Chapter6
advertisement

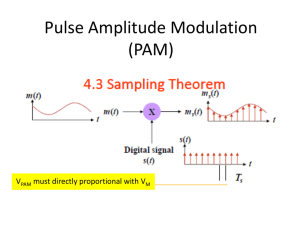
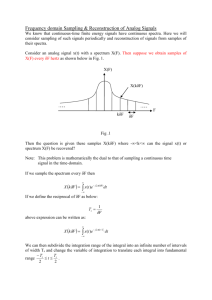
Chapter 6. Sampling and Pulse Modulation Husheng Li The University of Tennessee Chopper Sampling We introduce a switching function such that x_s(t)=x(t)s(t), where Nyquist Criterion The sampling rate should be at least twice the bandwidth of the signal, in order to fully reconstruct the signal. Otherwise, there will be aliasing effect. Ideal Sampling and Reconstruction We consider the ideal sampling function: The spectrum of the sampled signal is given by Reconstruction of Signal When the Nyquist criterion is satisfied, the signal can be reconstructed by using interpolation filter: Homework Deadline: Nov. 11, 2013 Sampling in Practice We need to consider three factors of sampling in practice: The sampled wave consists of pulses having finite amplitude and duration, rather than impulses. Practical reconstruction filters are not ideal filters. The message to be sampled are timelimited signals whose spectra are not and cannot be strictly bandlimited. Reconstruction Methods Aliasing The signal is filtered using a RC LPF antialiasing filter with bandwidth B>>W. The shaded area represents the aliased components that have spilled over the filter’s passband. Pulse-Amplitude Modulation If a message waveform is adequately described by periodic sample values, it can be transmitted using analog pulse modulation wherein the sample values modulate the amplitude of a pulse train. The process is called pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM). Flat-top Sampling and PAM More popular than the chopper circuit, we can use a sample-and-hold technique for PAM. Spectrum of Flat-top Sampling The spectrum of the flat-top sampling is the convolution of the ideal sampling spectrum and the spectrum of pulse: Aperture Effect The loss of high-frequency content is called aperture effect. The larger the pulse duration is, the larger the effect is. The aperture effect can be corrected in the signal reconstruction: Unipolar Flat-Top PAM We define the unipolar flat-top PAM as The resulting constant pulse rate f_s is particularly important for synchronization in time-division multiplexing. The spectrum of the unipolar PAM is obtained by replace X(f) with Pulse-Time Modulation The time parameters of a pulse train can also be modulated: PDM: pulse-duration modulation PPM: pulse-position modulation Generation of PDM or PPM Signal Reconstruction Properties of PDM/PPM PDM and PPM need very sharp rising time t_r. Then, the required bandwidth satisfies which could be much larger than PAM. The PDM and PPM have the potential for wideband noise reduction, since the information resides in the time location of the pulse edges, not the pulses themselves. Spectrum of PPM Using the distribution theory of impulses, we have PPM with nonuniform sampling is a combination of linear and exponential carrier modulation.