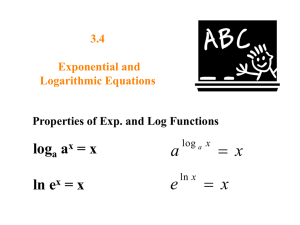
Chapter 4: More about
Relationships in 2 variables
Ms. Namad
Introduction
•
When 2 variable data shows a nonlinear
relationship, we must develop new techniques for
finding an appropriate model.
•
4.1 discusses how we can transform the data to
straighten a nonlinear pattern (hardest section).
•
4.2 will deal with relationships between
categorical variables
•
4.3 will tackle the issue of establishing causation
•
Scatterplot of brain weight
against body weight for 96
species of mammals:
4.1 Transforming to achieve
linearity
•
Scatterplot of brain weight
with Correlation
outliersbetween
removedbraindata:
weight and body
curved
weight is .86 but this
is misleading.
If we remove the elephant and
hippo, the correlation for the
other 95 species is r = .50.
After transformation:
•
We need linear data to do regression
•
Scatterplot and LSRL of the logarithm of brain
weight against the logarithm of body weight for 96
species of mammals
The effect is almost
magical - correlation is
.96.
Transforming (or reexpressing the data)
•
Changing the scale of measurement that was used
when the data was collected are LINEAR
TRANSFORMATIONS
•
As we know, these cannot straighten a curved
relationship. To deal with curved data, we
transform the data with other methods
•
Common transformations are logarithms or raising
to a positive/negative power
Example
•
Scatterplot of Atlantic Ocean rockfish weight versus length. When we cube the
length our data looks linear.
•
A least-squares regression on the transformed points (length3, weight) the
resulting equation is:
•
•
weight = 4.066 + .0147 x length3
If we superimpose our regression equation on our original data set, it
matches closely.
Transforming with Powers
(don’t memorize)
•
Facts about powers:
•
The graph of a power with exponent 1 (p = 1) is a straight line.
•
Powers greater than 1 give graphs that bend upward. The
sharpness of the bend increases as the power increases.
•
Powers less than 1 but greater than 0 give graphs that bend
downward.
•
Powers less than 0 give graphs that decrease as x increases.
Greater negative values of p result in graphs that decrease more
quickly.
•
The logarithm function corresponds to p = 0 (not the same as
raising to the 0 power which is just a horizontal line at y = 1)
Hierarchy of Power transformations at
work
Exponential Growth
•
.
Examples of Exponential
growth
•
Bacteria: The count of bacteria after x hours is 2x
•
The value of $24 invested for x years at 6% interest is
24 x 1.06x
•
Both are examples of the exponential growth model y =
abx for different constants a and b.
•
If an exponential model of the form y = abx describes the relationship between x and
y then we can use logarithms to transform the data to produce a linear relationship
(and vice versa- if a transformation of (x,y) data to (x, log y) straightens our data, we
know it’s exponential
The Logarithm Transformation
•
•
So how does this work? well if we have the equation y = abx and take the log of
both sides:
•
log y = log (abx)
•
= log a + log bx
•
= log a + log b (x)
Does this look familiar?!
Prediction in the Exponential
Growth Model
•
Regression is often used for prediction. In exponential growth the logarithms of
the responses rather than the actual responses follow a linear pattern so to do
prediction we need to “undo” the logarithm transformation to return to the
original units of measurement.
•
With the bacteria equation where y is our number of bacteria based on
number of years passed y, y = 2x to apply linear regression we take the log
of both sides and our regression equation is log y hat = log(2)(x) .
•
To predict the log of the number of bacteria after 15 years,
log of y hat = (log(2))(15) = 4.515
•
To find the ACTUAL predicted number of bacteria (y hat, not the log of
that number) we have to take the log inverse (10x) of 4.515
•
On calculator hit 2nd log, then type 10^x (4.515) and you get 32, 768!
•
*note- when the explanatory variable is years, transform the data to
“years since” so that the values are smaller and don’t create problems
when you perform the inverse transformation.
