ppt - K.f.u.p.m. OCW
advertisement

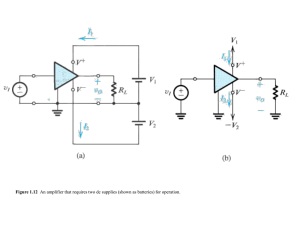
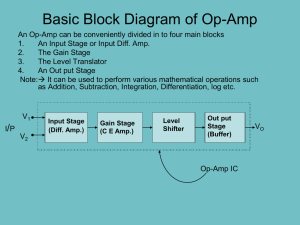
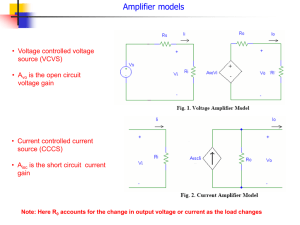
EE445:Industrial Electronics Outline Introduction Some application Comparators Integrators & Differentiators Summing Amplifier Digital-to-Analog (D/A) Converter Difference Amplifier Instrumentation Amplifiers Audio Amplifier Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) Op-amp – A high-gain dc amplifier that has high input impedance and low output impedance. The inverting (–) input and noninverting (+) input are signal inputs. The +V and –V inputs are supply voltage inputs. Differential Amplifier Differential amplifier – A circuit that amplifies the difference between two input voltages. The op-amp signal inputs are connected to a differential amplifier. The circuit amplifies the difference between the voltages at its inverting (-) and noninverting (+) inputs. Negative Feedback Negative feedback – A type of feedback in which the feedback signal is 180° out of phase with the input signal. Positive Feedback Positive feedback – A type of feedback in which the feedback signal is in phase with the input signal. Inverting Amplifier Operation The negative feedback path in the inverting amplifier: Reduces voltage gain (from its open-loop value). Increases bandwidth (relative to its open-loop value). Noninverting Amplifier Operation The negative feedback path in the noninverting amplifier: Reduces voltage gain (from its open-loop value). Increases bandwidth (relative to its open-loop value). Comparators Comparator – A circuit used to compare two voltages. Comparators are typically used in conjunction with digital circuits. A digital circuit is one designed to respond to alternating dc voltage levels. Comparator Operation Level Detector Level detector – Another name for a comparator used to compare an input voltage to a fixed dc reference voltage. Setting the Reference Level Vref R2 V R1 R2 Smoke Detector: A Comparator Application Integrators Integrator – A circuit whose output is proportional to the area of the input waveform. RC Integrator An ideal RC integrator would produce the triangular (ramp) waveform. The practical RC integrator produces the exponential waveform. Op-Amp Integrator The op-amp provides a constant-current source for the capacitor, causing it to charge at a linear rate. Differentiators Differentiator – A circuit whose output is proportional to the rate of change of its input signal. Summing Amplifiers Summing amplifier – An op-amp circuit that produces an output proportional to the sum of its input voltages. Vout V1 V2 V3 - R f R1 R2 R3 General-Class Equation General-class equation – An equation derived for a summing amplifier that is used to predict the circuit output for any combination of input voltages. Determine the Rf / R ratio for each branch. Represent each branch as the product of its resistance ratio and input voltage. Write the equation as the sum of these products. Summing Amplifier Analysis Rf R1 Rf R2 Rf R3 Rf R4 V1 V1 V2 0.2V2 V3 0.1V3 V4 0.05V4 - Vout V1 0.2V2 0.1V3 0.05V4 Digital-to-Analog (D/A) Converter Digital-to-analog (D/A) converter – A circuit that converts digital circuit outputs to equivalent analog voltages. - Vout V1 0.5V2 0.25V3 0.125V4 Averaging Amplifier Averaging amplifier – A summing amplifier that provides an output proportional to the average of the input voltages. - Vout V1 V2 V3 3 Difference Amplifier Difference amplifier – A summing amplifier that provides an output proportional to the difference between two input voltages. Also called a subtractor. Vout R3 (V2 - V1 ) R1 Instrumentation Amplifiers Instrumentation amplifier – A circuit used to amplify low-level signals in process control and measurement applications. ACL 2R 1 RG Audio Amplifier Audio amplifier – The final audio stage in communications receivers, used to drive the speakers. Thank You Any Q?