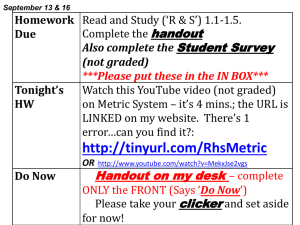
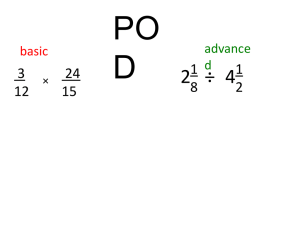
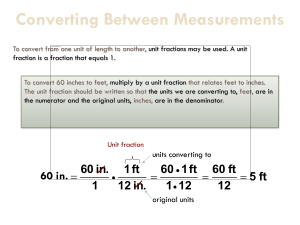
MJ2 - Ch 1.8 Metric Measurement
advertisement

MJ2 Ch 1.8 – Metric Measurements Bellwork • 1. 2. 3. 4. Identify if the sequence is arithmetic or geometric and name the next 3 numbers 2, 8, 32, 128… 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0… 3, 15, 75, 375… 3, 6, 9, 12… Assignment Review • No homework… • Please note: If you were not here yesterday for the class activity you are to read text p. 34 & 35 and then complete text p. 36 # 12 – 23 • This assignment will count as a test grade and is due next class… Before we begin… • Please take out your notebook and get ready to work… • It is expected that you are familiar with the Customary Measurement System that we use in this country…. • This system measures in Feet & inches, gallons & quarts, and pounds & ounces…to name a few. • This customary system is mostly used in the United States. • In other countries they use the Metric Measurement System…which, is what we will explore today… Objective • Students will convert metric units of length, capacity, and mass Measurement Categories • Like the customary system, in the metric system we can categorize measurements into the following: – Linear (length) Measurement – Liquid (capacity) Measurement – Weight (mass) Measurement Linear Measurement Vocabulary • Please write down the following terms: • In the metric system you need to know the what the following prefixes mean. Prefix Meaning in words Meaning in Numbers kilo- Thousands 1,000 centi- hundredths 0.01 milli- thousandths 0.001 Linear Measurement • In the metric system the meter (m) is the base unit. • A meter is a little more than a yard…and we all know how long a yard is…don’t we? Linear Measurement • One kilometer is equivalent to 1,000 meters • One meter is equivalent to 100 centimeters and 1,000 millimeters • The metric prefix indicates the place value position of the measurement Linear Measurement • In the metric we can visually see the order of the measurement from largest to smallest with the following diagram • Also listed are the abbreviations for each Kilometers (km) Meters (m) Centimeters Millimeters (cm) (mm) • In order to convert measurements in the metric system you need to know the relationship of each of the terms Converting Linear Measurement • To convert units from larger to smaller you multiply • To convert units from smaller to larger you divide • Here is what it looks like: (Please copy the diagram and use it to help you convert measurement) Converting Linear Measurement x 100 x 1000 Kilometers (km) 1000 Meters (m) x 10 Centimeters (cm) 100 Millimeters (mm) 10 Example 1 • To convert from meters to centimeters you multiply because meters is bigger than centimeters Multiply 4.5 m = __?__cm 4.5 x 100 = 450 4.5 m = 450 cm Example 2 • To convert from meters to kilometers, you divide because meters is smaller then kilometers Divide Therefore 2600 m = ? km 2600 1000 = 2.6 2600 m = 2.6 km Your Turn • In the notes section of your notebook convert the following measurements 1. 550m = ? Km 2. 3.7m = ? Cm Please make sure that you are writing the original problem so you can refer back to it. Liquid Measurement Vocabulary • The liter (L) is the base measurement unit of liquids in the metric system • One Kiloliter (kL) is equivalent to 1,000 liters • One liter (L) is equivalent to 1,000 milliliters (mL) Converting Liquid Measurement • To convert units from larger to smaller you multiply • To convert units from smaller to larger you divide • Here is what it looks like: (Please copy the diagram and use it to help you convert measurement) Converting Liquid Measurement • The categories for liquid measurement, in order from largest to smallest are: x 1000 x 1000 Kiloliter liter Milliliter (kL) (L) (mL) 1000 1000 Example 1 • To convert liters to milliliters you multiply by 1,000 because liters are larger than milliliters. Multiply Therefore 3.2 L = ? mL 3.2 x 1,000 = 3200 3.2 L = 3,200 mL Example 2 • To convert from liters to kiloliters you divide by 1,000 because liters is smaller than kiloliters Divide Therefore 1,640 L = ? kL 1,640 1,000 = 164 1,640 L = 164 kL Your Turn • In the notes section of your notebook convert the following measurements 1. 0.75 kL = ? L 2. 8,800 mL = ? L Please make sure that you are writing the original problem so you can refer back to it. Weight Measurement Vocabulary • In the metric system the gram (g) measures mass – the amount of matter in an object • The base unit for mass is kilogram • One kilogram (kg) is equivalent to 1, 000 grams (g) • 1 gram (g) is equivalent to 1,000 milligrams (mg) Converting Mass • To convert units from larger to smaller you multiply • To convert units from smaller to larger you divide • Here is what it looks like: (Please copy the diagram and use it to help you convert measurement) Converting Mass x 1000 kilograms (kg) 1000 x 1000 grams (g) milligrams (mg) 1000 Example 1 • To convert from kilograms to grams you multiply by 1,000 because kilograms are larger then grams Multiply Therefore 8.43 kg = ? g 8.43 x 1,000 = 8,430 8.43 kg = 8,430 g Example 2 • To convert from milligrams to grams you divide by 1,000 because milligrams is smaller than grams Divide Therefore 500 mg = ? g 500 1000 = 0.5 500 mg = 0.5 g Your Turn • In the notes section of your notebook convert the following mass measurements 1. 23.5 g = ? mg 2. 9,014 g = ? kg Please make sure that you are writing the original problem so you can refer back to it. Summary • In the notes section of your notebook summarize the key concepts covered in today’s lesson. • Today we discussed: – How to convert larger units to smaller units in the metric system – How to convert smaller units into larger units in the metric system Assignment • Workbook p. 37 – Use your notes to help you with the conversions NOTICE: QUIZ TOMORROW ON CH 1.8 (CONVERTING METRIC MEASUREMENT)