CPF Project - Hot Stamping - ERC/NSM
advertisement

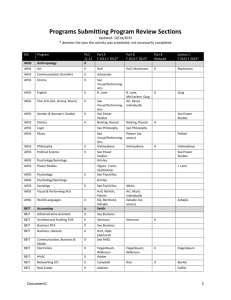
Center for Precision Forming (www.cpforming.org Taylan Altan, Director (e-mail: altan.1@osu.edu) A short Review March 2014 1 INTRODUCTION • The Ohio State University (OSU) has established the Industry/University Cooperative Research Center (I/UCRC) on Precision Forming (CPF) focusing on research needs of metal forming industry • Funding is provided member companies. by National Science Foundation (NSF) and • CPF (www.cpforming.org) benefits from research conducted at the Engineering Research Center for Net Shape Manufacturing (ERC/NSM – www.ercnsm.org) 2 OBJECTIVES • Improve existing metal forming processes/products and develop new innovative processes, tooling and equipment • Conduct projects in close collaboration with industry and transfer the results to the member companies • Train and educate engineers in the fundamentals and practice of metal forming science and technology 3 CPF is supported by NSF and member companies, interested in metal forming 4 CURRENT PROJECTS Project CPF-1.1 – Warm Forming of Al Alloys Project CPF-1.4 – Forming of AHSS in a Servo Press – Die Design Project CPF-2.1 – Material Properties and Formability Project CPF-2.2 – Forming Al in a Servo Press Project CPF 3.3 – Friction/Lubrication/Wear Project CPF-5.1 – Bending and Springback in Forming of AHSS and Copper Alloys Project CPF-5.2 – Blanking / Piercing Project CPF-5.2 A – Hole Flanging and Edge Cracking Project CPF-5.5 - Hot Stamping Project CPF 5.6 Practical Method for Predicting Fracture Using FE Simulation 5 CPF-1.1 - Warm Forming of Al, Mg, Ti & SS in an Aida Servo Drive Press Insulation plate Die ring Heaters Sheet Punch Blank holder Water inlet Cushion pins AZ31B-O AA5754-O T(°C) RT 250 300 LDR 2.1 Velocity : 2.5-50mm/sec 2.5 2.9 Cup diameter: 40 mm T(°C) RT 275 275 LDR 2.6 3.2 6 CPF-1.4 - Forming of AHSS in a Servopress Forming of AHSS in Servo Press 980 MPa (145 ksi) 590 MPa (85 ksi) 440 MPa (65 ksi) 270 MPa (40 ksi) Can we use servo drive properties to improve formability and reduce springback in forming AHSS? 7 CPF-1.4 - Forming of AHSS Forming of AHSS in Servo Press Punch Blank holder Materials of interest: DP 600 DP 980 And others Die Bottom die set Die design (manufactured by Shiloh) for testing AHSS. Top die set 8 CPF-1.4 - Forming of AHSS in a Servopress Forming of AHSS in Servo Press 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Straight Bending Shrink Flanging Stretch Flanging U-Bending Curved U-Bending Deep Drawing 9 CPF-1.4 – Forming of AHSS in a Servopress CPF/Shiloh die set (for 300 ton servo-press) DIE R1 R4 R3 R5 R6 R2 Parameter Notation Value Concave side radius R1 601.6 mm Convex side radius R2 598.4 mm R3 51.6 mm R4 56.6 mm R5 61.6 mm R6 66.6 mm Cavity corner radii 10 CPF-1.4 – Forming of AHSS in a Servopress Example: Shrink and Stretch Flanging BLANK DIE 11 CPF-1.4 - Forming of AHSS in a Servopress Forming of AHSS in Servo Press Thinning (%) 9.0 5.8 2.7 -0.4 -3.5 -6.6 -9.7 -12.8 Min = Max = Max. Thinning ~ 9% -12.8 9.0 Deep drawn sample DP 600, t0 = 0.83 mm Draw depth = 50 mm 12 CPF-2.1 Material Characterization Viscous