Heat and Temperature
advertisement

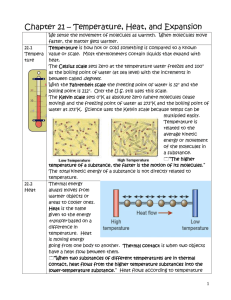
Heat and Temperature Temperature The measure of the average kinetic energy of all of the particles within an object. Temperature and Energy All particles are moving and have kinetic energy. We can not measure the KE of each molecule, so we take an average of each one. Taking temperature is finding the average KE of molecules. Feeling hot or cold is a rough estimate. It is subjective. Thermometer A device that measures temperature Most thermometers rely on the expansion of either fluids or metal to work. Electric thermometers rely on a change in current. Temperature Scales Image/Text/Data from the University of Illinois WW2010 Project Celsius-Fahrenheit Celsius – Fahrenheit Conversion Equation Fahrenheit temperature = (9/5 X Celsius temperature) + 32.0 TF = 9/5t + 32.0 Fahrenheit-Celsius Fahrenheit – Celsius Conversion Equation Celsius temperature = 5/9 (Fahrenheit temperature – 32.0) T = 5/9(TF – 32.0) Kelvin Based on Absolute Zero (theoretical) The temperature at which an object’s energy is minimal Celsius – Kelvin Conversion Equation Kelvin temperature = Celsius temperature + 273 T = t + 273 Relating Temperature to Energy Transfer as Heat You feel hot and cold because of transfer of energy. Molecules must come into contact with one another. Hot = absorbing energy from object Cold = releasing energy from object Heat The transfer of energy from the particles of one object to those of another object due to a temperature difference between the two objects Thermal Energy Actions that Increase Thermal Energy Raise the temperature of the object Explanation Thermal Energy Actions that Increase Thermal Energy Explanation Raise the temperature of the Increases the kinetic object energy of the atoms or molecules Thermal Energy Actions that Increase Thermal Energy Raise the temperature of the object Pull atoms or molecules that attract one another farther apart Explanation Increases the kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules Thermal Energy Actions that Increase Thermal Energy Raise the temperature of the object Pull atoms or molecules that attract one another farther apart Explanation Increases the kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules Increases the potential energy of the atoms or molecules Thermal Energy Actions that Increase Thermal Energy Raise the temperature of the object Pull atoms or molecules that attract one another farther apart Add mass to the object, without changing its temperature Explanation Increases the kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules Increases the potential energy of the atoms or molecules Thermal Energy Actions that Increase Thermal Energy Raise the temperature of the object Pull atoms or molecules that attract one another farther apart Add mass to the object, without changing its temperature Explanation Increases the kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules Increases the potential energy of the atoms or molecules More molecules at the same level of energy means more total energy in the object. Thermal Energy Equation Q = m ΔT C Q = change in thermal energy (J) m = mass (kg) ΔT = change in temperature (˚C) C = specific heat (J/kg ˚C) Problem Plug and Chug Q = 0.5 kg • 60 ˚C • 800 J/kg ˚C mass x change of temp x specific heat Q = 24,000 J