Footings and Foundations
advertisement
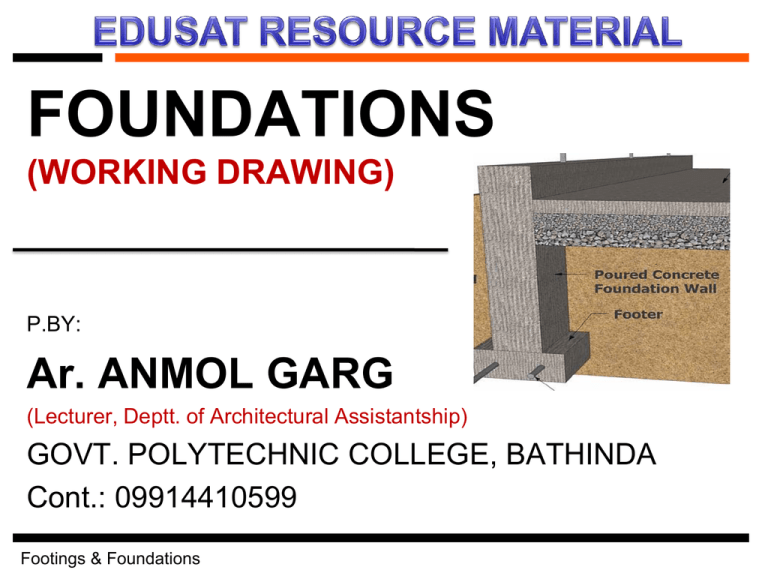
FOUNDATIONS (WORKING DRAWING) P.BY: Ar. ANMOL GARG (Lecturer, Deptt. of Architectural Assistantship) GOVT. POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE, BATHINDA Cont.: 09914410599 Footings & Foundations INTRODUCTION TO FOUNDATIONS Function of a foundation is to transfer the structural loads from a building safely into the ground. A larger and heavier building of masonry, steel, or concrete would require its foundations to go deeper into earth such that the soil or the rock on which it is founded is competent to carry its massive loads. Footings & Foundations Foundation Components Footing Footings & Foundations Foundation Components (to attach wood stud sill plate) (moves water away from building) (to keep water off of foundation wall) (separates slab from foundation wall) (to keep water off of slab) (moves water away from building) Footings & Foundations (to keep water off of slab & moisture barrier) Site Preparation •Remove trees and any debris •Remove top soil (4-6” below surface) Footings & Foundations Site Layout •Ensure lot lines are known & setbacks are complete •Layout building perimeter •Use batter boards •Establish building corners & building perimeter •Use surveying instruments Footings & Foundations Excavation •Excavate foundation along line created by batter boards •Excavate remainder of soil inside perimeter •Don’t excavate inside soil if slab on grade •If deep foundation, taper edges to prevent collapse •If soil unstable, or very deep - use shoring Footings & Foundations Pour Footings •Construct formwork (if required) •Install reinforcement (rebar) for footings •(protrudes above footing to tie-into foundation wall) •Pour concrete footings •Smooth / finish surface Footings & Foundations Rules of Thumb •Footing shall be below frost line •Footing width usually 2x height •Typical size (24” wide x 12” tall) •Rebar is usually 3” from edge of concrete •Crawl spaces should have rigid insulation along the interior face of the foundation wall Footings & Foundations TYPES OF FOUNDATION Major Building Parts Superstructure Substructure Foundation Footings & Foundations TYPES OF FOUNDATION Two types foundations : Shallow and Deep – Depends on whether the load transfer is at deeper depths or shallower depths - Need for these two types (soil strength, ground water conditions, foundation loads, construction methods and impact on adjacent property) Footings & Foundations TYPES OF FOUNDATION Shallow foundations (column footings without or with tie/grade beams, individual or combined wall footing, slab on grade, raft) - Deep foundations (caissons with or without sockets, end bearing or friction piles, pile groups), made of concrete (regular or site-cast) or steel or wood Footings & Foundations Shallow Foundations Requirements – Suitable soil bearing capacity – Undisturbed soil or engineered fill Basic types or configurations – Column footings – Wall or strip footings Footings & Foundations Combination Spread & Strip Footing Footings & Foundations Shallow Foundations Stepped strip footings Grade Beams Footings & Foundations /// /// \\\ \\\ /// \\\ Shallow Foundations Mat foundation Floating (Mat) foundation Footings & Foundations Deep Foundations - Purpose Transfer building loads deep into the earth Basic types – Drilled (& poured) – Driven Footings & Foundations Pile material Steel; H- piles, Steel pipe Concrete; Site cast or Precast Wood; Timber Composite Footings & Foundations Driven Piles Footings & Foundations Precast Concrete Plies Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations Footings & Foundations P.BY: Ar. ANMOL GARG (Lecturer, Deptt. of Architectural Assistantship) GOVT. POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE, BATHINDA Cont.: 09914410599 Footings & Foundations