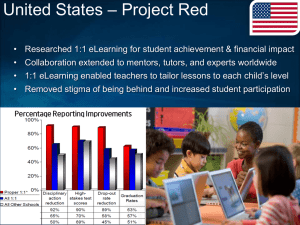
Performance Analysis: Intel Xeon Phi
Coprocessor 7120P in the Dell
PowerEdge R720 Server
This Dell technical white paper explains the performance gain and
power efficiency with Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor 7120P on Dell
PowerEdge R720 server.
Saeed Iqbal, Shawn Gao, and Kevin
Tubbs
High Performance Computing
Engineering
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
This document is for informational purposes only and may contain typographical errors and
technical inaccuracies. The content is provided as is, without express or implied warranties of any
kind.
© 2013 Dell Inc. All rights reserved. Dell and its affiliates cannot be responsible for errors or omissions
in typography or photography. Dell, the Dell logo, and PowerEdge are trademarks of Dell Inc. Intel and
Xeon are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries. Microsoft,
Windows, and Windows Server are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation
in the United States and/or other countries. Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this
document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products. Dell disclaims
proprietary interest in the marks and names of others.
June 2013 | Rev 1.0
ii
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
Contents
Executive Summary ................................................................................................. 5
Introduction .......................................................................................................... 6
The PowerEdge R720 ................................................................................................ 6
Easy to Extend, Easy to Configure .............................................................................. 7
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors ...................................................................................... 7
Why Use the PowerEdge R720 for Heterogeneous Computing?............................................... 7
Intel Xeon Processors ............................................................................................. 8
Why Use Bright Cluster Manager for Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor-Based HPC? ............................. 9
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor-Based HPC Features ............................................................. 9
Overview of the Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor 7120P ........................................................... 10
Test Cluster Configuration ........................................................................................ 11
Benchmarks.......................................................................................................... 12
Results ............................................................................................................... 12
Memory Bandwidth ............................................................................................... 12
High Performance Linpack (HPL) ............................................................................... 14
Summary and Performance/Watt Comparison with CPU only ............................................. 15
Conclusion ........................................................................................................... 16
References........................................................................................................... 16
Tables
Table 1.
Key Features of the Intel Xeon Phi coprocessor 7120P............................................ 10
Table 2.
Compute node configuration detail .................................................................. 11
Table 3.
Benchmarks details ..................................................................................... 12
Table 4.
Results of the performance comparison with CPUs ................................................ 15
Table 5.
Performance/watt comparison ....................................................................... 15
Figures
Figure 1.
The front and back view of PowerEdge R720 ........................................................ 6
Figure 2.
The PowerEdge R720 server ............................................................................ 8
Figure 3.
Host-to-Device (H2D) and Device-to-Host (D2H) BW for the 7120P Coprocessor (MIC-0) .... 13
Figure 4.
The measured Device-to-Device bandwidth of the 7120P coprocessor ......................... 13
Figure 5.
HPL performance results with 7120P coprocessors (percent HPL efficiency) ................. 14
Figure 6.
HPL power consumption results with 7120P coprocessors ........................................ 15
iii
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
iv
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
Executive Summary
Organizations that leverage heterogeneous computing architectures are likely to have two key
questions about the latest Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor: How much performance gain can be expected
from the coprocessor, and what is the power efficiency?
To answer these questions, we measured the performance gain and power efficiency with Intel Xeon
Phi Coprocessor on the Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 server. Our analysis used standard and synthetic
benchmarks that model real-world applications. In this paper, we present and analyze the results and
highlight key points.
The PowerEdge R720 with the Coprocessor showed up to a 6.6X speedup and 2.5X improvement in the
energy efficiency on High Performance Linpack (HPL) when compared to a CPU-only configuration. HPL
is a common benchmark for high-performance computing (HPC) applications.
5
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
Introduction
This white paper explores the performance gain and power efficiency achieved with the Dell
PowerEdge R720 server when accelerated by the Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor. The following is a brief
overview of the two key technologies explored in this paper—the PowerEdge R720 server series and the
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor.
The PowerEdge R720
The Dell PowerEdge R720 is Dell’s 12th generation 2U, 2-sockets, server that is designed to run complex
workloads using highly scalable memory, I/O capacity, and flexible network options. The system
features Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2600 product family, up to 24 DIMMS, up to sixteen 2.5-inch
SATA/SSD internal hard drives giving a maximum of 24TB internal storage. PCI Express® (PCIe) 3.0
enabled expansion slots, and a choice of NIC technologies
The PowerEdge R720 is a general-purpose platform with highly expandable memory (up to 768GB) and
impressive I/O capabilities to match. The R720 can readily handle demanding workloads, such as data
warehouses, e-commerce, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), databases, and high-performance
computing (HPC). 1
The PowerEdge R720 is ideal for customers who need to balance high-performance requirements,
including scientific research, oil and gas, life sciences, healthcare, and electronic design automation
(EDA), with resource limitations.