Pressure Bulge (VPB) Test Laser Sensor Downward motion clamps the sheet Continued downward motion forms the bulged sheet Test Sample Viscous Medium Pressure Transducer Stationary Punch Before Forming After Forming 13 CPF-2.1 Material Characterization – Flow Stress Viscous Pressure Bulge (VPB) Test True Stress (MPa) 1000 Uniform Strain from Tensile Test = 0.16 800 True Stress (ksi) 145 Tensile data with Power Law (σ=Kεn) 116 600 Useful strain 87 from Bulge Test = 0.49 400 58 200 Material, DP600, 1 mm 0 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 True Strain VP Bulge Test 29 Tensile Test 0.4 0.5 14 CPF-2.1 - Material Characterization – VPB Test Test sample Before bursting After bursting 15 CPF-2.1 - Material Characterization – VPB Test 16 CPF-2.1 - Determination of Sheet Formability Using VPB Test Graph shows dome height comparison for SS 304 sheet material from eight different batches/coils [10 samples per batch]. Dome height before burst (in) (mm) 1.6 40 (in) 1.6 Maximum bulge height before fracture 1.4 1.2 30 1.2 1 20 0.8 0.8 0.6 10 0.4 0.4 0.2 0 A B C D E F G H Coil/Heat/Supplier Batch / Coil / Heat / Supplier ID Highest formability G , Most consistent F Lower formability and inconsistent H 17 CPF-2.1 - Materials Tested with VPB Test at CPF (data available to CPF members) St 14 St 1403 AISI 1018 AKDQ 1050 DR 120 DDS BH 210 HSS DP500 DP 590 DP 600 Steels DP 780-CR DP 780-HY Bare DP 980 Y-type X Bare DP 780 T-Si type GA DP 780 T- AI Type GA DP 780 Y-type U GA DP 780 Y-type V DQS-270F GA-Phosphate coated DQS-270D GA-Phosphate coated DP 780 TRIP 780 DP 980 Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys AA 6111 AA 5754-O X626 -T4P AZ31B AZ31B-O Stainless Steels SS 201 SS 301 SS 304 SS 409 SS 410 (AMS 5504) SS 444 LDX 2101 18 CPF-2.1 - Material Characterization – Dome Test Dome Test (Frictionless) When the blank is well lubricated, it fails at the center of the dome. Necking / fracture moves with increased friction. 19 CPF-2.1 - Formability Stretch Bending DP780 Underbody structural part Challenge: This type of fracture cannot be predicted using conventional Forming Limit Curve (FLC). DP980 B-pillar inner 20 Ref: Shi and Chen 2007 CPF-2.2 - Forming of Al Alloys in a Servo Drive Press (AIDA) Die set built by Honda Thinning (%) 28.4 20.5 12.7 4.9 -2.9 -10.7 -18.5 -26.3 Min = Max = -26.3 28.4 Material draw-in Maximum thinning ~28% Draw depth = 155 mm 21 CPF-3.3 - Friction/Lubrication – Cup Draw Test Evaluation of Lubricants Performance evaluation criteria (cups drawn to same depth): i. Higher the Blank Holder Force (BHF) that can be applied without fracture in the drawn cup, better the lubrication condition ii. Smaller the flange perimeter, better the lubrication condition (lower coefficient of friction) 22 CPF-3.3 - Friction – Cup Draw Test Cup Draw Test Lubrication performance: Shorter Perimeter Higher BHF before fracture 23 CPF-3.3 - Friction / Tribology Temperatures in Cup Draw Test – DP 600 Contact area with die Challenges: 1) Higher contact pressure and higher temperature are detrimental for lubricants, 2) Temperature and pressure additives are needed 24 Ref: Kim et al 2009 CPF-3.3 - Friction / Lubrication Evaluation