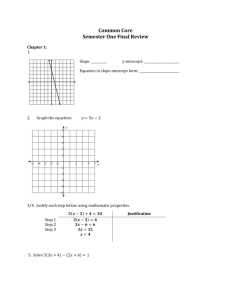
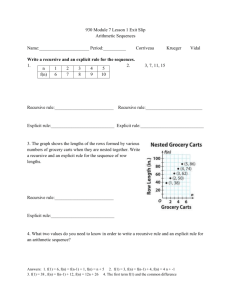
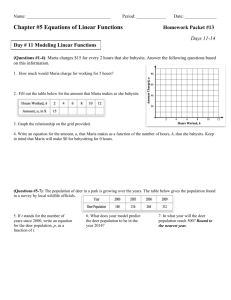
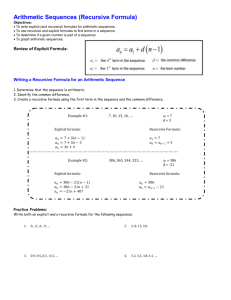
Linear Equations: Recursive, Explicit, y=mx+b Forms
advertisement

Overview of Chapter 3 • Slope • Y=mx+b • Line of best fit • Barbie Bungee • Point-slope equation • Systems of Equations Graphing Elimination Substitution Recursive Explicit Linear Equations 3.1 Goal • Given one form if a linear equation, convert it to one of the other forms. Remember when….? • What does the graph of an arithmetic sequence look like? • We know there is another way calculate linear equations other than knowing the previous term right? • Recursions are ONE type of equation. We will learn the other EQUIVALENT forms. Recursive • 𝑈𝑛 = 𝑈𝑛−1 + 𝑑 • Find the next term by looking at the previous Explicit • 𝑈𝑛 = 𝑎 ∙ 𝑛 + 𝑏 • b = Y-intercept. The initial value (𝑈𝑜 ) in the recursion. • a= Slope (d in the recursion) • Nice because you do not have to know the previous term to find the next. Linear • y=mx+b • m=slope • b=y-intercept • Linear uses x and y. So… You will be given one of the three types just discussed, and will be asked to write it in a different way. Example 1 • Given the recursion 𝑈0 = 2, 𝑈𝑛 = 𝑈𝑛−1 + 6 1. Find the explicit formula 2. Find 𝑈22 using the explicit 3. Find n such that 𝑈𝑛 = 86 Example 1: answers 1. 𝑈𝑛 = 6𝑛 + 2 slope initial value 2. 𝑈22 = 6 22 + 2 𝑈22 = 134 3. 86=6n+2 n=14 You try! • Given the recursion 𝑈0 = 5, 𝑈𝑛 = 𝑈𝑛−1 − 2 1. Find the explicit formula 2. Find 𝑈8 using the explicit 3. Find n such that 𝑈𝑛 = −35 Example 2 • You spend $2 a day on lunch and have $17 left after today. Write a recursive and explicit formula modeling this situation. So: Recursive: 𝑈1 = 17 𝑎𝑛𝑑 Explicit: 𝑈𝑛 = −2𝑛 + 17 𝑈𝑛 = 𝑈𝑛−1 − 2 Example 3 • Write an equation in the form y=a +bx of the line the passes through the points of an arithmetic sequence with 𝑈0 = 20 and a common difference of -5.7. • Answer: 𝑈0 = 𝑦 − 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡 = 𝑎 = 20 -5.7=slope=b y=20-5.7x Homework • 3.1 • Problems: 1,4,5