Calculator Example
Depth
(meters)
•
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Light
Intensity
4.5
Some college students collected data on the intensity of light at various depths in a lake:
(lumens)
168
120.4 86.31 61.87 44.34 31.78 22.78
2
•
Make a scatter plot, describe the form
•
To achieve linearity take the natural log (ln) of light intensity (define L3 as ln(L2) )
•
Calculate the regression equation on your transformed data (so x is your depth and y is the ln of
light intensity): stat-calc-8 LinReg (a + bx) L1, L3
•
ln(y hat) = 6.789 -.333(x)
•
The intercept provides an estimate for the average value of the natural log of the light
intensity at the surface of the lake (depth 0 meters) while the slope indicates that the natural
log of light intensity decreases on average by .3330 lumens for each one meter increase in
depth.
•
Construct and interpret a residual plot (x list is L3, Y list is RESID). Plot shows our model is
appropriate and r is now strong so this was a good way to straighten our data.
•
Perform the inverse transformation to express light intensity as an
exponential function of depth in the lake (ln inverse is e^x on your
calculator..2nd ln):
•
y hat = (e^(6.789)) (e^(-.333x) )
•
•
* To undo an ln or a log transformation: y = ea+bx or y = 10a+bx
Or, to
or, to see it in the more familiar exponential form, this is the same
as yhat = (e^a)(e^b)^x NOTE: Log or Ln can be used interchangeably
•
Construct a scatterplot of the original data with this model
superimposed (plot it in y = and go to your original statplot). Is your
exponential function a satisfactory model for the data?
•
Use your model to predict the light intensity at a depth of 22 meters.
•
The actual reading at that depth was .58 lumens.
Power Law Models
•
Geometry tells us to expect area to go up with the square of a
dimension such as diameter:
•
Ex: area of circle
square of the radius!
changes with the
x
r ( )
2
•
2
x
2
x
2
2
This is a Power Law Model
of4 the4 form
•
y = axp (different from exponential Y = abx)
•
When you take the log of both sides to achieve linearity
( log y = log a + p log x) you see that power p is the slope
of the straight line so the slope is a good estimate of the p
in the underlying power model. The greater the scatter of
the points in the scatterplot about the fitted line, the
smaller our confidence in the accuracy of this estimate
•
If taking the logs of both variables produces a linear
scatterplot, a power law is a reasonable model for the
Prediction in Power Law
Models
•
If transforming your data with (logx, logy)
straightens it, then you are working with a Power
Law model instead of an exponential one
(remember our transformation for exponential
functions was (x, logy).
•
Get your a and b for regression line of transformed
data on calculator
•
Undo your ln or log transformations to get your
regression equation for the original data:
•
yhat = 10^a (x)^b
Summary: Exponential vs.
Power
•
If the relationship is exponential then the plot of the log (x) versus y
should be roughly linear. If the relationship between these variables
follows a power model, then a plot of log (x) vs. log (y) should be
fairly linear.
•
In an exponential model you are transforming the response variable.
In a power model you are transforming both.
•
Our eyes are a bad judge of curves so we need to do both
transformations, make a scatter plot of each, and compare the
residual plot and r values of each to see which did a better job of
linearizing the data.
•
We can fit exponential growth and power models to data by finding
the least-squares regression line for the transformed data, then
doing the inverse transformation
Summary of what you need to
know
•
•
When data doesn’t look straight, try both transformations: (x,y) to (x, logy) or (x,
lny) and (logx, logy) or (lnx, lny)- log and natural log are both fine!
Check which transformation did a better job straightening:
•
Make a scatterplot of each transformation. Do LinReg a+bx to check your r
for each. The stronger the r, the better.
•
Also do a residual plot for each transformation to see which better fits the
data (for exponential trial: L1, RESID. For Power Law trial: L3, RESID)
•
•
If your first transformation was better than it’s an underlying exponential
function fitting your data. If the second transformation was better than it’s a
power model.
Find the regression equation for your original untransformed data:
•
If it was exponential, yhat = (10^a)(10^b)^x
Relationships between
categorical variables
4.2
•
Categorical
variables
and
Some variables are categorical by nature (sex,
race, marginal
occupation), others
are created by grouping
distributions
values of a quantitative variable into classes.