of Lubricants for Forming Al 5182-0 (1.5 mm) 25 CPF-3.3 - Forming of AHSS / Die Wear Die Wear in Forming of AHSS Die Insert Press Motion Die Insert r = 5 mm t0 = 0.77 mm Punch (Stationary) Press Motion r = 5 mm r = 20 mm Dp = 152.4 mm Ironing t ≈ 0.70 mm Currently with DP590 In future, Stainless Steel 26 CPF-5.1 – Bending and springback in Forming AHSS and Copper Alloys Schematic of 3 point bending tooling at OSU 27 CPF-5.2 - Blanking/Piercing of AHSS Blanking / Piercing Schematic of piercing Blanked edge (obtained from FE simulations) Roll over zone (Zr) Shear zone (Zr) Fracture zone (Zf) Burr zone (Zb) vp = punch velocity fb = blank holder force dp = punch diameter dd = die diameter rp = punch corner radius rd = die corner radius db = blank holder diameter t = sheet thickness Punch-die clearance (% of sheet thickness) = (dd-dp)/2t*100 28 CPF-5.2 - Blanking/Piercing of AHSS Reduction of strains at blanked surface 3 2.5 Single shear Conical with flat tip Effective strain 2 1.5 Flat Humped Conical 1 0.5 Conical with spherical tip Humped 0 0.6 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 3.6 Distance from the top surface of the sheet (mm) 29 CPF-5.2A – Hole Flanging/Edge Cracking Hole Expansion Test Schematic of hole expansion test Before and After Hole Expansion (conical punch) dd DIE rd dh θ dp Blank Holder fb Punch db vp vp=punch velocity fb=blankholder force θ=punch angle (conical) dd=diameter of the die db=diameter of blankholder rd=die radius dh=diameter of pierced hole in the blank dp=punch diameter (hemispherical) 30 CPF-5.5 - Hot Stamping Easier to Form 22MnB5 At ~950°C (1750ºF) Austenite 3-5 min.s in Furnace Less force and springback Mn-B alloyed steel (As delivered) Ferrite-Pearlite Quenched in the die >27°C/s (~49°F/s) Quenched Martensite 31 Ref: Grote 2009, Gutermuth 2011. CPF-5.5 - Hot Stamping FE Simulation of parts with uniform properties Colors other than gray: Thinning >20%. Part stamped at the participating company 32 CPF-5.5 - Hot Stamping FE Simulation of cooling channel analysis Nodal temperature - Membrane 230 200 171 142 112 83 54 25 1.3 mm roof rail die, After 10 stampings. 33 CPF-5.5 - Hot Stamping FE Simulation of cooling channel analysis After 10 stampings. 34 CPF-5.5 - Hot Stamping FE Simulation of parts with tailored properties Soft zone: 310 – 330 HV 920 – 1020 MPa (~135 – 150 ksi) Literature: [George 2011] , 400°C dies = 790-840 MPa [Feuser 2011], 450°C dies = ~850 MPa Hardened zone: 485 – 515 HV 1500 – 1590 MPa (~220 – 230 ksi) 35 Prediction of fracture/necking from strain or thickness variations (tensile data from Jim Dykeman-Honda HRA) 1400 0.6 1200 0.5 Major Strain (mm/mm) Stress (MPa) CPF–5.6 - New Project: Prediction of Fracture 1000 800 600 400 0.3 0.2 0.1 200 0 0.4 0 0 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 Strain (mm/mm) 0.1 0.12 0.14 0 50 100 Time (s) 150 200 36 Questions / Comments? For more information , please contact: Dr. Taylan Altan (altan.1@osu.edu), Ph-614-292-5063 Center for Precision Forming –CPF (www.cpforming.org) 339 Baker Systems,1971 Neil Ave, Columbus, OH-43210 Non-proprietary information can be found at web sites: www.cpforming.org www.ercnsm.org 37