ch. 12 real3 - Physics-YISS
advertisement

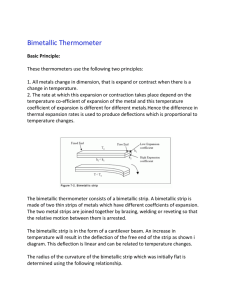
12.4 Linear Thermal Expansion Normal Solids • Ex. Glass jar too tight, hot water over lid. • Linear expansion – increase in any one dimension of a solid, linear is the expansion occurring along a line. • L – length • T – temp. • Length and temp. is directly proportional. Thermal Expansion • Change in length is proportional to both (initial) L and change in Temp. • Proportionality constant _____, is called the coefficient of linear expansion. Linear Thermal Expansion of a Solid Thermal Expansion • Coefficient of linear expansion ___ has the unit of _____. • Value of the ____ depends on the nature of the material. Coefficients of Thermal Expansion for Solids and Liquids Example 3: Buckling of a Sidewalk Expansion Joint Usefulness • Anti-scalding device: shuts off the flow of water when it becomes too hot, • Higher temp expands the actuator spring and pushes the plunger forward, shutting off the flow. Practice Problem 9. A steel section of the Alaskan pipeline had a length of 65 m and a temperature of 18 C when it was installed. What is its change in length when the temperature drops to a frigid -45 C? Thermal Stress • Change in temp. causes a force, stress on the material. • Can cause structural damage. Stress Example 4: The Stress on a Steel Beam • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JA5nTv EU3MA&feature=relmfu Practice Problem 90. A cylindrical brass rod (cross sectional area = 1.3 x 10^-5 m2) hangs vertically straight down from a ceiling. When an 860N block is hung from the lower end of the rod, the rod stretches. The rod is then cooled such that it contracts to its original length. By how many degrees must the temperature be lowered? Homework Problems: 10 11 13 14 24 The Bimetallic Strip • Made from two thin strips of metal that have different coefficients of linear expansion. • Brass • Steel • When the strip is heated, the brass, having the larger value of ____, expands more than the steel. • The strip bends into an arc, with the longer brass piece having a larger radius than the steel piece. • When the strip is cooled, the bimetallic strip bends in the opposite direction. Video of bimetallic strip • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WzX5tp C8Bs8 Bimetallic strips used in appliances • Automatic coffee maker turns off when the coffee is brewed to the selected strength. • Brewing cycle is on: electricity passes through the heating coil that heats the water. • Flows because the contact mounted on the bimetallic strip touches the contact mounted on the “strength” adjustment knob. • Strip gets hot enough to bend away, electricity stops because it no longer has a continuous path along which to flow. • Brewing cycle is shut off. Pg. 368 • http://home.howstuffworks.com/therm2.ht m Conceptual example 5: Do Holes Expand or contract when the temperature increases? Example 6: A Heated Engagement Ring 12.5 Volume Thermal Expansion • The volume of a normal material increases as the temperature increases. • Change in V is proportional to the change in T. Volume Thermal Expansion • ____ like _____ is _______. • Values for ____ depend on the nature of the material. • Values are larger for liquids than solids. Example 8: An Automobile Radiator • Some substances do not expand when heated. • When water is heated its volume decreases until the temperature reaches 4 C. Above 4 C water behaves normally, and its volume increases as the temp. increases. • The density (mass per unit volume) of water is greatest at 4 C. Freezing pond • When the temp drops the top layer of water becomes 4 C and denser than the warmer water below. • The denser water sinks and pushes up the deeper and warmer water, which in turn is chilled at the surface. • The process continues until the temp. of the entire pond reaches 4 C. • Further cooling of the surface water below 4 C makes it less dense than the deeper layers then the surface layer does not sink but stays on top. 12.6 Heat and Internal Energy • An object with a high temperature is said to be “hot.” • Heat – flows from a hotter object to a cooler object when the two are placed in contact. • From HOT to COLD. • Arrival or departure of heat prompts the brain to identify the coffee cup as being hot and the glass as being cold. Heat is a form of Energy Definition of Heat Internal Energy • Sum of the molecular kinetic energy, molecular potential energy, and other kinds of molecular energy. • Energy of a substance decreases when it is transferred to another object (HEAT). • Heat is the transfer of energy, and object doesn’t contain heat. 12.7 Heat and Temperature Change: Specific Heat Capacity • Solids and liquids • Heat = Q • Heat Q is directly proportional to the change in temperature and to the mass m. Metals have a lower c. why? Put one hand on the metal part of desk and another hand on the wooden part. Example 9: A Hot Jogger Example 10: Taking a Hot Shower Example 11: Heating a Swimming Pool Example 12: Measuring the Specific Heat Capacity H.W. pg. 389 25. 26. 28. 40. 42. 44.