direct variation
advertisement

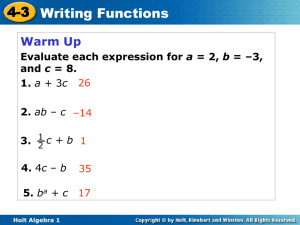
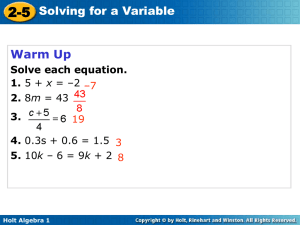
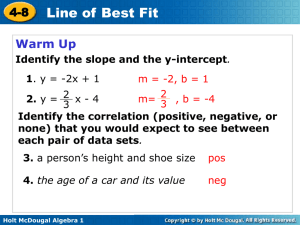
5-5 Direct Variation Learning Target Students will be able to: Identify, write, and graph direct variation. Holt Algebra 1 5-5 Direct Variation A recipe for paella calls for 1 cup of rice to make 5 servings. In other words, a chef needs 1 cup of rice for every 5 servings. y 5x or " y varies directly w ith x " Holt Algebra 1 5-5 Direct Variation A direct variation is a special type of linear relationship that can be written in the form y = kx, where k is a nonzero constant called the constant of variation. Holt Algebra 1 5-5 Direct Variation Tell whether each equation represents a direct variation. If so, identify the constant of variation. y = 3x k 3 3x + y = 8 3 x y 8 does not 3x 3x y 3x 8 represent direct variation. –4x + 3y = 0 4 x 4 x 3y 4x Holt Algebra 1 y 4 3 x k 4 3 5-5 Direct Variation What happens if you solve y = kx for k? x k x y x So, in a direct variation, the ratio the constant of variation. Holt Algebra 1 is equal to 5-5 Direct Variation Tell whether the relationship is a direct variation. Explain. T h e relatio n sh ip rep resen ts d irect variatio n . k y x Holt Algebra 1 3. 5-5 Direct Variation Tell whether each relationship is a direct variation. If it is, explain. T h e relatio n sh ip rep resen ts d irect variatio n . k y x Holt Algebra 1 4. 5-5 Direct Variation The value of y varies directly with x, and y = 3, when x = 9. Find y when x = 21. y x 3 9 y7 Holt Algebra 1 y 3 21 9 9 y 63 5-5 Direct Variation y 2x distance (mi) A group of people are tubing down a river at an average speed of 2 mi/h. Write a direct variation equation that gives the number of miles y that the people will float in x hours. Then graph. y 12 9 6 3 1 2 3 4 time (h) Holt Algebra 1 5 x 5-5 Direct Variation The perimeter y of a square varies directly with its side length x. Write a direct variation equation for this relationship. Then graph. P x 4x x P x x x Perimeter 20 15 10 5 x HW pp. TBD Holt Algebra 1 1 2 3 4 side length 5 x 5-5 Direct Variation Learning Targets Write a linear equation in slope-intercept form. Graph a line using slope-intercept form. Holt Algebra 1 5-5 Direct Variation Graph the line given the slope and y-intercept. y intercept = 4 R ISE RUN 2 y 5 2 5 Holt Algebra 1 x 5-5 Direct Variation Graph the line given the slope and y-intercept. slope = 4; y-intercept = R ISE RUN y 4 1 1 4 x Holt Algebra 1 5-5 Direct Variation Graph the line given the slope and y-intercept. slope = 2, y-intercept = –3 R ISE RUN y 2 1 1 2 Holt Algebra 1 x 5-5 Direct Variation Graph the line given the slope and y-intercept. slope = R ISE RUN , y-intercept = 1 y 2 3 2 3 Holt Algebra 1 x 5-5 Direct Variation Write the equation that describes the line in slope-intercept form. slope = ; y-intercept = 4 y mx b y 1 4 Holt Algebra 1 x4 5-5 Direct Variation Write the equation that describes the line in slope-intercept form. slope = –9; y-intercept = y mx b y 9 x 5 4 Holt Algebra 1 5-5 Direct Variation Write the equation that describes the line in slope-intercept form. slope = 2; (3, 4) is on the line y mx b 4 2 3 b 46b 6 6 2 b y 2x 2 Holt Algebra 1 5-5 Direct Variation Graph the line described by the equation. y = 3x – 1 R ISE RUN y 3 1 1 3 Holt Algebra 1 x 5-5 Direct Variation Graph the line described by the equation. 2y + 3x = 6 y 3x 3x 2 y 3 x 6 2 y 2 2 3 x3 2 R ISE RUN Holt Algebra 1 3 2 3 2 x 5-5 Direct Variation HW pp. 329/10-34 even & pp. 338-340/13-29,31 Graph the line described by the equation. y = –4 y y mx b y 0x 4 x Holt Algebra 1