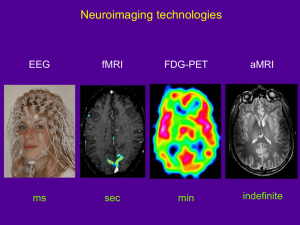
MRI
advertisement

MRI Phillip W Patton, Ph.D. RAPHEX General Question 2001 D43: In MRI, the RF frequency is dependent on the: A. Diameter of the body part being imaged. B. Magnetic field strength. C. Pulse Sequence. D. RF coil. E. Relaxation time. RAPHEX Answer to 2001 Question D43 B. The frequency used in MRI depends on the product of the magnetic field strength and the gyromagnetic ratio of the element being imaged. Since most MRI is of hydrogen atoms, the frequency depends only on the magnetic field strength. RAPHEX General Question 2001 D46: Gradient fields in MRI are principally used to: A. Maintain a uniform magnetic field in the field of view. B. Eliminate perturbations in the magnetic field due to site location. C. Shorten T1 to reduce scan time. D. Provide spatial localization. E. Measure the spin coupling. RAPHEX Answer to 2001 Question D46 D. Gradient fields are used to modify the magnetic field so that resonance will be slightly different at different points in the volume of interest. It is then possible to localize these points. RAPHEX General Question 2002 D51:A higher intensity MRI signal is produced by: A. B. C. D. Long T1, long T2. Long T1, short T2. Short T1, long T2. Short T1, short T2. RAPHEX Answer to 2002 Question D51 C. The MRI signal strength depends on the value of the magnetization vector along the constant field (z) axis, which is then tipped into the x-y plane to produce the MRI signal. A short T1 implies a rapid return of the magnetization to the z axis following excitation by the RF field. A long T2 implies a long dephasing time for the individual nuclei involved in producing the magnetization. Both these effects will lead to a large value of magnetization and a large MRI signal. RAPHEX General Question 2003 D53:For hydrogen imaging in a 1.0 T MRI unit, the frequency of the RF signal is about ________ . A. B. C. D. E. 40 Hz 40 kHz 40 MHz 400 MHz 4 GHz RAPHEX Answer to 2003 Question D53 C. The frequency for hydrogen is 42 MHz x magnetic field strength in tesla. Raphex 2001 Diagnostic Questions D43. In MRI, the RF frequency is dependent on the: A. Diameter of the body part being imaged B. Magnetic field strength C. Pulse sequence D. Relaxation time E. RF coil RAPHEX Answer to 2001 Question D43 B. The frequency used in MRI depends on the product of the magnetic field strength and the gyromagnetic ratio of the element being imaged. Since MRI is mainly of hydrogen atoms, the frequency depends only on the magnetic field strength. Raphex 2001 Diagnostic Questions D46. Gradient fields in MRI are principally used to: A. Eliminate perturbations in the magnetic field due to site location B. Maintain a uniform magnetic field in the field of view C. Measure the spin coupling D. Provide spatial localization E. Shorten T1 to reduce scan time RAPHEX Answer to 2001 Question D46 D. Gradient fields are used to modify the magnetic field so that resonance will be slightly different at different points in the volume of interest. Raphex 2000 Diagnostic Questions D48. In MRI images, motion during the scans results in ghost images which appear in the ______ direction. A. Amplitude B. Frequency encoding C. Phase encoding D. Relaxation E. Slice thickness RAPHEX Answer to 2000 Question D48 B. Motion usually appears as a series of ghost images of reduced intensity displaced in phase encoded direction. Raphex 2001 Diagnostic Questions D50. Which of the following does NOT generally affect the total exam time of an MRI study? A. # of acquisitions B. # of frequency encoding steps C. # of phase encoding steps D. # of pulse sequences in the study E. TR RAPHEX Answer to 2001 Question D50 A. frequency encoding steps are determined only by the resolution setting of the ADC. Raphex 2003 Diagnostic Questions D54. In MRI the signal-to-noise ratio can be increased by all of the following except: A. Switching from a volume to a surface coil B. Increasing the number of acquisitions C. Increasing the static magnetic field strength D. Decreasing the slice thickness E. Increasing TR RAPHEX Answer to 2003 Question D54 D. Raphex 2001 Diagnostic Questions D45. Superconducting magnets, compared to resistive magnets: A. Are less expensive B. Are more easily turned off C. Do not require liquid helium D. Have higher field strength RAPHEX Answer to 2001 Question D45 D. Superconducting magnets have field strengths of 0.3 – 10 T, while resistive magnets have strengths below 0.2 T. Raphex 2003 Diagnostic Questions D57-D59. Match the following MRI terms. (Answers may be used more than once.) A. Gradient fields B. RF C. Shim coils D. T1 E. T2 D57. Used to adjust magnetic field uniformity D58. Used to localize MR signal D59. Used to tip the net magnetization of spins Raphex 2003 Diagnostic Answers D57-D59. Match the following MRI terms. (Answers may be used more than once.) A. Gradient fields B. RF C. Shim coils D. T1 E. T2 D57. Used to adjust magnetic field uniformity D58. Used to localize MR signal D59. Used to tip the net magnetization of spins C A B Raphex 2000 Diagnostic Questions D49. Patients who have MRI scans should be screened to eliminate those who have: A. Internal steel fragments B. Metallic prostheses C. Pacemakers D. Surgical clips E. All of the above RAPHEX Answer to 2000 Question D49 E. Pacemakers can be affected an cause the pulse rate to change dramatically. Some surgical clips are magnetic and can move causing bleeding. Metallic prostheses can heat due to the RF pulses distorting the images. Steel workers with small fragments in their eyes have lost vision during an MRI scan. Raphex 2002 Diagnostic Questions D57. All of the following are MRI artifacts except: A. Chemical shift B. Ring C. Susceptibility D. Wrap-around E. Zipper RAPHEX Answer to 2002 Question D57 B. Bounce point artifact refers to a zero signal that can occur with certain inversion recovery pulse sequences. Chemical shift is a displacement difference between lipids and water. Zipper is a series of “dropouts” due to RF problems. Wrap-around represents aliasing due to the FOV being smaller than the object size.