Figure 1.
The front and back view of PowerEdge R720
1
Source from Dell PowerEdge R720 and R720xd Technical Guide. Download at: http://i.dell.com/sites/content/sharedcontent/data-sheets/en/Documents/dell-poweredge-r720-r720xd-technical-guide.pdf
6
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
Easy to Extend, Easy to Configure
The PowerEdge R720 enables users to mix and match the requirements of the compute and storage to
find the right combination for particular resource-intensive workloads. With its extendable
architecture, the PowerEdge R720 platform allows organizations to configure storage-dense or
compute-dense server in a general purpose chassis design, and repurpose hardware based on workload
needs. As demands change, the platform can be reconfigured or scaled out, extending the life and
value of the organization’s investments.
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors are based on the Intel Many Integrated Core (MIC) Architecture and use the
familiar x86 standard programming model. It extends hardware support to higher degrees of
parallelism with power savings and shares parallel processing with general purpose processors (CPUs). 2
They also deliver applications for computational finance, computational physics, molecular dynamic,
seismic processing, ray tracing, and finite element analysis. Phi Coprocessors have shown excellent
performance in compute intensive applications requiring double precision floating point operations.
Typically they are targeted to broader supercomputing market but can be used in other workloads.
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors are ideal for today’s most aggressive high-performance computing
workloads.
Why Use the PowerEdge R720 for Heterogeneous Computing?
The PowerEdge R720 server is designed to offer an ideal computing platform for compute-intensive
applications. The PowerEdge R720 can accommodate up to two Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors 7120P,
each with a x16 PCIe Gen2 connection, two Intel® Xeon® E5-2600 series processors with up to eight
cores each, 24 DIMM slots, and up to sixteen 2.5-inch SATA/SSD drives for internal storage per compute
node. Figure 2 shows a PowerEdge R720 compute node.
2
Source: http://software.intel.com/en-us/mic-developer.
7
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
Figure 2.
The PowerEdge R720 server
The PowerEdge R720 allows organizations to match the system architecture to the targeted workloads.
With two of the fastest server processors available, and up to two of the most advanced coprocessors
available in one server, users can potentially speed processing up to an order of magnitude. It can be
configured with both CPUs and Coprocessors, and it can be loaded with more local storage and less
compute, or vice-versa, depending on the demands of specific workloads or applications.
Intel Xeon Processors
The Intel Xeon E5-2600 processor family I/O latency is dramatically reduced with Intel Integrated I/O,
which eliminates data bottlenecks, streamlines operations, and increases agility. The E5-2670
processor consumes 115W, but offers a substantial performance gain over the Intel Xeon 5500-series
processor. In addition it delivers the following advantages:
Up to 8-cores per processor
Intel Turbo Boost 2.0 technology
Dual QPI links
The Intel Sandy Bridge micro-architecture
8
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
Why Use Bright Cluster Manager for Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor-Based HPC?
Our test environment uses Bright Cluster Manager® (BCM). BCM is one of the leading feature-rich
cluster management software platforms. It removes the complexity from provisioning, management,
and monitoring of HPC clusters. With BCM, an administrator can easily and quickly install, manage, and
monitor multiple clusters simultaneously from a single GUI.
BCM includes powerful management and monitoring capabilities that leverage functionality in Intel
Xeon Phi coprocessors to take maximum control and gain insight into their status and activity over
time. Supported metrics include temperatures, memory usage, network, PSU voltages and currents,
and system LED states.
BCM allows for alerts and actions to be triggered automatically when the coprocessor metric thresholds
are exceeded. Such rules are configurable to suit the user’s requirements and any built-in cluster
management command, Linux command, or shell script can be used as an action. For example, if a user
would like to automatically receive an email and shut down a node when its coprocessors temperature
exceeds a set value, this can easily be configured in BCM.
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor-Based HPC Features
BCM offers the following features specifically for Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor based HPC:
Ease of setup – BCM provides tools to install and configure coprocessors as accelerators or as
compute nodes. The coprocessors are configured and treated as first class compute devices
giving the same level of monitoring and configuration as all compute nodes
Ease of use - BCM packages drivers, runtime, SDK, OFED, and flash utilities to make
provisioning and integration of compute nodes with Intel Xeon Phi coprocessors very easy.
Ensured kernel compatibility - BCM always compiles the driver at boot time, against the
running kernel, to ensure compatibility. The driver compilation takes about 15 seconds.
Detailed monitoring - BCM captures several important performance metrics, which can be
selected and displayed by users; examples include the temperature, memory usage, and power
information in the cluster.
