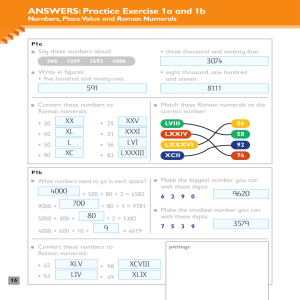
Progression in Written Methods
advertisement
…… Primary School Parents Meeting on: Progression through Calculations Do I need jottings ? Can I do it in my head? Shall I use a pencil and paper method? Do I need to use a calculator? Starter • • • • • (use a calculator!) Think of a number between 1 and 9 Multiply by 2 (x 2) Add 5 (+5) Multiply by 50 (x50) If you have had your birthday this year add 1 760. If not add 1759. • Subtract the year of your birth. Aims • To look at the ways in which the teaching of mathematics has changed; • To look at how children calculate; • Try activities to develop calculation strategies; • To look at ways in which parents can help their children How has mathematics changed? • Daily mathematics lesson; • Emphasis on mental calculations; • Interactive whole class and group teaching; • Enjoyable practical approaches; • Mathematics with understanding Calculations Ways to help children to remember… • Practice with just one fact a day, or try a ‘fact of the week’ • Practice ‘fact families’, e.g. 6+8=14, 8+6+14, 14-6=8, 14-8=6 • Work from answers back to facts – how many facts do you know with an answer of 12? • Make an addition or multiplication table and cross out all those facts you already know. Now focus on those you need to learn. • Encourage children to work out their own ways to remember facts • Draw pictures to accompany particular facts. • Repeat it and repeat it! Skills of mental calculation • Remembering number facts and recalling them without hesitation. • Using facts that are known by heart to figure out new facts. • Applying understanding of place value and ability to partition numbers into parts • Understanding and using the laws of arithmetic and relationships between the four operations to find answers and check results • Having a repertoire of mental strategies to do calculations with some thinking time • Solving word problems Mental gymnastics • Think of a number and keep doubling it. How far can you go? • Face the person next to you and alternate! • In two’s – one person recites all the numbers from 1 to 100 • The other person raises their hand at any number that can be divided by 3 or … • Divided by 4 or … • Divided by 3 and 4 or … • Divided by 5 You can use your number square to help you! Mental calculations Children are encouraged to count in different ways and to calculate mentally. Number lines – Bead bar / number stick / individual number lines / Number ladders Calculations The aim is that children will always be able to recognise when calculations can be done ‘ in their heads’ and choose effective and efficient strategies to work out the answers. Overview Up to Year 3 the emphasis is on: o working mentally, o calculations recorded in horizontal number sentences o some jottings for more challenging numbers o Models and Images In Year 3-6 children will be gradually taught more formal written methods of calculation but they will still use mental methods and jottings where appropriate. Developing children’s mental picture of number system o DEMONSTRATE on a number line children’s response to a calculation. o DISPLAY number lines and washing lines around the room for the children to access. o MODEL the use of number lines and tracks to aid calculation from YR and empty number lines from Y2 o CONTINUE to demonstrate, display and model use of a number line all the way to Y6! Early Recording So - how can we give children the best foundations for success with written calculations? o We need to encourage children to use mental calculation strategies for smaller/ simpler numbers. o We need to encourage children to ask the question “Can I do it in my head?” or “Can I do it in my head with jottings/ a number line?” Laying the foundations for addition and subtraction o Partitioning o Rounding o Compensating o Counting on o Bridging through 10s, 100s, 1000s boundaries o Addition and subtraction facts Laying the foundations for multiplication and division o Doubling/ Halving o Grouping/ equal groups/ equal jumps o Repeated addition/ subtraction o Arrays o Multiplication and division facts Multiply • Slap, clap, click (not as violent as it sounds!) • ‘Show me’ – 1.The product of a multiplication 2.A multiple of 2, 3, 5, 10, 4, etc 3.A number that is exactly divisible by 3, 5, 2, 10, 4, etc 4.A common multiple of 2 and 3, 3 and 5, 3 and 10 1.In groups have a go at ‘Hot Seat’ You can use your number square or calculator to help Common calculation errors! 