conservation of Momentum and Collision Lecture Slides
advertisement

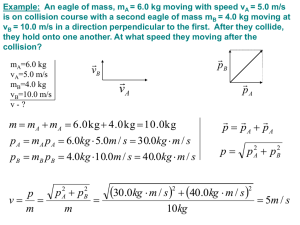
Conservation of Momentum and Collision Kimal Honour Djam ASFA A child jumps from a small boat to a dock. Why does she have to jump with more effort than she would need if she were jumping through an identical displacement, but from a boulder to a tree stump? A 5.0-kg object and a 10-kg object, both resting on a frictionless table, are connected by a massless compressed spring. The spring is released and the objects fly off in opposite directions. The 5.0-kg object has a velocity of 8.0 m/s to the left. What is the velocity of the 10-kg object? A 0.060-g handball is thrown straight toward a wall with a speed of 10 m/s. It rebounds straight backward at a speed of 8.0 m/s. (a) What impulse is exerted on the wall? (b) If the ball is in contact with the wall for 3.0 ms, what average force is exerted on the wall by the ball? (c) The rebounding ball is caught by a player who brings it to rest. In the process, her hand moves back 0.50 m. What is the impulse received by the player? (d) What average force was exerted on the player by the ball? A 2000-kg car traveling to the right at 30 m/s is chasing a second car of the same mass that is traveling in the same direction at 10 m/s. (a) If the two cars collide and stick together, what is their speed just after the collision? (b)What fraction of the initial kinetic energy of the cars is lost during this collision? Where does it go? A 5.0-kg object with a speed of 4.0 m/s collides head-on with a 10-kg object moving toward it with a speed of 3.0 m/s. The 10-kg object stops dead after the collision. (a) What is the post collision speed of the 5.0-kg object? (b)Is the collision elastic? A 2.0-kg block moving to the right with a speed of 5.0 m/s collides with a 3.0-kg block that is moving in the same direction at 2.0 m/s. After the collision, the 3.0-kg block moves to the right at 4.2 m/s. Find the velocity of the 2.0-kg block after the collision HOMEWORK • You kick a soccer ball whose mass is 0.43 kg. The ball leaves your foot with an initial speed of 25 m/s. (a) What is the magnitude of the impulse associated with the force of your foot on the ball? (b) If your foot is in contact with the ball for 8.0 ms, what is the magnitude of the average force exerted by your foot on the ball? • A 0.15-kg baseball traveling horizontally is hit by a bat and its direction is exactly reversed. Its velocity changes from +20 m/s to -20 m/s. (a) What is the magnitude of the impulse delivered by the bat to the ball? (b) If the baseball is in contact with the bat for 1.3 ms, what is the average force exerted by the bat on the ball? • A 3.0-kg block moving at 4.0 m/s has a head-on elastic collision with a stationary block of mass 2.0 kg. Use conservation of momentum and the fact that the relative speed of recession equals the relative speed of approach to find the velocity of each block after the collision. Check your answer by calculating the initial and final kinetic energies of each block.