Management of Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors - BCM allows user to set alerts to be triggered
automatically based on user defined criteria. These triggers can be integrated with cluster
management commands, command line, and Linux scripts. These features can be extended to
cluster-level status and health management with easy visualization of the entire cluster.3
3
For more information on these BCM monitoring and management capabilities http://info.brightcomputing.com/webinarmanaging-intel-xeon-phi/
9
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
Overview of the Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor 7120P
The Intel Xeon Phi coprocessors were introduced in November 2012. The 7120P coprocessor is the highend coprocessor of the Intel Xeon Phi series, which is specifically targeted toward the HPC market.
Compared to multi-core processor like Intel Xeon, the Phi coprocessor has many lower power cores and
wider vector processing units. Intel implemented the following features to achieve the main design
goal, “more performance and more efficiency”:
Highly Parallel. The coprocessor support three types of parallelism: data parallel, thread
parallel, and process parallel, and delivers higher aggregate performance and memory
bandwidth.
Highly Programmable. The coprocessor is more than an accelerator because it is fully
addressable and dependent in the cluster. Intel Xeon Phi coprocessor is fully supported by Intel
Cluster Studio XE and programmable by standard C/C++/Fortran.
A comparison of the key features is shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Key Features of the Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor 7120P
SKU
Architecture Codename
7120P
Knights Corner
Instructions
512-bit SIMD
Cores and
Frequency
61 cores
1.23GHz
Memory and Speed
Power
16 GB
5.5GHz GDDR5
300W
Performance
(Single Precision)
2.4 TFLOPS
Performance
(Double Precision)
1.2 TFLOPS
More detailed information about how the double precision performance number shown above is
determined.4
4
Please see the blog posting by Dr. Mark Fernandez at http://dell.to/YjFuN0
10
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
Test Cluster Configuration
The test cluster consisted of two PowerEdge R720 compute nodes with two Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors
7120P each. Each PowerEdge R720 had a standard dual-socket Sandy Bridge EP motherboard with Intel
Xeon E5-2670 @ 2.6GHz CPU. In the PowerEdge R720 the memory was configured as two DIMMs per
channel and four channels per processor. This means that 16 slots among the 24 DIMM slots were
populated by 8-GB DIMMs for a total of 128 GB @ 1600MHz of memory. There were four internal drives
in each PowerEdge R720 server. The PCIe connections to the coprocessors were internal.
The test cluster used BCM 6.1 as clustering software. BCM 6.1 is based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
(RHEL) 6.3. Table 2 gives the compute node configuration detail.
Table 2.
Compute node configuration detail
Component
Value
Server
PowerEdge R720
Architecture
Sandy Bridge EP
Processor
Dual Intel Xeon E5-2670 @ 2.6GHz
Memory
128GB @ 1600MHz
Infiniband
Mellanox ConnectX-3 FDR Adapter (CX353A)
Cluster size
2 Servers
MPSS version
2.1.6720-13
Coprocessor Power
Consumption
300W
OS
RHEL 6.3
11
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
Benchmarks
The table below describes the benchmarks 5 used in this study.
Table 3.
Benchmarks details
Benchmarks
Domain
Benchmark data set
SHOC_download
Coprocessor to main memory bandwidth
NA
SHOC_readback
Main memory to Coprocessor bandwidth
NA
Stream
Memory bandwidth
NA
High Performance Linpack
Compute Intensive
N=165888, NB=1280
Results
The performance results are shown in this section. Our analysis suggest that the PowerEdge R720 and
7120P coprocessor combination can drive significant gains in terms of both performance and power
efficiency for demanding scientific applications.
Memory Bandwidth
Functionally, the Coprocessors are used as applications accelerators. Initially, with processing
compute-intensive applications, the data is transferred from the host server to the Coprocessor. And
the results produced are sent back to the host. Consequently, high performance is dependent on fast
data transfer between memory (host) and the coprocessor (device).
Three bandwidths are of interest in any accelerated host server:
Host-to-device bandwidth - The rate at with data can be transferred from the host sever
memory to the coprocessor memory via the CPU. Measured by SHOC_download.
Device-to-host bandwidth - The rate at which data can be returned from the coprocessor
memory to the host memory. Measured by SHOC_readback.
Device-to-device memory bandwidth - The rate at which data transfers take place inside the
coprocessor. ECC can affect the device–to-device memory bandwidth. For this study, ECC was
enabled. Measured by Stream.
Note that usually the coprocessors (devices) in the system are marked as MIC-#, where # is the order
number of the coprocessors being listed by command ‘micinfo’.
5
Source: http://ft.ornl.gov/~kspafford/misc/shoc.pdf
12
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
Figure 3.