99 +101 1901 158 + 184 612 4 1 945 - 237 712 1 1 1 2000 108 902 Dartboard Activity Rules: You have 3 darts. You can hit the same section of the board more than once, but all three must score. Show how you could score each of these totals. Demonstrate the first one Work with a partner Do you always make the totals in the same way? How might you differentiate this game? Addition- Progression o Mental calculation supported by: Modelling of method by teacher Jottings Number lines o Expanded method using partitioning o Compact ‘carrying’ method Jottings When do children still use jottings/ number lines?? • When they can calculate mentally and need a little support. • When they are not completely secure with ‘carrying’. • When they are dealing with addition of decimals, negative numbers, time, measurement scales, etc. • Stage 1: Mental method using partitioning: 47 + 76 = (40 + 70) + (7 + 6) = 110 + 13 = 123 • Stage 2/3: Use an expanded layout 47 + 76 110 13 123 47 + 76 13 110 123 Subtraction - Progression • Mental calculations supported by: Modelling of method by teacher Jottings Number line • Expanded decomposition using partitioning • Compact decomposition 78 – 12? How do you work out…. 74 – 57? Using a Number line for Subtraction • Counting Back 78 – 12 -10 -2 66 68 78 • Counting on to find the Difference 74 – 57 +10 57 +3 67 +4 70 74 When do children still use jottings/ number lines?? o When they can calculate mentally and need a little support. o When they are calculating the difference between two numbers relatively close together. o When not completely secure with decomposition o When calculating with decimals. o When decomposition is made difficult by ‘trapped zeroes’. Stage 1: Mental method using partitioning. 76 – 32 = (70 – 30) + (6– 2) = 44 Stage 2: Expanded vertical layout Stage 3: Compact decomposition Ongoing methods: mental methods and subtraction using a number line Multiplication - Progression o Mental calculation supported by: Jottings Number lines Modelling of method by teacher o Understanding of multiplication as: an array repeated addition scaling o Grid method Multiplication facts ITP Multiplication Facts ITP Using a number line 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 60 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Grid method of multiplication 6 10 3 60 18 so 6 x 13 = 78 60 + 18 = 78 Grid ITP Division - Progression o Mental calculations supported by: Jottings Number lines Modelling of method by teacher o Understanding division as sharing and grouping. o Visualising division using: arrays repeated subtraction This child has used a strategy of grouping tallies to find the answer. This child has used a strategy of counting equal groups to find the answer. Table Trios and Multiplication Clocks! Division - Progression Chunking Step 1: Demonstrate practically by repeatedly subtracting groups of objects and keeping count Step 2: Model on a number line Step 3: Model vertical method •Stage 1: Short division. i.e. TU ÷ U, HTU ÷ U Known as the ‘chunking’ method. 6 72 - 60 x 10 12 - 6 x1 6 - 6 x1 0 Answer = 12 9 97 - 90 x 10 7 Answer = 10 r 7 Stage 3 Long division (HTU ÷ TU) 15 432 - 150 282 - 150 132 - 60 72 - 60 12 x 10 x 10 x4 x4 Answer = 28 r 12 15 432 - 300 132 120 12 x 20 x8 Answer = 28 r 12 How to help your child with mathematics! Visual maths • Number lines 1 2 3 • Noticing numbers 23 4 5 6 Rhymes/songs • 5 little speckled frogs; • 10 huge dinosaurs (bottles); • 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 once I caught a fish alive; Sorting • Socks • Cars • Shoes Measures • Keep a record of your child's growth; • Scales and balances e.g. see-saws • Capacity – different containers to play with in the sink or bath; Rectangle Spot the Shape 1 and 2 Shape and space • Recognising shapes around them e.g. doors, windows, cans, boxes etc • Construction sets, Lego, • Shapes of cakes, biscuits, sandwiches. How can parents help? • Count with their child • Play number games • Involve children in shopping activities • Involve children when taking measurements or weighing items • Take note of numbers in real life e.g. telephone numbers, bus numbers, lottery numbers etc • Give children opportunities to use money to shop, check change etc •Talking about the mathematics in football e.g.. How many points does your favourite team need to catch the next team in the division? • When helping their children calculate use the method that they have been taught. Key Messages To develop written calculation strategies, children need: o Secure mental strategies from YR. o A solid understanding of the number system. o Practical, hands on experience including counters and base 10 apparatus. o Visual images including number lines and arrays. o Experience of expanded methods to develop understanding and avoid rote learning. o Secure understanding of each stage before moving onto the next. o The questions at the forefront of their minds: ‘Can I do it in my head? If not which method will help me?’