Torque
advertisement

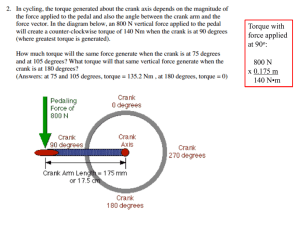
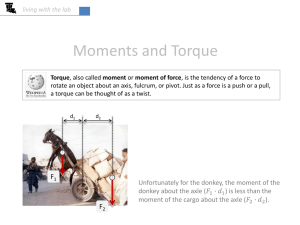
Torque Torque is defined as the tendency to produce a change in rotational motion. Torque is a twist or turn that tends to produce rotation. * * * Applications are found in many common tools around the home or industry where it is necessary to turn, tighten or loosen devices. What makes something rotate in the first place? TORQUE How do I apply a force to make the rod rotate about the axis? Not just anywhere! AXIS TORQUE • To make an object rotate, a force must be applied in the right place. • the combination of force and the distance from the axis to the point of application (L) is called TORQUE. lever arm, L Axis Force, F Torque = force times lever arm Torque = F L Torque example F L What is the torque on a bolt applied with a wrench that has a lever arm of 30 cm with a force of 30 N? Torque = F L = 30 N 0.30 m =9Nm For the same force, you get more torque with a bigger wrench the job is easier! Units for Torque Torque is proportional to the magnitude of F and to the distance L from the axis. Thus, a tentative formula might be: t = FL Units: Nm or lbft t = (40 N)(0.60 m) = 24.0 Nm, t = 24.0 Nm, 60 cm 40 N Direction of Torque Torque is a vector quantity that has direction as well as magnitude. Turning the handle of a screwdriver clockwise (negative) and then counterclockwise (positive) will advance the screw first inward and then outward. Sign Convention for Torque By convention, counterclockwise torques are positive and clockwise torques are negative. Positive torque: Counter-clockwise, out of page cw ccw Negative torque: clockwise, into page Line of Action of a Force The line of action of a force is an imaginary line of indefinite length drawn along the direction of the force. F1 F2 Line of action F3 The Moment Arm The lever arm of a force is the perpendicular distance from the line of action of a force to the axis of rotation. F1 F2 L L L F3 Calculating Torque • Read problem and draw a rough figure. • Extend line of action of the force. • Draw and label Lever arm. • Calculate the Lever arm if necessary. • Apply definition of torque: t = FL Torque = force x Lever arm Torque • If we know the angle between F and r, we can calculate torque! t = F L – r is the total length – F is force L = r sin t = r sin F Hinge (rotates) r Direction of rotation L – is angle between F and r • The SI unit of torque is the Nm. F Extend the line of action Example 1: An 80-N force acts at the end of a 12-cm wrench as shown. Find the torque. L • Extend line of action, draw, calculate L t = (80 N)(.12m sin 60o) = 8.31 N m Net Torque An object is in “Equilibrium” when: 1. There is no net force acting on the object 2. There is no net Torque In other words, the object is NOT experiencing linear acceleration or rotational acceleration. v a 0 t 0 t What mass is needed for the levers to be in equilibrium? Weights are attached to 8 meter long levers at rest. Determine the unknown weights below ?? 20 N ?? 20 N 20 N ?? What mass is needed for the levers to be in equilibrium? Upward force from the fulcrum produces no torque (since r = 0) r1 = 4 m r2 = 4 m 0 = -F2r2 + F1r1 0 = -(F2)(4)+ (20)(4) F2 = 20 N … same as F1 F1 = 20 N F2 =?? What mass is needed for the levers to be in equilibrium? r1 = 4 m r2 = 2 m 0 = -F2r2 + F1r1 0 = -(F2)(2) + (20)(4) F1 = 20 N F2 = 40 N F2 =?? (force at the fulcrum is not shown) More interesting problems (the pivot is not at the center of mass) Masses are attached to an 8 meter long lever at rest. The lever has a mass of 10 kg. Determine the unknown weight below. CM 20 N ?? More interesting problems (the pivot is not at the center of mass) Trick: gravity applies a torque “equivalent to” (the weight of the lever)(Rcm) tcm =(mg)(rcm) = (100 N)(2 m) = 200 Nm CM ?? 20 N Weight of lever Masses are attached to an 8 meter long lever at rest. The lever has a mass of 10 kg. Masses are attached to an 8 meter long lever at rest. The lever has a mass of 10 kg. Determine the unknown weight below. CM R1 = 6 m Rcm = 2 m R2 = 2 m 0 = -F2r2 + F1r1 + FcmRcm 0 = -(F2)(2) + (20)(6)+(100)(2) Fcm = 100 N F2 = 160 N F1 = 20 N F2 = ?? Diving board A 8 meter long diving board with a mass of 40 kg. a. Determine the downward force of the bolt. bolt tcm = (392 N) 2 m = 784 Nm F1 r1 = F2 r2 + tcm The Pivot point is not at the center of mass Diving board A 8 meter long diving board with a mass of 40 kg. a. Determine the downward force of the bolt. (Balance Torques) bolt R1 = 2 Fbolt = ? N F1 r1 = tcm = 784 Nm R =2 cm Fcm = 392 N F1 = 784Nm = 392 N 2m Diving board A 4 meter long diving board with a mass of 40 kg. b. Determine the upward force applied by the fulcrum. (Balance Forces) F = 784 N bolt Fbolt = 392 N Fcm = 392 N The total upward force has to equal the total downward for the object to be stable. Remember: An object is in “Equilibrium” when: a. There is no net Torque t 0 b. There is no net force acting on the object F 0 Torque with two supports FL Fcm Fr 1. Label all the forces 2. Choose a pivot point 3. Write the equation for net torques Torque with two supports F1 F2 Fcm Lcm cm L4 L1 T net = 0 -F1 L1 + Fcm L cm + F2 (0)=0 Pivot point What is the force exerted at each end? 0 = F1 (0) -755 (1.40) – 167 (2.75) + F2 (5.50M) F2 = 276 N F2 + F1 = 755 + 167N F1 = 646 N Pick a pivot pt. F1 F2