 ft × 3 ft × 8 ft or 144 ft3 11-6 Volume of Rectangular Prisms V= wh Volume of rectangular prism V = 6.2 • 2.8 • 8.1 Replace with 6.2, w with 2.8, and h with 8.1. V = 140.686 Multiply, then round to the nearest foot. Answer: The storage space in the closet is about 141 cubic feet. 11-6 Volume of Rectangular Prisms Check for Reasonableness Compare to the estimate. 141 ≈ 144. 11-6 Volume of Rectangular Prisms A tissue box is 12 inches long, 5 inches wide and 5 inches high. Find the amount of space contained within the box for tissues. A. 300 cubic inches B. 250 cubic inches C. 125 cubic inches D. 315 cubic inches 11-7 Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 11-6) Main Idea and Vocabulary California Standards Key Concept: Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism Example 1 Example 2 Using a Net to Build a Cube 11-7 Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms • I will find the surface areas of rectangular prisms. • surface area 11-7 Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms Standard 5MG1.2 Construct a cube and rectangular box from two-dimensional patterns and use these patterns to compute the surface area for these objects. 11-7 Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms 11-7 Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms Find the surface area of the rectangular prism. Find the area of each face. top and bottom: 2( w) = 2(8 × 4) or 74 11-7 Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms front and back: 2( h) = 2(8 × 3) or 48 two sides: 2(wh) = 2(4 × 3) or 24 Add to find the surface area. Answer: The surface area is 74 + 48 + 24 or 136 square centimeters. 11-7 Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms Find the area of a rectangular prism that is 12 in long, 6 in wide, and 5 in high. A. 320 square inches B. 300 square inches C. 324 square inches D. 342 square inches 11-7 Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms A box measures 13 inches long, 7 inches wide, and 4 inches deep. What is the surface area of the box? S = 2 w + 2 h + 2wh S = 2(13 × 7) + 2(13 × 4) + 2(7 × 4) Surface area of a prism = 13, w = 7, h = 4 S = 2(91) + 2(52) + 2(28) Simplify within parentheses. S = 182 + 104 + 56 Multiply. S = 342 Add. Answer: The box has a surface area of 342 square inches. 11-7 Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms A flat screen television measure 48 inches long, 2 inches wide, and 25 inches high. What is the surface area of the TV? A. 2,692 square inches B. 2,700 square inches C. 1,874 square inches D. 2,962 square inches Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 Five-Minute Checks Area of Triangles Using a Net to Build a Cube Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 Lesson 11-1 (over Chapter 10) Lesson 11-2 (over Lesson 11-1) Lesson 11-3 (over Lesson 11-2) Lesson 11-4 (over Lesson 11-3) Lesson 11-5 (over Lesson 11-4) Lesson 11-6 (over Lesson 11-5) Lesson 11-7 (over Lesson 11-6) Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Chapter 10) Draw the three-dimensional figure whose top, side, and front views are shown. Use isometric dot paper. top side front A. B. Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Chapter 10) Draw the three-dimensional figure whose top, side, and front views are shown. Use isometric dot paper. top side front C. D. Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Chapter 10) Draw the three-dimensional figure whose top, side, and front views are shown. Use isometric dot paper. B. Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Chapter 10) Draw the three-dimensional figure whose top, side, and front views are shown. Use isometric dot paper. top A. side B. front Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Chapter 10) Draw the three-dimensional figure whose top, side, and front views are shown. Use isometric dot paper. top C. side D. front Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Chapter 10) Draw the three-dimensional figure whose top, side, and front views are shown. Use isometric dot paper. C. Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-1) Find the perimeter of each square or rectangle. length 7 in, width 4 in A. 11 in B. 28 in C. 3 in D. 22 in Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-1) Find the perimeter of each square or rectangle. sides 13 cm A. 52 cm B. 25 in C. 36 cm D. 62 cm Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-1) Find the perimeter of each square or rectangle. length 14 ft, width 10 ft A. 24 ft B. 48 ft C. 144 ft D. 140 in Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-1) Find the perimeter of each square or rectangle. sides 25 yd A. 100 yd B. 25 yd C. 255 ft D. 125 ft Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-2) Find the area of each parallelogram. base 14 yd, height 8 yd A. 128 yd2 B. 28 yd2 C. 248 yd2 D. 112 yd2 Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-2) Find the area of each parallelogram. base 13 ft, height 11 ft A. 143 ft2 B. 141 ft2 C. 144 ft2 D. 144 yd2 Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-2) Find the area of each parallelogram. base 8 in, height 6 A. 48 in2 B. 44 in2 C. 52 in2 D. 48 ft 1 in 2 Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-2) Find the area of each parallelogram. base 9.6 cm, height 5.2 cm A. 49.92 cm2 B. 45.12 cm2 C. 14.8 cm2 D. 24.8 cm2 Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-3) Solve. Use the make a model strategy. Cans of tuna are stacked into a 4-layer pyramid-shaped display. The bottom layer is 8-cans long and 4-cans wide. There is 1 less can in the length and width of each layer above it. How many cans are on display? A. 48 cans B. 52 cans C. 44 cans D. 70 cans Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-4) Find the area of each triangle. base 5 ft, height 5 ft A. 25 ft2 B. 25 ft C. 12.5 ft2 D. 12.5 ft Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-4) Find the area of each triangle. base 48 cm, height 23 cm A. 557 cm2 B. 71 cm2 C. 554 cm2 D. 600 cm2 Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-4) Find the area of each triangle. base 5.2 cm, height 3.2 cm A. 2.32 cm2 B. 8.32 cm2 C. 15.23 cm2 D. 18.32 cm2 Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-4) Find the area of each triangle. base 5 in, height 7 1 in 2 1 A. 12 in 2 1 B. 30 2 in C. 2 in 3 D. 18 in 4 Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-5) Tell what strategy you used. Desta saved $1 the first week. After that she saved $2 more each week than she had the week before. How much money did she save in the tenth week? A. $22 B. $24 C. $19 D. $34 Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-6) Find the volume of each prism. length 8 yd, width 7 yd, height 3 yd A. 168 yd3 B. 18 yd3 C. 59 yd3 D. 88 yd3 Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-6) Find the volume of each prism. length 12 cm, width 8 cm, height 5 cm A. 240 cm3 B. 480 cm3 C. 144 in D. 25 in Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-6) Find the volume of each prism. length 5 1 ft, width 3 ft, height 9 ft 4 A. 144 ft3 3 3 B. 141 ft 4 C. 3,444 in D. 1,333 cm Measurement: Perimeter, Area, and Volume 11 (over Lesson 11-6) Find the volume of each prism. length 2.4 cm, width 17.1 cm, height 3.6 cm A. 156.222 cm3 B. 147.744 cm3 C. 24 cm3 D. 444 in This slide is intentionally blank.