Capacitors - Kelso High School
advertisement

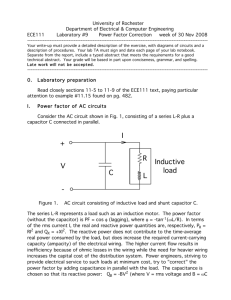
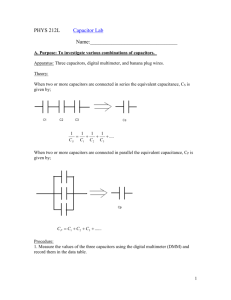
Capacitors - + Circuit symbol Experiment: To find how the charge on a capacitor varies with potential difference across it. Large capacitance Charge, Q (C) Small capacitance Potential difference across capacitor (V) Charge is directly proportional to potential difference. Q = constant x V Q = CV where C is the capacitance of the capacitor C = Q ÷ V or the gradient of the graph C=Q 1 farad (F) equals 1 coulomb (C) per volt (V) V Careful as C is for coulombs and capacitance 1 Farad is a very large unit so smaller units are often used. µF micro farad x10 -6 nF nano farad x10 -9 pF Pico farad x10 -12 Charge (C) Potential difference across capacitor (V) Energy stored in the capacitor equals the are under the QV graph = ½QV As E = ½ QV and Q = CV show that:E = ½CV2 and E = ½ Q2 C Tutorial Questions p67 Qu 7 to 14 How a capacitor charges and discharges click here V V Large capacitance Max V is supply voltage Large resistance t t Current /A Max I Current /A Max I Large capacitance Max I 60 Time / s Max I = V ÷ R Large resistance 60 Time / Charging and discharging a capacitor A capacitor – Current and and A.C. Current frequency Current is directly proportional to frequency A resistor – Current and and A.C. Current frequency Current is not dependant on frequency Uses of a capacitor 1. This capacitor passes AC signals but blocks DC signals. Used between the stages of an audio system to pass on the audio signal (AC) without any steady voltage (DC) which may be present. 2. This capacitor blocks AC and lets DC through. Used in audio systems to remove high frequency hiss. 3. Camera flash Neon bulb 4. To smooth a voltage which rectifies (changes) AC to DC Tutorial Questions 15 to 23 and SAQs to page28


![Sample_hold[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005360237_1-66a09447be9ffd6ace4f3f67c2fef5c7-300x300.png)