Analyzing Randomized Control Trial: ITT vs. PP vs. AT Proceedings
advertisement

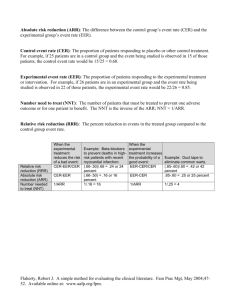
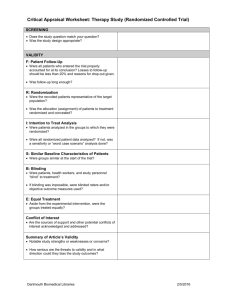
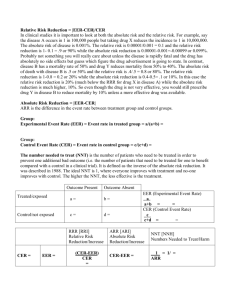
Analyzing Randomized Control Trial: ITT vs. PP vs. AT Proceedings from Journal club….. Vikash Basic Analysis of RCT: • To calculate: – Relative Risk (RR) – Relative Risk Ratio (RRR) – Attributable Risk (AR) – Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR) – Number Needed to treat (NNT) • For Time dependant analysis – Survival Analysis by Kaplan- Mier or by Cox Proportional Model. • Then, Apply test of Significance. • For Dichotomous Outcome: Disease Present • Disease Absent Total Experiment a al Group b a+b Control Group d C+d c RR = ID (Exposed)/ ID (Unexposed) = a/a +b / c /c +D • RRR = 1 – RR • ARR = ID (Unexposed) - ID (Exposed) • Attributable Risk = (OR – 1) PE / 1+ [ (OR-1) PE] x 100 • Where OR = Odds Ratio = ad / bc • Number Needed to treat (NNT) = 1/ARR TB No TB Total Cont. Isoniazid 40 160 200 Isoniazid 6 month 50 150 200 • RR = 0. 4 /0.5 = 0.8 • RRR = 0.2 • ARR = 0.2 – 0.25 = - 0.05 • NNT = 1/ARR = 20 Intention to treat Analysis • Also called As randomized or Method Effectiveness analysis. • Compare outcome according to the randomized group (Gold Standard). • Adherence to intervention not necessary. Advantages: • Randomization is maintained: – Treatment assignment is based on chance alone. – Randomization provides Theoretical foundation for Statistical test of significance. Disadvantages: – Doesn’t take into account Protocol violation. • Group may not be comparable at the end. – Not adhering to treatment or vice versa. – Eligibility for the trial was incorrect. – Loss to follow up. • Estimates of non – complied in the efficacy dilutes difference between groups. • Analysis may underestimate adverse effect. Why gold standard ? • Randomization is maintained • Difficulty in defining compliance. • Effect in complied group may be due to factor of compliance. Per Protocol Analysis: • • • • Analyze only those who fully complied to protocol. Doesn’t included cross- over in final analysis. Provides fair idea of efficacy for treatment. May be Biased (randomization compromised) As treated Analysis: • Subject analyzed according to treatment taken or not. (no relation with randomization). • Non compliant from treatment and vice versa analyzed accordingly. • AT is shown if ITT shows no effect ( why trial done). Randomize Intervention Group Control Group Got Treatment Did NOT get treatment Got Treatment Did NOT get treatment Interntionto-Treat YES YES NO NO Per protocol YES DROP DROP NO As Treated YES NO YES NO • Hypothetical Example: RCT to see the effect of Aspirin in incidence of Myocardial Re-infarction in patient with h/o MI. Re- infarct Aspirin 40 (5) Placebo 50 (4) No Reinfarct Total (adhere d to t/t) 200 240 (210) 190 240 (200) • ARR by ITT = 20.833% - 16.66% = 4.17% • ARR by PP = 23% - 16.66% = 6.34% • ARR by AT = 21.25% - 16.25% = 5% References: • Redmond C, Armitage P editors. Biostatics in Clinical Trials. 1st ed. Sussex. John Wiley & Sons ltd. 2001. p243- 6. • Haynes RB, Sacket DL, Guyat GH, Tugwell P. Clinical Epidemiology. 3rd ed. Baltimore. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.2006. p 95 & 116. • Fletcher RW, Fletcher SW. Clinical Epidemiology: the essential. 4th ed. Baltimore. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2005. p 136-9.