•
Age Group Female
Male
Total
15-17yrs
89
61
150
18-24
5668
4697
10,365
25-34
1,904
1,589
3,494
35 or older
1,660
970
2,630
The distributions of sex alone and age alone are
Total
9,321
7,317
16,639
called marginal distributions because they appear
at the bottom and right margins of the two-way
table.
Describing Relationships
•
Since counts are often hard to compare, we take
percents.
•
Ex: women make up 54.7% of the traditional
college age group, but they make up 63.1% of
students 35 and older. Women are more likely
than men to return to college after working for a
number of years.
•
When we compare the % of women in two age
groups we are comparing 2 conditional
distributions
Simpsons Paradox
•
Transportation of victims by helicopter, we see that
32% died compared with only 24% of the others.
This seems discouraging. Heli
Road
Victim died
64
260
Victim
Survived
136
840
Total
200
1100
•
The explanation is that the helicopter is sent mostly to
serious accidents so that the victims transported by
helicopter are more often seriously injured and likely to die
with or without helicopter evacuation. Here is the same
data broken down by seriousness of accident:
Lurking variable?
Seriouss
Heli
•
nonserious
Road
Heli
Road
60 accidents,
16 84% 200
If youDied
compare48
less serious
survived by heli
vs. 80%
by road.
Survived
52
40
84
800
Total
100
100
100
100
Establishing Causation
4.3
Beware the post-hoc fallacy
“Post hoc, ergo propter hoc.”
To avoid falling for the post-hoc
fallacy, assuming that an observed
correlation is due to causation, you
must put any statement of
relationship through sharp
inspection.
Causation can not be established
“after the fact.” It can only be
established through well-designed
experiments. {see Ch 5}
Explaining Association
Strong Associations can generally be explained by
one of three relationships.
Causation:
x causes y
Common Response:
x and y are reacting to
a lurking variable z
Confounding:
x may cause y, but y may instead be
caused by a confounding variable z
Causation
Causation is not easily established.
The best evidence for causation comes from
experiments that change x while holding all other
factors fixed.
Even when direct causation is present, it is
rarely a complete explanation of an association
between two variables.
Even well established causal relations may not
generalize to other settings.
Common Response
“Beware the Lurking Variable”
The observed association between two variables
may be due to a third variable.
Both x and y may be changing in response to
changes in z.
Consider the fact that students who are smart
and who have learned a lot tend to have both
high SAT scores and high colelge grades. The
positive correlation is explained by this common
response to students’ ability and knowledge.
Confounding
Two variables are confounded when their effects on
a response variable cannot be distinguished from
each other.
Confounding prevents us from drawing conclusions
about causation.
We can help reduce the chances of confounding
by designing a well-controlled experiment.
Confounding Example
•
Mothers with high BMI have a strong correlation with
daughters with high BMI. Gene inheritance no doubt
explains part of the association between BMI of daughters
and their mothers, but can we use r or r squared to say how
much inheritance contributes to the daugthers’ BMI’s? No!
•
Mothers who are overweight also set an example of little
exercise, poor eating habits, and lots of television so their
daughters pick up these habits to some extent, so the
influence of heredity is mixed up with influences from the
girls’ environment.
•
The mixing of influences is what we call confounding.
Examples
4.41: There is a high positive correlation: nations with
many TV sets have higher life expectancies. Could we
lengthen the life of people in Rwanda by shipping them
TVs?
4.42: People who use artificial sweeteners in place of
sugar tend to be heavier than people who use sugar.
Does artificial sweetener use cause weight gain?
4.43: Women who work in the production of computer
chips have abnormally high numbers of miscarriages.
The union claimed chemicals cause the miscarriages.
Another explanation may be the fact these workers
spend a lot of time on their feet.
cont.
4.44: People with two cars tend to live longer than
people who own only one car. Owning three cars is even
better, and so on. What might explain the association?
4.45: Children who watch many hours of TV get lower
grades on average than those who watch less TV. Why
does this fact not show that watching TV causes low
grades?
Cont.
4.46: Data show that married men (and men who are
divorced or widowed) earn more than men who have
never been married. If you want to make more money,
should you get married?
4.47: High school students who take the SAT, enroll in an
SAT coaching course, and take the SAT again raise their
mathematics score from an average of 521 to 561. Can
this increase be attributed entirely to taking the course?