Host-to-Device (H2D) and Device-to-Host (D2H) BW for the 7120P Coprocessor (MIC-0)
Figure 3 shows the two bandwidths for the 7120P coprocessor on a PowerEdge R720 server. As
described in the previous sections, the PowerEdge R720 has two 7120P devices (MIC-0 and MIC-1). The
MIC-0 bandwidths to each of the two CPUs are shown in Figure 3. The host-to-device bandwidth of MIC0 and CPU 0 and CPU 1 were measured at about 6.7 GB/sec, while the device-to-host bandwidth was
measured at 6.8 GB/sec for both CPUs. At this time, the 7120P supports PCIe Gen2 standard only.
Figure 4 shows the device-to-device bandwidth measure at the MIC 0 devices and its comparison with
or without turbo. Figure 4 shows about 2 percent improvement in the internal device-to-device
bandwidth.
Figure 4.
The measured Device-to-Device bandwidth of the 7120P coprocessor
13
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
High Performance Linpack (HPL)
High Performance Linpack (HPL) is a dense linear system solver, which is historically used to benchmark
HPC systems. HPL was run with the problem size of N=116736 (NB=1280) for single node and N=165888
(NB=1280) for cluster runs. The results of the HPL performance are shown in Figure 5. Performance of
the single node (left) and cluster (right) are shown. In each case, the HPL efficiency as a percentage of
the theoretical performance is displayed on the bar. Compared to the CPUs, the acceleration was
about 6X with 7120Ps.
Figure 5.
HPL performance results with 7120P coprocessors (percent HPL efficiency)
On a single node, with CPUs only, the PowerEdge R720 achieved 314 GFLOPS. With two 7120Ps, it
achieved about 2.094 TFLOPS. So the 7120P provides a 6.7X fold performance increase. Similarly, for
the cluster, the combined sustained performance of the four CPUs was 625 GFLOPS. When this is
accelerated using four 7120P coprocessors, the performance increased to 4111.7 GFLOPS, showing an
increase of 6.6X.
In general, the HPL efficiency of CPU-only systems is high, 94.1 percent and 93.9 percent in our tests.
The drop in overall HPL efficiency of the heterogeneous CPU and Coprocessors system compared to a
CPU-only system was expected.
The results of the HPL power consumption tests are shown in Figure 6. The power consumption of the
CPU-only system was lower than CPU + coprocessors systems. The single node results (left) and cluster
consumption (right) are shown. The results show the total power consumption of the compute node
(PowerEdge R720). Numbers on the bars represent the ratio of the CPU + coprocessors systems
compared to the CPU-only case. The power consumption of a single node CPU-only system was about
433 watts. When accelerated by two 7120P coprocessors, it increased to 1120 watts, showing an
increase of 2.6X. Similarly, for the cluster case, the CPU-only power consumption was about 861 watts,
and with four 7120P coprocessors used for acceleration increased to 2243 watts, showing an increase of
2.6X.
14
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
Figure 6.
HPL power consumption results with 7120P coprocessors
Summary and Performance/Watt Comparison with CPU only
Table 4 shows the summary of the performance acceleration due to 7120P coprocessors on the dualnode cluster. The HPL results are for dual nodes with two coprocessors per node.
Table 4.
Results of the performance comparison with CPUs
Application
CPU-Only
7120P
Delta
HPL
625 GFLOPS
4111.7 GFLOPS
6.6X increase
Table 5 shows the 7120P performance/watt data of HPL on the dual-node cluster, compared to a CPUonly cluster.
Table 5.
Performance/watt comparison
Application
CPU-Only
7120P
Delta
HPL
0.726 GFLOPS/watt
1.833 GFLOPS/watt
2.5X increase
15
Performance Analysis: Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor 7120P on Dell™ PowerEdge™ R720 Server
Conclusion
The Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor 7120P demonstrated substantial performance and power-efficiency
gains when compared to the CPUs only. When two coprocessors were used per node on the HPL
benchmark, compared to CPUs only, the performance is increased by more than six fold and the
performance per watt is improved by more than two fold.
A key finding was that the Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor 7120P works seamlessly with the PowerEdge 720
server to enhance performance and improve the overall energy consumption, resulting in a powerful,
easy-to-use and energy efficient HPC platform.
References
1. Intel Xeon Processor E5 Family (Servers)
http://ark.intel.com/products/family/59138/Intel-Xeon-Processor-E5-Family/server
2. Intel Xeon Processor E5 Family Specifications
https://www-ssl.intel.com/content/www/us/en/processors/xeon/xeon-e5-family-specupdate.html
3. Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor
http://software.intel.com/en-us/mic-developer
4. Bright Cluster Manager
http://www.brightcomputing.com/resources/Bright-Cluster-Manager-Brochure.pdf
16