2.3 - Polynomial and Synthetic Division
advertisement

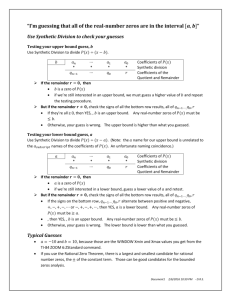
Warm up!! •Pg. 130 #’s 16, 22, 36, 42, 52, 96 2.3 - Polynomial and Synthetic Division Long Division of Polynomials 1) Divide 2) Factor 3) Find Zeros Now try this one yourself: Divide 5x2 – 17x – 12 by x – 4 Answer: 5x + 3 Example: Divide 6x3 – 19x2 + 16x – 4 by x – 2 Answer: 6x2 – 7x + 2 Which means that… 6x3 – 19x2 + 16x – 4 = (x – 2)(6x2 – 7x + 2) 6x3 – 19x2 + 16x – 4 = (x – 2)(2x – 1)(3x – 2) Zeros: x = 2 x = ½ x = ⅔ Can check zeros on calculator Rules of Long Division If the divisor goes into the equation evenly then it is a factor and a zero. If the quotient has a remainder then it is not a factor. The proper form of writing the remainder is adding it to the quotient and over the divisor. Division Algorithm Also written as: Improper F(x) = q(x) + r(x) d(x) d(x) Proper F(x)/d(x) is improper because f(x) ≥ d(x). R(x)/d(x) is proper because r(x) ≤ d(x). Using Division Algorithm you can write it like this: Division Algorithm x3 – 1 = x2 + x + 1 x–1 Example: Divide x3-1 by x-1 – Write in descending powers – Insert zeros where there are missing power x2 + x + 1 x – 1 √(x3 + 0x2 + 0x – 1) Because it equals 0, x3 – x2 3 -1 is divisible by x-1 x x2 + 0x x2 – x x–1 x–1 0 Synthetic Division • Synthetic division is a shorthand, or shortcut, method of polynomial division in the special case of dividing by a linear factor. – Used when finding zeroes of polynomials. Example: Divide x2 + 5x + 6 by x – 1 *Rational roots test determines that +/- 1, 2, 3, and 6 are possible zeros. • Synthetic provides the same quotient but in a quicker fashion. Let’s divide: x2 + 5x + 6 by x – 1 • If r = 0, (x – k) is a factor. • If r = 0, (k, 0) is an x intercept of f. *k is a zero • The remainder r gives the value of f at x = k, if r = f(k) (Remainder Theorem) Remainder Theorem To evaluate polynomial function f(x) when x=k, divide f(x) by x-k – Remainder will equal f(k) Example 1: Evaluate f(x) = 3x3 + 8x2 + 5x – 7 for x = -2 So f(-2) = -9, r = -9 Example 2: Evaluate f(x) = x3 – x2 – 14x + 11 for x = 4 So f(4) = 3, r = 3 Repeated Division Multi-step synthetic division… Find all the zeros of the following polynomial function given (x – 2) and (x + 3) are factors… f (x) = 2x4 + 7x3 – 4x2 – 27x – 18. Solution: Using synthetic division with the factor (x – 2), you obtain the following. 0 remainder, so f(2) = 0 and (x – 2) is a factor. Repeated Division (Continued) Take the result of this division and perform synthetic division again using the factor (x + 3). 0 remainder, so f(-3) = 0 and (x +3 ) is a factor. Because the resulting quadratic expression factors as 2x2 + 5x + 3 = (2x + 3)(x + 1) the complete factorization of f (x) is f (x) = (x – 2)(x + 3)(2x + 3)(x + 1). Try #60 on page 141 Factor Theorem/Repeated Division Example 1: Show that (x – 2) and (x + 3) are factors and find all the zeros of f(x) = 2x4 + 7x3 – 4x2 – 27x – 18 x = 2, -3, -3/2, -1 Example 2: Show that (x + 2) and (x – 1) are factors and find all the zeros of f(x) = 2x3 + x2 – 5x + 2 x = ½, -2, 1 • Graph should confirm zeros Homework Page 140 #’s 5 – 35 (5’s), 47, 51, 55, 59, 61, 69, 73