presentation - Kent State University
advertisement

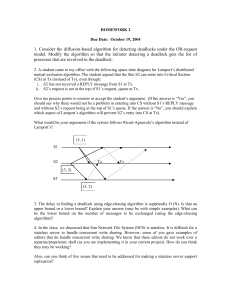
Ho-Ramammorthy 2 phase snapshot algorithm PRESENTATION Chao Ma Kent State University November 25th 2013 Outline Introduction Algorithm Summary Experimental Setup Main program Test program Conclusions Result Graphics Output Results Future work Code defense Introduction The point of this experiment is to test the efficiency of Ho and Romamoorthy Two-Phase deadlock detection algorithm by using two methods below: vary the number of sites of basic algorithm message exchanges to test the frequency of deadlocks vary the number of sites of basic algorithm message exchanges to test consuming time Algorithm every site maintains a status table, containing status of all local processes resources held, resources waiting on periodically, coordinator requests all status tables, builds a WFG, and searches it for cycles no cycles - no deadlock If cycle is found, coordinator again requests all status tables, again builds a WFG, but this time uses only those edges common to both sets of status tables Experimental Setup Main program The main program have two parts, one is message passing system that is a process of sending and receiving messages, another is deadlock detector system that updates message passing system and detect the cycle by only using id common to both sets, this process is like a WFG graph. Message passing system Deadlock detector system Output of deadlock detect Experimental Setup Test program The role is to test the frequency and time consumming of deadlock detection algorithm by varying numbers of sites. Deadlocks compute function Deadlock detector system Varying numbers of sites Time record function The result output of all tests Experimental Setup Conclusions Through analysing and comparing by varying numbers of sites, the result could be reflected as two changing curves. With the increase of numbers, the curve of frequency of deadlock detection is steady increase, however every time of test result reflects floating different that need many times of test to make an accurate statistical result With the increase of numbers, the time consuming curve is slightly increase and to some extent depend on the effect of processing speed of PC Show result Graph The numbers of sites (id) Show result Graph The number of sites(id) Show result Future work To simulate my program on a real distributed network to search for deadlocks To test my program with much larger number of processes that could make the statistics more precise To observe its performance based on various and complex message passing situation Reference "Advanced Concepts in Operating Systems" by Mukesh Singhal and Niranjan G. Shivaratri K.M. Chandy, J. Misra, and L.M. Haas "Distributed deadlock detection", ACM Transactions on Computer Systems, 1(2), pp 141-156, May 1983 Questions? Thank you